Osmosis, Diffusion & Active Transport L/O
advertisement
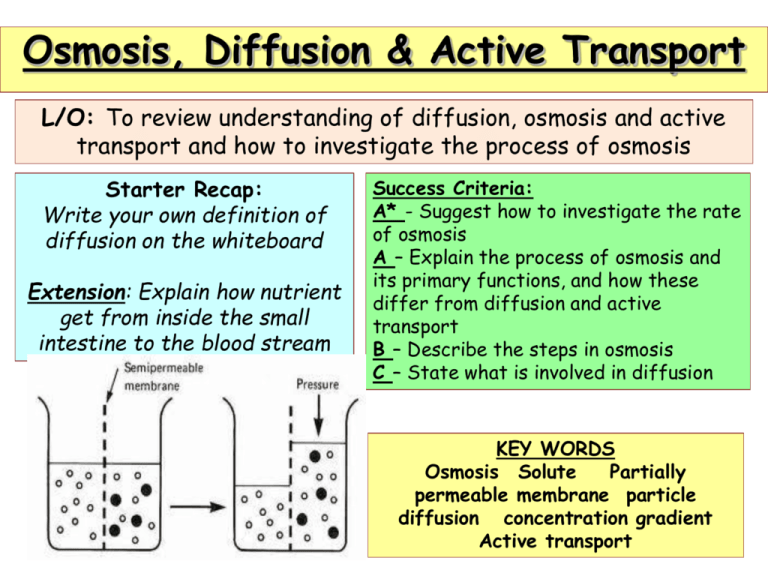
Osmosis, Diffusion & Active Transport L/O: To review understanding of diffusion, osmosis and active transport and how to investigate the process of osmosis Starter Recap: Write your own definition of diffusion on the whiteboard Extension: Explain how nutrient get from inside the small intestine to the blood stream Success Criteria: A* - Suggest how to investigate the rate of osmosis A – Explain the process of osmosis and its primary functions, and how these differ from diffusion and active transport B – Describe the steps inEnquirers osmosis CORE: Independent C – State what is involved in diffusion KEY WORDS Osmosis Solute Partially permeable membrane particle diffusion concentration gradient Active transport If you open a can of pop, gas particles spread out into the air. This is another example of diffusion. Definition: Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of high concentration, to an area of lower concentration. Osmosis Solute molecule Many water molecules Weak Solution What will happen in this situation? Fewer water molecules Strong Solution Partially permeable membrane What will happen in this situation? Osmosis in blood cells Liquid is more concentrated Liquid and cell cytoplasm are the same concentrations Inside cells are more concentrated Cells become flaccid when water moves out of them. Cells become turgid due to water pressure when water moves into them Osmosis vs. Diffusion Similarities Differences What are the similarities and differences between the two? Osmosis vs. Diffusion: PEER ASSESS Similarities Differences Movement of molecules from areas of high concentration to low concentration Osmosis is movement of water only/ Diffusion any small molecules Movement of small particles/molecules Both found in all plant and animal cells to move substances in and out Osmosis moves across a partially permeable membrane/ Diffusion moves more generally What are the similarities and differences between the two? How to kill a slug? QUESTIONS: Using your knowledge of osmosis explain how to remove the slugs that are eating Farmer Gile’s lettuces! Include an explanation using the following key words: • Concentration gradient • Osmosis • Diffusion • Solute • Particle Active Transport This is when substances are absorbed against their concentration gradients. This uses energy. Explain how this process uses active transport and where this might be found. OSMOSIS Recap Net flow of water is from areas of high concentrations of water molecules to low concentrations of water molecules Water molecules move in both directions Sugar cannot cross the partially permeable membrane as they are too large Net flow of water is from dilute solutions to concentrated solutions Cold Call Questions! 1. What is an independent variable? 2. What is a dependent variable? 3. What is a systematic error? 4. What makes something reliable? 5. What makes something valid? 6. What is diffusion? 7. Give an example of diffusion? 8. What is osmosis? 9. What is different about osmosis and diffusion? 10.Name one place in the body where diffusion happens? 11. What happens to a red blood cell if it is placed in a salt solution? 12.What happens to a red blood cell if placed in a pure water solution? THE EXPERIMENT Method: 1. Weigh 4 different 1cm3 of potato cube on scales (RECORD EACH WEIGHT) 2. Place each potato chip into a boiling tube with different sugar solutions 3. Leave for 20mins and complete questions while waiting! 4. Remove chips, dry and re-weigh. 5. Calculate the change in mass of each chip in each concentration THE EXPERIMENT Label the potato boiling tube so you know which cube is which! Method: Complete the workshe et while you are waiting for the results! DRAWING A TABLE Solution sugar concentration (%) Initial Mass (g) Final Mass (g) Change in mass (g) Change in mass of potato (g) INTERPRETING RESULTS Sugar solution (%) Plot a graph of your results and explain what happens at each stage • Success Criteria: • A* - Suggest how to investigate the rate of osmosis • A – Explain the process of osmosis and its primary A* functions, and how these differ from diffusion and active transport • B – Describe the steps in osmosis • C – State what is involved in diffusion What have I learnt? On the exit ticket complete what target you archived you know you achieved (i.e. what can you do). Look at the success criteria to help you 5 min