Population Ecology Quiz Study Guide
advertisement
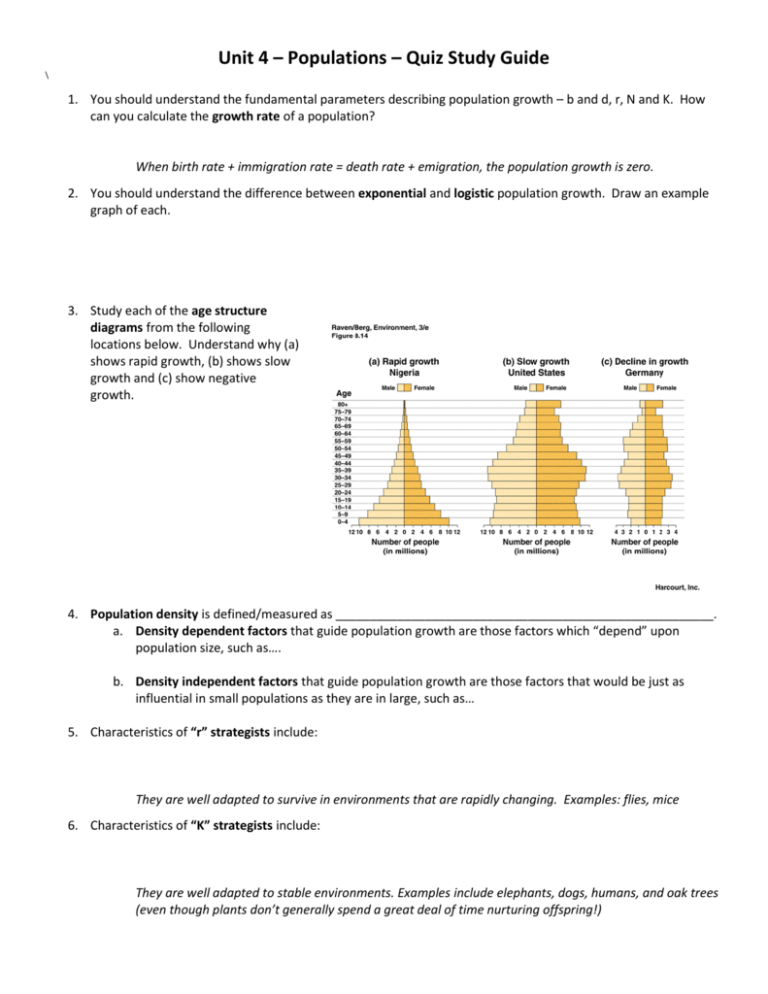
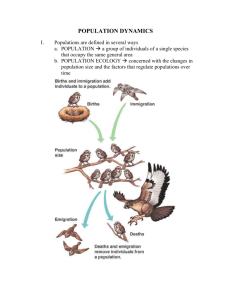
Unit 4 – Populations – Quiz Study Guide \ 1. You should understand the fundamental parameters describing population growth – b and d, r, N and K. How can you calculate the growth rate of a population? When birth rate + immigration rate = death rate + emigration, the population growth is zero. 2. You should understand the difference between exponential and logistic population growth. Draw an example graph of each. 3. Study each of the age structure diagrams from the following locations below. Understand why (a) shows rapid growth, (b) shows slow growth and (c) show negative growth. 4. Population density is defined/measured as _______________________________________________________. a. Density dependent factors that guide population growth are those factors which “depend” upon population size, such as…. b. Density independent factors that guide population growth are those factors that would be just as influential in small populations as they are in large, such as… 5. Characteristics of “r” strategists include: They are well adapted to survive in environments that are rapidly changing. Examples: flies, mice 6. Characteristics of “K” strategists include: They are well adapted to stable environments. Examples include elephants, dogs, humans, and oak trees (even though plants don’t generally spend a great deal of time nurturing offspring!) 7. Survivorship curves represent the number of individuals surviving at each age for a given species. Define each type, draw the graph curve, and give an example. a. Type I: ____________________________ b. Type II: _____________________________ c. Type III: ______________________________ 8. The carrying capacity, shown on the graph to the right (dashed line, marked K) is _______________________ _____________________________________________. It can change seasonally, and is not a fixed quantity. a. A population reaches its carrying capacity based on limiting factors. 9. Spatial distribution patterns of organisms occur in many ways. a. There are “clumps” (most common): ______________________________________________ b. Uniform or “regular” distribution patterns: ____________________________________________ c. Random pattern (the least common): _________________________________________________ 10. Scientists study populations to gather information about the structure, growth, and potential decline of a species. Scientists sample (estimate) these populations through two methods: random (quadrant) and markrecapture. Summarize each and discuss the benefits/which type of population would be best sampled. Population growth is affected by a lot of factors. A population is _______________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________. Population ecology is the study of how individuals within a population interact with one another. a. Symbiotic interactions: _________________________________________________________________ Define, explain how each species involved is affected, and give an example for each type of interaction. i. Predation ii. Mutualism iii. Commensalism iv. Competition