ideal gases
advertisement

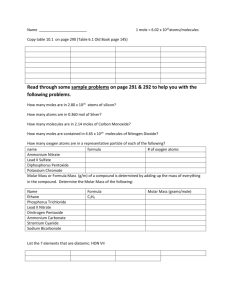
Unit 1 Gases Ideal Gases Objectives Compute the value of an unknown using the ideal gas law. 2. Compare and contrast real and ideal gases. 1. Avogadro’s Principle and Molar Volume Avogadro’s principle states that equal volume of all gases, measured under the same conditions of pressure and temperature, contain the same number of particles. At STP, the volume of one mole of gas is 22.4 L(this is called the molar volume) 1dm3 = 1 L; 1L= 1000mL ; 1mL= 1cm3 From last year, to convert between grams and moles of a substance we used its molar mass. Avogadro’s Law Converting between moles and grams: How many moles are 98.32g CO2? Calculate molar mass CO2 (use periodic table) Molar mass= 12 + (2 x 16) =44.0 g/1 mol To convert grams to moles: 98.32g x 1 mol = 2.23 mol CO2 44g 2. How many grams of carbon dioxide, CO2, will occupy a volume of 500.0 mL at STP? V= 500.0mL =0.5 L Molar mass CO2= 44g/mol At STP, molar volume is : 22.4L/1 mol Classwork: p 132 # 1 (a,b), 2(b,c), 3 (b,c) The ideal gas law Considers that amount of gas varies. New variable n: number of moles of gas (mol) Ideal gas constant (R) R= 8.314 L kPa (when pressure is measured in kPa) mol K R= 0.0821 L atm (when pressure is measured in atm) mol K Ideal gas law: PV= nRT (T must be in Kelvin) Using the ideal gas law 1. A deep underground cavern contains 2.24x106 L of methane gas (CH4) at a pressure of 1500 kPa and a temperature of 315K. How many moles of CH4 does the cavern contain? Using the ideal gas law 2. How many moles of oxygen will occupy a volume of 2.5 L at 1.2 atm and 25C? (0.123 moles) Classwork: p 133 # 7,8 and p141 # 3,4 Ideal gas variations For calculating molar mass M= mRT PV M: molar mass (g/mol) m: mass (g) For calculating density D= MP D: density (g/L) RT Sample problem 1. What is the molar mass of sulfur dioxide, SO2, if 300 mL of the gas has a mass of 0.855 g at STP? 2. At what temperature will 5.00g of Cl2 exert a pressure of 115 kPa at a volume of 750 mL? 3. If the density of a gas is 1.2 g/L at 0.920 atm and 20C, what is its molar mass? Classwork: p 133 #5,6, 9 and p141 #2,5