Populations & Population Growth
advertisement

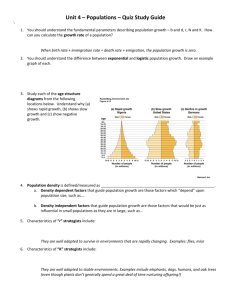
Populations & Population Growth Populations Random sampling- take a representative sample Population size - number of members in a population 2 ways to estimate population size: 1. Random sampling – used mainly for plants; samples and counts organisms in random plots 2. Mark & recapture – used mainly for animals; captures, marks, and releases animals, then samples the population again Populations Population growth – an increase in the size of a population fluctuations Leveling off Exponential growth Beginning growth Populations • Carrying capacity – the maximum number of individuals in a population that an area can support Populations • Limiting factor – anything that limits the survival of an organism – Can stop an increase in the size of a population – Ex.: food & shelter availability, climate, temperature, number of predators – Affects carrying capacity (if food increases, carrying capacity increases) Population Growth • There are 2 types: – Logistic growth • Looks like an S-curve • Levels off at carrying capacity (K) • At K, birth rate = death rate Population Growth – Exponential Growth • Looks like a J-curve • Population keeps increasing rapidly • Birth rate and death rate are constant • Limiting factors stop population from growing indefinitely large (ex.: food, space, etc.)