Imperialism/Spanish
advertisement

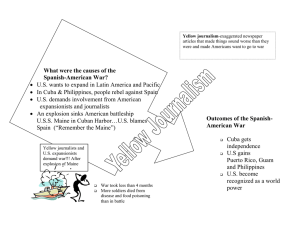
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v =ekytTpFy96o U.S. History ► Wednesday, Nov. 7 You will need a full sheet of paper to start notes for the Unit Increasing Influences and Challenges ►You will be using them for Daily Learning Target Assessments and then handing them in, so writing information down is important. ► Imperialism ►What do you think this means? Write down a definition. ►Definition: The extension of a nation’s power over other lands. ►Based on this definition, is the United States an imperialistic country in 2012? Explain. The Big Picture ► U.S. foreign relations took a new turn at the end of the 19th century. Global competition for empire led the U.S. into war with Spain and intervention in Latin America. The U.S. forged a new role as an emerging world power. Focus ► What inspired imperialist activity? ► How did the U.S. gain lands? ► What caused the SpanishAmerican War? ► How did actions within America push us into war? ► How did the U.S. treat conquered or acquired lands? I can. . . Evaluate, take, and defend positions on the various U.S. foreign policies in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries Analyze the causes and consequences of the Spanish-American War Identify and evaluate the factors that influenced U.S. imperialism in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries and the ensuing debate over imperialism What led to the U.S. quest? ►Economic Interests Industrial Revolution Close of the Frontier ►Military Needs Alfred Thayer Mahan What led to the U.S. quest? ►Example of European Nations The scramble for territory ►Ideology American Nationalism Josiah Strong’s Our Country First Acquisitions ► Alaska Purchased from Russia (1867) ►Sec. of State William Seward Reduce foreign possessions in NA Vast natural resources Statehood (1959) Importance ►Resources: timber, fur, fish, coal, oil, gold ►Polar air routes ►Close to Russia (air bases) First Acquisitions ► Hawaii Acquired (Taken!) ►Supply and fueling station ►Drew missionaries ►American investors Statehood (1959) Importance ►Sugar and pineapples ►Pearl Harbor How it happened ► Wealthy white planters gained influence and power within Hawaiian society due to prosperous sugar sales to the U.S. ► A group plots against the king and forces him to sign a new constitution in 1887 – the Bayonet Const. (Pearl Harbor ours) ► 1890 – when the economy went south they try to restore control (U.S. ousts Liliuokalani in 1893; annexed in 1898) The SpanishAmerican War An American Empire in the Making Simmering Unrest in Cuba ►Cuba was a Spanish possession ►Since 1868 they had launched a series of revolts ►Spain was weakening ►Jose Marti Exiled in NY, he forms the Cuban Revolutionary Party (1892) and leads a revolt in 1895 The Butcher ► Spain responds with Valeriano Weyler Camps set up for civilians ►Some 200,000 die Why U.S. interest? ► Geographic proximity – 90 miles away ► Economic interests - $100 mil. in trade; $50 mil. invested ► Humanitarian concerns – deaths of especially women and children due to hunger and disease The Media’s Role ► American’s were already sympathetic American tradition of Revolution Plus it gets a European nation out ► But the “information” they received concerning Weyler fed it ► Two competing media moguls are key William Randolph Hearst – NY Journal Joseph Pulitzer – NY World Yellow Journalism ► ► ► Scandalous stories and large shocking illustrations Sensationalized news stories They sent reporters, but relied on Cuban sources The de Lome Letter President McKinley was openly criticized by Spain’s Minister to the U.S. ► Cuban spy acquires it ► Published in the NY ► ► Journal In February The Explosion of the Maine ► ► ► ► The U.S.S. Maine had been sent to Havana Harbor on a visit (protection; show of force) Feb. 15, 1898 – the Maine mysteriously explodes: 260 killed Yellow journalists go into high gear But no declaration of war until April 25th War in the Philippines ► The first action took place here because that is where the Spanish fleet was ► Adm. George Dewey sent here by Asst. Sec. of the Navy Teddy Roosevelt ► Dewey held his fire (nearest resupply was 7,000 miles away) ► We had new steel-hulled and iron ships ► Took only hours War in Cuba ► ► Teller Amendment – we will not take you over U.S. military not prepared: Wool uniforms Bad beef Hodge-podge of soldiers War in Cuba ► ► ► Rough Riders – led by Teddy Roosevelt Buffalo soldiers Cavalry unit – not really; horses left in America or drowned Consequences of the War ► Treaty of Paris Spain gives up claims to Cuba Puerto Rico and Guam ceded to U.S. Philippines to the U.S. for $20 million ► It was a “Splendid Little War” ► But cost $250 million and 2,000 lives (most from yellow fever) Arguments for Annexing the Philippines Duty to spread values and culture Christianize the Filipinos ► Economic and strategic importance Trade routes to China and the rest of the Asian markets Get it before it falls to a European power ► Opponent’s Views ► ► ► ► It’s a violation of our own Declaration of Independence (the idea of self government) African Americans didn’t want to export oppression It would open the door to new immigrants It would undercut the American worker American Rule ► ► Annexation in 1899 Rebellion led by Emilio Aguinaldo He had already set up a new government and proclaimed himself president He was prepared to fight American Rule ► The Insurrection 3 years by U.S. accounts; until 1913 by the Filipinos 4,000 U.S. deaths 200,000+ Filipino deaths (about 20,000 military; the rest “as a result of the war and disease”) Some estimates as high as 1 mil. They call it the Philippine-American War American Rule ► Charges of brutality and torture on both sides ► Many famous Americans were outspoken against this conflict American Anti-Imperialist League formed William Jennings Bryan, Mark Twain, Andrew Carnegie