Poster Template - UNC Eshelman School of Pharmacy FAO
advertisement
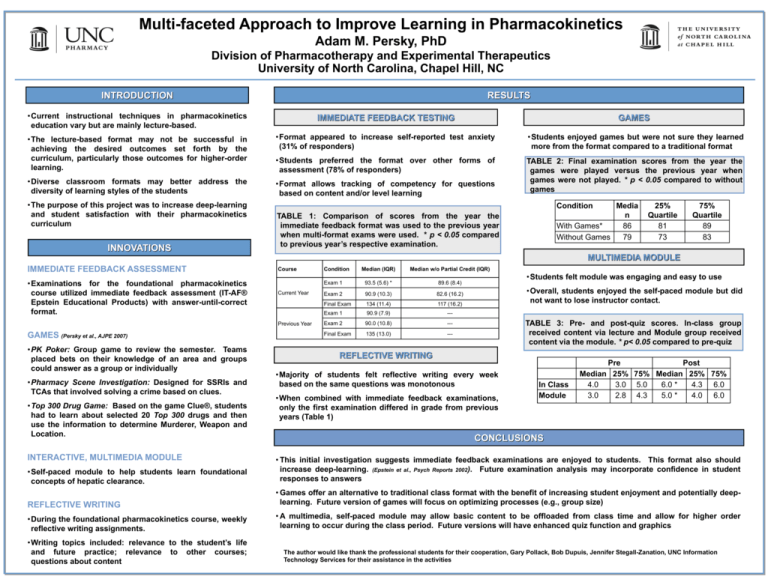
Multi-faceted Approach to Improve Learning in Pharmacokinetics Adam M. Persky, PhD Division of Pharmacotherapy and Experimental Therapeutics University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC RESULTS INTRODUCTION • Current instructional techniques in pharmacokinetics education vary but are mainly lecture-based. IMMEDIATE FEEDBACK TESTING GAMES • The lecture-based format may not be successful in achieving the desired outcomes set forth by the curriculum, particularly those outcomes for higher-order learning. • Format appeared to increase self-reported test anxiety (31% of responders) • Students enjoyed games but were not sure they learned more from the format compared to a traditional format • Students preferred the format over other forms of assessment (78% of responders) • Diverse classroom formats may better address the diversity of learning styles of the students • Format allows tracking of competency for questions based on content and/or level learning TABLE 2: Final examination scores from the year the games were played versus the previous year when games were not played. * p < 0.05 compared to without games • The purpose of this project was to increase deep-learning and student satisfaction with their pharmacokinetics curriculum INNOVATIONS Condition Media n With Games* 86 Without Games 79 TABLE 1: Comparison of scores from the year the immediate feedback format was used to the previous year when multi-format exams were used. * p < 0.05 compared to previous year’s respective examination. 25% Quartile 81 73 75% Quartile 89 83 MULTIMEDIA MODULE IMMEDIATE FEEDBACK ASSESSMENT • Examinations for the foundational pharmacokinetics course utilized immediate feedback assessment (IT-AF® Epstein Educational Products) with answer-until-correct format. Course Current Year Previous Year GAMES (Persky et al., AJPE 2007) • PK Poker: Group game to review the semester. Teams placed bets on their knowledge of an area and groups could answer as a group or individually • Pharmacy Scene Investigation: Designed for SSRIs and TCAs that involved solving a crime based on clues. • Top 300 Drug Game: Based on the game Clue®, students had to learn about selected 20 Top 300 drugs and then use the information to determine Murderer, Weapon and Location. INTERACTIVE, MULTIMEDIA MODULE Condition Median (IQR) Median w/o Partial Credit (IQR) Exam 1 93.5 (5.6) * 89.6 (8.4) Exam 2 90.9 (10.3) 82.6 (16.2) Final Exam 134 (11.4) 117 (16.2) Exam 1 90.9 (7.9) --- Exam 2 90.0 (10.8) --- Final Exam 135 (13.0) --- • Students felt module was engaging and easy to use • Overall, students enjoyed the self-paced module but did not want to lose instructor contact. TABLE 3: Pre- and post-quiz scores. In-class group received content via lecture and Module group received content via the module. * p< 0.05 compared to pre-quiz REFLECTIVE WRITING • Majority of students felt reflective writing every week based on the same questions was monotonous • When combined with immediate feedback examinations, only the first examination differed in grade from previous years (Table 1) In Class Module Pre Post Median 25% 75% Median 25% 75% 4.0 3.0 5.0 6.0 * 4.3 6.0 3.0 2.8 4.3 5.0 * 4.0 6.0 CONCLUSIONS • Self-paced module to help students learn foundational concepts of hepatic clearance. • This initial investigation suggests immediate feedback examinations are enjoyed to students. This format also should increase deep-learning. (Epstein et al., Psych Reports 2002). Future examination analysis may incorporate confidence in student responses to answers REFLECTIVE WRITING • Games offer an alternative to traditional class format with the benefit of increasing student enjoyment and potentially deeplearning. Future version of games will focus on optimizing processes (e.g., group size) • During the foundational pharmacokinetics course, weekly reflective writing assignments. • A multimedia, self-paced module may allow basic content to be offloaded from class time and allow for higher order learning to occur during the class period. Future versions will have enhanced quiz function and graphics • Writing topics included: relevance to the student’s life and future practice; relevance to other courses; questions about content The author would like thank the professional students for their cooperation, Gary Pollack, Bob Dupuis, Jennifer Stegall-Zanation, UNC Information Technology Services for their assistance in the activities