Organismal Development 2 PPT
advertisement

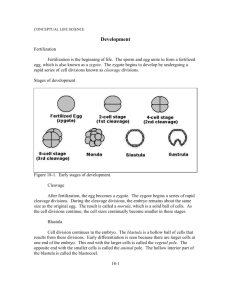
Organismal Development Part 5 Animal Development and Embryology Crashcourse Video • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k_9MTZg Ahv0 Cytoplasmic Determinants DNA controls the process of development in animals through the production of specific proteins and enzymes. 1. Cytoplasmic determinants – proteins produced in the cytoplasm that regulate mitosis and cell development. 2. Pattern genes – control the basic pattern of an organism. Ex. Frog, sponge, snake, human. 3. Positional genes – control the position of various structures throughout the developing organism. Ex. Brain, bones, skin, muscles. Early cells are considered totipotent. This means that they have the ability to turn into any other type of cell in the developing organism. As development progresses, cells begin to differentiate based on cell signals and DNA. Apoptosis in the hand Apoptosis – the programmed death of cells to create certain structures in the developing organism. In humans, we see this most commonly in our hands, feet, and the separation of important organs and other structures in the body. Failed Apoptosis with Hands Failed Apoptosis with toes Failed Apoptosis with the Tongue Cleavage Cleavage – rapid cell growth as development continues that leads to the creation of a blastula. Cells get smaller with each division, but the overall ball of cells stays the same size. Cells do not go through normal G1 and G2. Only S phase and M phase. Steps of Cleavage in Animals • 1. Blastulation – during this stage of development, cells continue to divide to create a hollow ball of cells called the blastula. – Two cell layers thick – Animal pole becomes head, vegetal pole becomes body. • 2. Gastrulation – during this stage of development, the hollow ball of cells begins to pinch in, creating a gastrula. – Three cell layers thick – Starting to create the mouth and anus. Animal vs Vegetal Poles of a Blastula Morula, Blastula, Gastrula Endoderm, Mesoderm, Ectoderm Three tissue layers of a developing organism. 1. Ectoderm – this layer of cells forms the skin and the CNS. 2. Mesoderm – this layer of cells forms the muscles, bones and kidneys. 3. Endoderm – this layer of cells forms the digestive tract organs, lungs and bladder. This is the tube that runs through the center of most organisms! Embryo Formation of the Embryo Different types of development • Dueterostomes - The anus is made first, and development moves towards the mouth. – Ex. Humans, fish, reptiles, starfish • Protostomes – The mouth is made first, and then development moves towards the anus. – Ex. Arthropods, mollusks, worms