Decision Making (Handouts).
advertisement

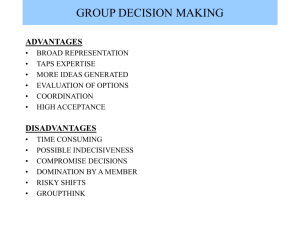
Decision Making An Army of One Agenda • • • • Questionnaire Introduction to group decision making Activity #1 Debriefing/Lecture Typical Approaches to Decision Making • • • • Stay with the status quo Change as little as possible Delay and avoid making the decision Choose the first likely solution • Encourage considered and thoughtful decision making where all of the alternatives are given a fair and thorough hearing Effective Decisions • • • • • Resources utilized effectively Time well used High quality decision (if possible to know) Implemented by all group members Problem solving ability of group enhanced (or not lessened). Individual vs. Group Decisions • Advantages of group decision making – – – – – Process gain More likely to identify and reject incorrect solutions More accurate memory of facts and events Greater informational resources Increased commitment for implementation • Disadvantages of group decision making – Time – Groupthink • Other Effects – Group polarization Groupthink • Groupthink- syndrome of bad decision-making 12.17 Group Polarization Group Polarization- tendency to shift toward more extreme positions after group discussion Risky Neutral Cautious Group Decisions Group 1 Group 2 800 800 700 700 600 600 500 500 400 400 300 300 200 200 100 100 0 0 A E MC A-D AVG MV Con A E MC A-D AVG MV Con 7 Methods of Group Decision Making • • • • Decision by authority without group discussion Decision by expert Averaging individual’s opinions Decision by authority with group discussion Decision by minority • Decision by majority • Consensus Decision Quality vs. Time Needed Highest Decision Quality Lowest Individual Average of Individuals Minority Control Majority Control Consensus Selecting the Appropriate Method • Guidelines for effective groups – #5 Ensure decisions are made using the appropriate method • How do you select appropriate method? • Vroom-Yetton Model – Select the method that allows you to make best quality decision that will be accepted by group members in the time allowed. Vroom-Yetton Normative Model Decision Processes A1 A2 C1 C2 G2 Decision Acceptance Decision Quality Time Situational Moderators 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Amount of relevant info possessed by leader and subordinates Likelihood subordinates will accept autocratic decision Likelihood subordinates will cooperate if allowed to participate Amount of disagreement among subordinates in their preferences Amount of problem structure (need for creativity) Decision Making Example You are the head of a personnel department which reports to the company president. The president has asked you to make recommendations on how to change and update the performance appraisal system. You are not sure about the approach to take. Your specialty is selection and you desire more information on performance appraisal. Fortunately, three members of your staff are experienced with the various aspects of performance appraisal. However, they rarely agree with each other on the best way to achieve something when it comes to performance appraisal. Fortunately, for this project, these employees will not implement the recommendations. Factors Hindering Group Decision Making • • • • • • • • • • Lack of group maturity Social loafing Free riding Defensive avoidance Groupthink Poor conflict management Egocentrism Lack of heterogeneity Premature closure Lack of individual incentives • How can we avoid these problems? Considered and Thoughtful Decision Making • Defining Problem • Gathering Information – Force field analysis • Formulating and Considering Alternatives – Potential Pitfalls • • • • • Failure to identify alternatives Premature elimination of alternatives Pressure for conformity Lack of inquiry and problem solving skills Lack of procedures to aid analysis • Deciding on a solution Summary • Groups have advantages over individuals in making decisions – Groups must work hard to leverage these advantages • How decisions are made impacts – Quality – Acceptance/implementation – Amount of time needed • Thoughtful decision making requires groups using these steps – – – – Defining Problem Gathering Information Formulating and Considering Alternatives Deciding on a solution