Charging Objects
advertisement

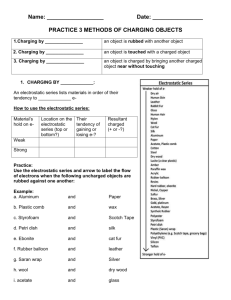
Charging Objects Key Terms Conductor materials that can conduct electricity This means that they can carry the electric charge from one area to another Examples: Metals! Salt water, human body Insulator materials that do not conduct electricity This means that the charge will stay still (static) Examples: rubber, plastic, wood Charging Objects 1. Charging by Contact Charging by Friction Charging by Conduction 2. Charging by Induction Charging by Contact - Friction Objects: Two Neutral Objects Action: Rub together, electrons transfer from one object to another Outcome: One negative object, one positive object The Electrostatic Series Material Charge Tendency Human Skin Weak Tendency to gain electrons Rabbit Fur Acetate Glass The object with the stronger tendency to gain electrons will become negatively charged. Human hair The object with the weaker tendency to gain electrons will be positively charged. Cat fur nylon wool Silk Paper Cotton Wood This chart is on page 473 Vinyl Polyester Ebonite Strong Tendency to gain electrons Charge by Contact - Conduction -5 charge -3 charge -4 charge -4 charge Objects: Two differently charged objects Action: Two objects come in contact with each other, electrons transfer between objects Outcome: Two objects share the same charge Also, commonly seen between a charged and neutral object Metal Leaf Electroscope Metal leaf electroscopes can be used the detect charge When a charged object comes in contact with the metal knob, the charge moves to the aluminum foil. Why does this happen? The metal knob, stem and foil all conduct electricity Remember: Laws of Electric Charge Grounding Objects do not remain charged indefinitely, eventually they will lose their charge. Symbol which denotes grounding The ground has an indefinite number of protons and electrons. Losing or gaining electrons has absolutely no affect on the charge of the ground. It will remain neutral Grounding When you have a build up of negative charge on your body (due to friction), this excess charge will make its way to the ground by traveling through a conductor The end result is that all objects are neutral, and the ground remains neutral If the build up of charge on your hand was positive, then electrons would travel up from the ground, through the door, to neutralize your hands p. 477 summary and questions Charging by Induction Objects: A charged object and a neutral object Action: Objects are brought close together (touching is not necessary). Electrons are NOT transferred, they simply move within an object. Outcome: The charged object and neutral object remain unchanged. There is a temporary build up of charge on the neutral object. Van de Graff Generator http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7qgM1A3pgkQ Questions p. 489 Q: 2, 3,