Review Guide for Mitosis & Meiosis- Answers
advertisement

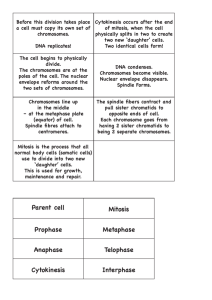
1 Answers for Review Guide for Mitosis & Meiosis 1. How do prokaryotes reproduce? Name the steps in order. Prokaryotes reproduce by binary fission. They: (a) copy the chromosome then (b)divide the cytoplasm 2. Name the stages in the cell cycle. Interphase, the Mitotic phase, & cytokinesis 3. What happens in the G1 phase? Protein synthesis- the cell gets larger 4. What happens in the S phase? DNA (the chromosomes) gets copied 5. What happens in the G2 phase? The cell doubles the number of organelles and the cell gets ready to divide 6. Together, the G1, S, And G2 phases make up what major phase in the cell cycle? Interphase 7. What are the four phases of the M phase? Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, & Telophase 8. What is a chromatid? A centromere? One side of a copied chromosome. The centromere is a region near the middle of a chromosome. When chromosomes are replicated (copied) the centromere is the only as yet uncopied region of the chromosome. It holds the chromatids together until they are pulled apart during anaphase. 9. What does the kinetochore do in cell division? It attaches the centromere of a chromosome to the spindle fiber. 10. What is the function of the centrioles in cell division? Of the spindle fibers? Centrioles move to the poles of the cells and organize the spindle fibers. Spindle fibers attach to the centromere region of a chromosome and eventually, will separate the chromosomes into 2 new cells. They also push the cell apart helping the cytoplasm to divide. 11. Describe what happens in each of the following phases, and draw a cell in that phase. a. Interphase – In between the cell division; cell grows & carries out daily living Chromosomes are replicated during the S phase b. Prophase- Preparatory; Spindle forms; Centrioles move to opposite poles; Chromosomes become visible; Nuclear membrane disappears c. Metaphase- Middle phase; Chromosomes line up along the equator. d. Anaphase – Apart phase; Centromeres divide; Chromatids separate and move to opposite poles 2 e. Telophase- Terminal phase; Nuclear membrane forms around each group of chromosomes; Chromosomes unwind 12. Describe what happens in cytokinesis and draw a cytokinesis cell. The cytoplasm divides by forming a cleavage furrow around an animal cell or a division plate I a plant cell 13. What kind of cell division produces haploid cells? Meiosis; 2 divisions; 4 haploid gametes formed 14. What kind of cell division produces diploid cells? Mitosis; 1 division, 2 diploid daughter cells formed 15. What is the formation of the male gamete called? What is the formation of the female gamete called? Male- spermatogenesis Female- oogenesis 16. How many cell divisions does meiosis require? Which division is called the reduction division? Why? Meiosis requires two cell divisions. The first division is called the reduction division because the number of chromosomes is reduced by half in the daughter cells formed by the first division. 17. During interphase I, what do the chromosomes do? Chromosomes are copied (replicated) 18. Define: a. Synapsis- homologous chromosomes zip together (In the clay chromosome lab, we stacked one homologous chromosome on top of another.) b. homologous chromosomes- Chromosomes of the same kind; they have the same sorts of genes in the same loci (locations) along the chromosome. c. Tetrad- Tetrad is two chromosomes or four chromatids (sister and nonsister chromatids) d. Locus- location of a specific gene on a specific chromosome; the “address” of the gene 19. Define: a. Autosomes- 22 out of the 23 pairs of chromosomes we have; they look alike b. Sex chromosomes- chromosomes that determine the sex of an individual; the 23rd pair that may not look alike 20. What combination of sex chromosomes produces a female? A male? Male- XY Female- XX 21. Briefly tell what happens in each of the steps of meiosis. Draw a picture if you want. a. Interphase I- Like Interphase in mitosis; chromosomes are replicated and more organelles are forms. b. Prophase I- Longest and most complex phase (90%); Chromosomes condense (coil up so you can see them); Synapsis occurs; Crossing over may occur 3 c. Metaphase I- Shortest phase; Tetrads lime up on the metaphase plate; Independent assortment occurs; Chromosomes separate randomly to the poles of the cells d. Anaphase I- Homologous chromosomes separate and move towards the poles Sister chromatids remain attached at their centromeres e. Telophase I- Each pole now has haploid set of chromosomes; Cytokinesis occurs and two haploid daughter cells are formed f. Prophase II- Same as prophase in mitosis; centrioles divide and move to the poles; the spindle apparatus forms and attaches to the centromeres of the chromosomes g. Metaphase II- Same as metaphase in mitosis; Chromatids lined up at equator h. Anaphase II- Same as anaphase in mitosis; Sister chromatids separate i. Telophase II- Same as telophase in mitosis; Nuclei reform; Cytokinesis occurs Remember: Four haploid daughter cells produced to form Gametes = sperm or egg 22. Why is genetic variation important? Name three ways it can happen. It allows organisms a chance to better adapt to their environment by giving them more choices for genes & therefore traits. Crossing over Independent assortment Random fertilization 23. Define: a. Karyotype- A method of organizing the chromosomes of a cell in relation to number, size, and type. b. Fertilization- The fusion of a sperm and egg to form a zygote. c. Zygote- A zygote is a fertilized egg.