Mason-Dixon Line
advertisement

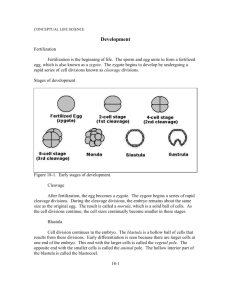
What kind of car are you? “In Nature, Nothing Is Superfluous, Nothing Is Wasted” -Leonardo DaVinci Animal Body Plans • Symmetry • Number of Tissue Layers • Gastric Design Asymmetry Bilateral Symmetry Radial Symmetry • Generally found only in aquatic animals Number of Tissue Layers • Acoelomatic = generally two tissue layers (i.e. flatworms) • Pseudocoelomatic = three tissue layers with fluid filled body cavity (i.e. nematodes) • Coelomatic = three or more tissue layers with lined body cavity Gastric Design • PROTOSTOMES • Mouth forms first • Simplest animals (i.e. Porifera, Nematoda) up through Annelida • May give rise to a two-way feeding system • DEUTEROSTOMES • Anus forms first • Insects Through Mammals • Ensures a one-way feeding system How Do Organisms Develop From A Zygote Into Their Final Forms? Determinative Embryology Human Fertilization • Fusion of ovum and sperm • Generally in the ampullary region of the fallopian tube • Sperm bind to corona radiata, and penetrate the zona pellucida by using acrosomal enzymes • Once sperm has penetrated and delivered DNA, egg hardens outside, preventing further sperm from fertilizing (cortical reaction) Zygote • Fertilized ovum • Formed by union of two haploid gametes (ovum & sperm) Early Animal Development • Cleavage = rapid mitotic divisions – Holoblastic – Meroblastic • Rate of cleavage depends upon the amount of yolk in the zygote (more = slower) Why is cleavage necessary? Reasons For Cell Division • Provide raw materials for other cells • Improve their surface area to volume ratios • Create an open space for cells to move into MORULA • Latin for “mulberry” • Earliest stage of embryonic development • Ball of blastomeres • Post 16 cell stage/Days 2-4 BLASTULA / BLASTOCYST • The resulting ball of cells produced by meroblastic cleavage is called a BLASTULA or BLASTOCYST • DAY 5 • Center of blastula is fluid-filled BLASTOCOEL Differences In Blastula Formation • In radially symmetrical animals, the blastocoel is large • In bilaterally symmetrical animals, there are two, unequally sized poles – Animal – Vegetal Morphogenesis What is the most important organ in the human body? GASTRULATION • Blastula undergoes meroblastic cleavage (unequal divisions) at one pole • As a result of these unequal divisions, one pole of the blastula begins to invaginate (‘cave in’) • The opening to the invagination is called the archenteron and the cavity is called the GASTRULA Organogenesis • Some of the cells of the original blastula are now pushed inside, lining the gastrula • Other cells migrate into the space previously occupied by blastocoel • As a result, three tissue layers are produced – ECTODERM – ENDODERM – MESODERM DERMAL LAYERS • ECTODERM (outside): brain, spinal cord, nerves, nose, ears, eye, skin • ENDODERM (inside): lining of digestive tract, pancreas, liver, lungs • MESODERM (middle): skeleton, muscle, gonads, kidneys DIFFERENTIATION • Changes that result in the formation of specialized organs or structures • Example: A second invagination of the ectoderm creates the neural tube (i.e. spinal cord and column)