Chapter 10
advertisement

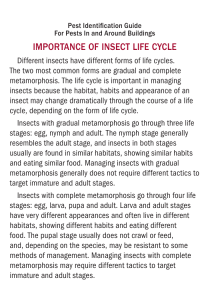
Chapter 10 Mollusks, Arthropods, and Echinoderms 7th Grade Science Mollusks • __________ - invertebrates with soft Mollusks unsegmented bodies that are often protected by a harder outer shell • _________ - a thin layer of tissue that covers Mantle the internal organs – produces the hard shell • _______ - crawling, digging, or catching prey foot • Examples of Mollusks – clams, snails, scallops, oysters Characteristics of Mollusks • _____________ - bilateral symmetry and a Body Structure digestive system with __________. Body Two openings parts are not repeated as in segmented worms – instead organs are located in one area. • _________________ Open circulatory system - blood is not always inside blood vessels – blood sloshes over the organs and returns to the heart. Obtaining oxygen • ____ gills - mollusks that live in water obtain oxygen through _______ and __________ cilia Blood vessels cilia • _____ - hair-like structures that move back and forth making the water flow over the gills • Gills remove oxygen from the water and passes it into the bloodstream • Wastes are also removed through the ______ gills into the water Three Main Groups • Mollusks are classified into three main groups based on _______________ Physical characteristics • Three main groups of mollusks are: 1. 2. 3. gastropods ___________ - single external shell or no shell __________ - two shells held together by hinges bivalves ___________ cephalopods - ocean dwelling – foot adapted to form tentacles around its mouth Gastropods • • • • ___________of mollusks Largest group Examples: _____________ Snails and slugs Live nearly everywhere on earth Some are herbivores ________, carnivores _________, and ________ scavengers • ________ - organ that is a flexible ribbon of radula tiny teeth to obtain food • Movement – creeping along on a broad foot _____ Bivalves • Oysters, clams, scallops, and mussels • Found in ________________ Water environments • ____________ - strain their food out of water Filter feeders as it flows over their gills • __________ omnivores • Movement - _____ larva float or swim, adults attach themselves to hard surfaces or use foot to move slowly their ____ Cephalopods • Octopuses, squids, cuttlefish • Only mollusks with a __________________ Closed circulatory system • _________ carnivores - captures prey using muscular tentacles. • ________ - uses to cut the flesh of its prey radula • ___________ Nervous system - most complex of all invertebrates, large eyes and excellent vision, large brains and ability to remember learned items. • Movement - ____________ Jet propulsion Arthropods arthropods • ___________ - spider, grasshopper, crabs, lobsters, centipedes and scorpions. • Classified into 4 major groups: 1. 2. 3. 4. crustaceans __________ __________ arachnids Centipedes and millipedes ___________________ insects ____________ Arthropods Body Structure • Arthropods are __________ invertebrates that have: External skeleton – _______________ – _______________ A segmented body Appendages - jointed attachments – ___________ joint “arthros” – Greek for ______ Foot or leg “podos” – Greek for __________ – Bilateral symmetry – ______ open circulatory system and a digestive system Two openings with ___________ – Reproduce sexually Outer Skeleton • ___________ - waterproof outer covering exoskeleton • Exoskeleton _________ the animal and protects prevents __________ Evaporation • Arthropods occasionally shed their exoskeleton and grow new ones that are larger. • __________ - the process of shedding the molting exoskeleton Segmented Body • Segmented bodies similar to an earthworm • Easy to see segments in _________ and centipedes millipedes __________. • An arthropod may have up to three segments: – _________ head – _________ Mid-section Hind section – ___________ identical Segments are _________ looking Jointed Appendages • ________ in ___________ give the animal Joints appendages ____________ and enable it to ________ flexibility move • ______________________ Appendages are highly specialized tools for moving, eating, reproducing, and sensing the environment • ________ - an appendage that is attached to antenna head that contains sense organs. the _____ • ____ legs and _____ wings are also appendages Diversity • Scientists have identified more species of arthropods – over a million – than all other species of animals combined! Crustaceans • ___________ - shrimp, crab, and pill bugs crustaceans • Crustaceans thrive in ________, freshwater ______, oceans or Damp places ___________ Body structure - two or three body sections, • ___________ five or more pairs of legs, and two pairs of antenna oxygen - most have gills to obtain oxygen • ______ food - scavengers, predators, herbivores • ____ Life Cycle of Crustaceans • Life cycle for many varieties begins as _______ larvae • metamorphosis ______________ - a process in which an animal’s body undergoes dramatic changes in form during its life cycle. • _________ develop into adults through larvae ____________. metamorphosis Arachnids • arachnids ________ - spiders, mites, ticks, and scorpions • Arachnids are _________ with two body arthropods sections, four pairs of legs, and no antennae • ____________ First body section - combined head and midsection • _____________ Second body section - hind section called the ________ abdomen abdomen • ___________ - contains the reproductive organs and part of the digestive system. Spiders / Mites/ Scorpions/Ticks • All spiders are ________ predators and most eat _______. insects • Adaptations include _____ fangs - used to inject venom and sucks in food • _______ and chiggers are parasites _________ Mites stinger at the end • __________ - adaptation is a _____ scorpions of its abdomen to inject venom into prey. ticks • ______ - parasites that live on the outside of hosts bodies Math / Analyzing Data pg. 341 Centipedes and Millipedes arthropods • Centipedes and millipedes are _________ with ____________ Two body sections and _____________. Many pairs of legs • First body section has a _____ head with one pair of _________ antennae • The second body section has a long _________ with many body segments abdomen • ___________ have one pair of legs attached centipedes to each segment Centipedes and Millipedes Continued “ one hundred feet” • Centipede means ______________ • Centipedes are very fast _______ predators that inject venom into their ____. prey Millipedes • ____________ - have more than 80 segments have _____ pairs of legs on each segment. two “thousand feet” • Millipede means _____________ - they do not have that many scavengers • Millipedes are _________ Section 2 Assessment • Page 342 (1 and 2) Insects • ________ - caterpillars, plant hoppers, insects dragonflies, and bees arthropods • Insects are ___________ with all of the following: Three body sections – _________________ Six legs – ________ One pair of antennae – _________________ – ________________ Two pairs of wings Body Structure • The three body sections are: head – ________ - most of the insects sense organs, two large compound eyes – keen at sensing movement. Simple eyes distinguish between light and darkness. thorax - midsection where wings and legs are – _______ attached. Insects are the only invertebrates that can fly – _________ abdomen - contain the internal organs Obtaining food • Insects feed on all of the following depending on their specialized and adapted _________: mouthparts – _________________________ Parts of plants – leaves or nectar Products that are made from plants – book lice – __________________________________ Animal – fleas and mosquitoes feed on the blood of – ______________________________________ living animals Animal droppings – dung beetle – _________________________ Decaying bodies of dead animals – burying beetles – ______________________________________ Life Cycle • Insects are born from tiny, hard shelled ___________ Fertilized eggs • After they hatch, insects begin a process of metamorphosis (either complete or gradual) ____________ before becoming an adult _____insect. • __________________ Complete metamorphosis - four stages – – – – egg _______ larvae - specialized for eating and growing ______ pupa - enclosed in a protective covering ______ _______ - beetles, butterflies, flies and ants adult Gradual Metamorphosis Gradual metamorphosis - no distinct larval phase. • ________________ • Egg hatches into a stage called a _____ nymph nymph • _________ - looks like an adult insect without wings • Grasshoppers, termites, cockroaches and dragonflies. Insect Ecology • ___________ - series of events in which one Food Chain organism eats another and obtains energy. • __________ - the study of food chains and ecology other ways that organisms interact with their environment sun • All food chains begin with the ____ • Next a _________ - an organism that makes producer its own food – grass and other plants. Insects and the Food Chain • ___________ - producers are the food that consumers provides energy. Some consumers also eat consumers other _________. • ___________ - breaks down the wastes and decomposers dead bodies of other organisms • Insects can either be _________ or _________ consumers decomposers in the food chain • Insects can be ______ for other consumers prey Insects as Consumers, Prey, and Decomposers 20% of the crops grown by • Insects eat about ____ humans as well as wild plants. consume plant materials – Caterpillars ________ prey – Caterpillars and other insects are _______ for other types of animals such as birds and fish. decomposers – Insects such as the carrion beetle are __________ - feed on the tissues of dead birds. Pollen and Disease Carriers • _________ - an animal that carries pollen pollinators among plants. Examples of insects as Bees, beetles, and flies pollinators are _______________. • Without pollinators some plants would not be able to _________ reproduce • Insects that carry diseases often have Sucking mouth parts that pierce the skin of their ______________ prey that provides an opening for the disease malaria to enter the organisms body - ______ Controlling Pests pesticides • _________ - use of chemicals to control pests • Pesticides have also killed _________ pollinators traps and other • Humans have also used ____ Living things (such as other insects) to control __________ pests. Biological control • _______________ - a natural predator or disease released into an are to fight a harmful insect. Echinoderms Echinoderms • _____________ - invertebrates with an internal skeleton and a system of fluid filled tubes. • All echinoderms live in ________ Salt water • The internal skeleton of the echinoderms is called an __________ Endoskeleton - made up of hard plates which give the animal a bumpy texture. • ______________ Radialy symmetrical usually in multiples of 5 Movement Water vascular system • _________________ - the internal system of fluid-filled tubes • The water vascular system contracts and forces water into the _______ Tube feet - the ends of the tube feet are sticky and they act like suction cups. suction • The ________ allow the stickiness and __________ echinoderms to grip the surface beneath them Reproduction and Life Cycle eggs are usually fertilized in the ______ water • _____ • Fertilized egg develops into a swimming ______ . larvae larvae undergo ___________ metamorphosis and become • ______ ______ echinoderms. adult • 4 major groups of echinoderms: __________, __________, _________, Sea stars Brittle Stars Sea Urchins Sea Cucumbers __________