DAY 2 - Psychodynamics
advertisement

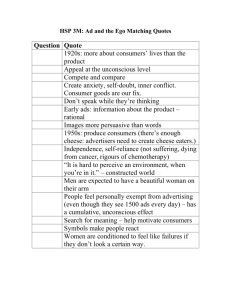
Focuses on trying to get inside the head of individuals in order to make sense of their relationships, experiences and how they see the world. • The major causes of behavior have their origin in the unconscious unlocking the unconscious mind is the key to understanding & changing human behaviour • The conscious & unconscious mind are in constant conflict therapy focuses on resolving these conflicts • Our behavior and feelings as adults are rooted in our childhood experiences can lead to psychological illness Created a school of thought called Psychoanalysis a person's development is determined by events in early childhood This school of thought emphasized the influence of the unconscious mind on human behavior Conflicts that occur between the conscious & unconscious mind, can materialise in the form of mental or emotional disturbances as we grow, our personalities are shaped by repressed childhood thoughts & experiences Freud believed that the human mind was composed of 3 elements: the ID, the EGO, and the SUPEREGO These elements form our personality ID functions in the unconscious mind and is responsible for instinctive and primitive behaviors. The ID is driven by the pleasure principle, which strives for immediate gratification of all desires, wants, & needs. EGO functions in the conscious & unconscious mind and is responsible for controlling the impulses of the ID The EGO is driven by the reality principle, which strives to satisfy the ID's urges in realistic & socially acceptable ways. SUPEREGO functions in the conscious mind and is responsible for our sense of right and wrong. The SUPEREGO is driven by the morality principle & acts to suppress the ID’s urges and make the EGO behave morally rather than realistically. His work supported the belief that not all psychological illnesses were caused by biological means and that many human behaviours were the result of repressed, unconscious thoughts rooted in childhood experiences. He believed that balancing a person’s psyche would allow the person to reach his or her full potential. Jung believed the human psyche exists in three parts: • the ego (the conscious mind) • the personal unconscious and • the collective unconscious Jung believed the collective unconscious was a reservoir of all the experience and knowledge of the human species. Jung contributed a great deal to the study of personality. He theorized that our personalities were a mix of functional types: 1. Introversion vs Extroversion 2. Sensing vs Intuition 3. Thinking vs Feeling 4. Judging vs Perceiving Jung believed that we “consciously” gravitated to one functional type while our “unconscious” gravitated to the opposite type. Erikson differed from Freud in a couple of ways: 1. He believed that humans continue to develop over their lifetime rather than just in childhood 2. He believed individual growth depends on society, not just personal experiences He also believed that adolescents experienced an identity crisis a time of extreme self-consciousness Both Freud and Erikson believed that children matured and developed through stages Freud believed that children developed through a series of psycho-sexual stages. These stages occurred one after the other. If an individual became fixated at any one stage, they could not move on to the next stage in a healthy way. Erikson believed that children developed through a series of psycho-social stages where certain needs must be met at each stage or their social development in later life would be impaired. Her studies of child development have become the groundwork for our understanding of mother-infant attachment AND how it influences behaviour in later life. She is most well known for her “Strange Situation” experiment http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QTsewNrHUHU&feature=related