Charging by Contact PPt
advertisement

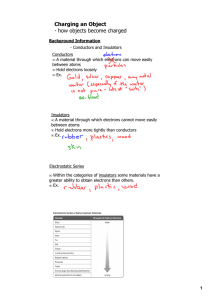
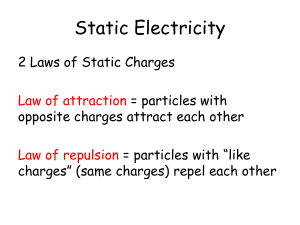
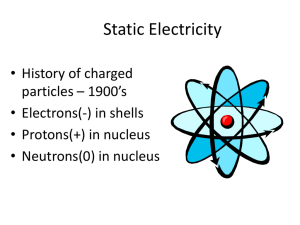
MINDS ON • Think of a time you got a shock from something. Did it hurt? Why? • What do you think happened? • How do you prevent it? • Is there a time or place when you tend to get more or less shocks? CHARGING BY CONTACT Write Yellow Text Only LEARNING GOALS • I will be able to use the electrostatic series to identify charges when charging objects by friction. • I will be able to determine the change in charge when objects are charged by contact. 1. CHARGING BY FRICTION • Occurs when two neutral materials are rubbed together. • When this happens • One material will attract extra electrons (become negative) • One material will give up extra electrons (become positive) Material THE ELECTROSTATIC SERIES Human Skin + Rabbit Fur (Likely to surrender electrons) Acetate Glass Human Hair Nylon Wool list of materials arranged in order of their tendency to gain electrons. Cat Fur Silk Paper • How does it work? Cotton Wood material lower on list will take electrons from material higher on list Amber Rubber Balloon Vinyl Polyester Ebonite Plastic (Likely to gain electrons) - THE BALLOON DEMONSTRATION • Consider a rubber balloon being rubbed on a cotton sweater. 1. To which material were electrons transferred? Why? 2. What is the overall charge of both materials after the contact? 3. Why does the balloon stick to the sweater? TRY THIS • Activity p473 of text book! • Work with elbow partner. • Follow procedures 1-5 and answer questions A, B, C. 2. CHARGING BY CONDUCTION • Transferring of charges by direct contact: • End result: charges are equal. 3. GROUNDING • The removal of excess electric charge on an object by connecting it to the earth. • You have experienced this when: • Shocked by a car door • Shocked by a door handle after walking on carpet • You have seen a lightning storm • After grounding, the object returns to a neutral charge. Symbol for grounding APPLICATIONS 1. Electrostatic dusters (swiffers) • 2. Uses static electricity to attract dust from floors Electrostatic precipitators • Uses static electricity to attract ash and dust particles from smoke stacks • Can reduce harmful particle emissions by 99% LEARNING GOALS REVISITED • I will be able to use the electrostatic series to identify charges when charging objects by friction. • I will be able to determine the change in charge when objects are charged by contact. YOUR TURN • P477 #1-3, 5,6,8.