Environmental Hazards - Georgia Tech OSHA Consultation Program
advertisement

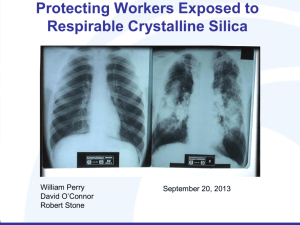
Chapter 4: Environmental Hazards Lead Can you name some materials in a house that might contain lead? What is Lead? •Chemical element •Pb: Latin “Plumbum” •Plumber, Plumb bob •Heavy,soft (malleable) metal 49 In Indium 114.82 50 Sn Tin 118.69 51 Sb Antimony 121.75 81 Tl Thallium 204.37 82 Pb Lead 207.19 83 Bi Bismuth 208.980 What’s the Matter with Lead? • Highly toxic poison • Accumulates in body tissues • Harms many body systems – blood – nerves, brain – reproductive How Can I Be Exposed to Lead? • Deteriorated lead paint • Burning or cutting metals containing or painted with lead – Plumbing lines – Solder joints – Corrosion resistant metal coatings What Steps Do I Take First? • Before you begin work, have a “Competent Person” determine if workers will be potentially exposed to lead • If workers are potentially exposed, determine if the concentration of these exposures exceeds OSHA limits • If workers conduct “Trigger Tasks”, certain controls are required TRIGGER TASK 1 (< 10 x the PEL) • Manual demolition of structures • Hand scraping or sanding • Heat guns • Using power tools with dust collection systems • Spray painting TRIGGER TASK 2 (10-50 X PEL) • Using power tools without dust collection systems attached • Movement/removal of enclosures • Cleanup where dry expendable abrasives are used • Lead containing mortar, rivet busting TRIGGER TASK 3 (>50 x the PEL) • Abrasive blasting • Welding or torch cutting metals containing lead or lead based paint Respiratory Protection (Minimum requirements) • Trigger task 1 – ½ mask air purifying respirator with high efficiency filters (HEPA) • Trigger task 2 – Full face piece respirator with high efficiency filters (HEPA) • Trigger task 3 – Supplied air pressure/demand respirator Other Requirements • Personal protective clothing, such as disposable jump suits • Change areas for work clothing and shoes • Hand washing facilities • Biological monitoring (Blood Lead) • Training METHODS OF COMPLIANCE Lead in Construction • Exposures > PEL (From Day One) – Engineering Controls – Respiratory protection – Compliance program – Mechanical ventilation – Administrative controls – Good work practices Silica Silica • What is Silica? • Where is it found on construction sites? • When does silica become hazardous? What are the Health Effects of Silica? • Silicosis • Affects alveolar surface of lungs – Decreases elasticity – Prevents oxygen/CO2 exchange • Lung X-ray is required to diagnose silicosis • Silica also contributes to tuberculosis, heart disease, and lung cancer What Jobs Cause Exposure? • Cutting concrete slabs • Finishing and grinding on concrete • Block and brick cutting • Jack hammering on concrete • Abrasive blasting Control Silica Using Wet Methods • Water suppression of dust is effective • Minimal water use is required • Planning for water supply is required Using Ventilation to Control Dust • Use when wet methods are not feasible • Collect dust at the source • Supplement with respirators • Avoid contaminating co-workers Asbestos Asbestos 1. Surfacing Material 2. Thermal System Insulation (TSI) 3. Miscellaneous Photo: oldhouseweb.com Health Effects of Exposure to Asbestos • Asbestos exposure can cause: – Asbestosis – Mesothelioma – Lung Cancer – Other Illnesses/Cancers FEDERAL ASBESTOS REGULATIONS (Occupational Exposures) 1. OSHA Asbestos in Construction Asbestos in General Industry 2. EPA Worker Protection Rule Major Elements of OSHA’s Asbestos Standard 29 CFR 1926.1101 (Construction) – Exposure monitoring • Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL) of 0.1 f/cc, 8 hour TWA • Excursion Limit of 1.0 f/cc, 30 minutes – Employee training and education – Regulated areas Major Elements of OSHA’s Asbestos Standard (cont.) – Defines 4 Classes of work activity • Training for each class of work activity – Engineering and work practice controls – Protective equipment – Medical surveillance – Recordkeeping MOLD Mold • Molds are microscopic organisms found everywhere. • Some molds can cause adverse health effects. How to Recognize Mold • Sight—Usually appears as colored woolly mats • Smell—Often produces a foul, musty, earthy smell Hidden Mold in Buildings How to Protect Yourself • Avoid mold spores • Use respiratory protection. • Protect your skin How to Protect Yourself (continued) • Wear goggles • Avoid getting mold or mold spores in your eyes. Cleanup of Mold • Disinfect hard, water resistant, non-porous surfaces • Consider discarding water-damaged porous materials. • After working with moldcontaminated materials, wash thoroughly, including the hair, scalp, and nails. Regulation of Mold Cleanup • • • • • No exposure limits No federal rules State and local rules may apply State/local certification may apply Specific contractual obligations may apply