Week#8 - mrmilewski
advertisement

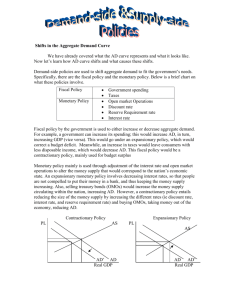
AP Macro Week#7 Fall 2014 Economics 10/20/14 http://mrmilewski.com • OBJECTIVE: Continue examination of Chapter#27 AP Macro-II.B • Language objective: Work on computers in library. • I. Admin Stuff -attandance & library • Homework: Finish homework on learnsmart Economics 10/21/14 http://mrmilewski.com • OBJECTIVE: Continue examination of Chapter#27 AP Macro-II.B • Language objective: Talk about basic macroeconomic relationships. • I. Journal#23 -notes on basic economic relationships • Homework: Questions (6-9) p565 & Problems (6-7,9) p.566. Interest-Rate-Investment • Expected rate of return • The real interest rate • Investment demand curve LO3 27-4 (r) and (i) 16% $0 14 5 12 10 10 15 8 20 6 25 4 30 2 35 0 LO3 Investment (billions of dollars) 40 Expected rate of return, r and real interest rate, i (percents) Investment Demand Curve 16 14 Investment demand curve 12 10 8 6 4 2 ID 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 Investment (billions of dollars) 27-5 Shifts of Investment Demand • Acquisition, maintenance, and • • • • • LO4 operating costs Business taxes Technological change Stock of capital goods on hand Planned inventory changes Expectations 27-6 Expected rate of return, r, and real interest rate, i (percents) Shifts of Investment Demand Increase in investment demand Decrease in investment demand 0 LO4 ID2 ID0 ID1 Investment (billions of dollars) 27-7 Global Perspective LO4 27-8 Instability of Investment • Variability of expectations • Durability • Irregularity of innovation • Variability of profits LO4 27-9 Instability of Investment Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis, http://www.bea.gov. LO4 27-10 The Multiplier Effect • A change in spending changes real GDP more than the initial change in spending Multiplier = change in real GDP initial change in spending Change in GDP = multiplier x initial change in spending LO5 27-11 The Multiplier Effect (1) Change in Income (2) Change in Consumption (MPC = .75) (3) Change in Saving (MPS = .25) $5.00 $3.75 $1.25 Second round 3.75 2.81 .94 Third round 2.81 2.11 .70 Fourth round 2.11 1.58 .53 Fifth round 1.58 1.19 .39 All other rounds 4.75 3.56 1.19 $20.00 $15.00 $5.00 Increase in investment of $5.00 Total Cumulative income, GDP (billions of dollars) 20.00 $4.75 15.25 13.67 $1.58 $2.11 11.56 $2.81 8.75 $3.75 5.00 $5.00 1 LO5 2 3 4 5 All others 27-12 Multiplier and Marginal Propensities • Multiplier and MPC directly related • Large MPC results in larger • increases in spending Multiplier and MPS inversely related • Large MPS results in smaller increases in spending Multiplier = LO5 1 1- MPC Multiplier = 1 MPS 27-13 Multiplier and Marginal Propensities MPC Multiplier .9 10 .8 5 .75 4 .67 .5 LO5 3 2 27-14 The Actual Multiplier Effect? • Actual multiplier is lower than the • • • • LO5 model assumes Consumers buy imported products Households pay income taxes Inflation Multiplier may be 0 27-15 Squaring the Economic Circle • Humorous small town example of the • • • multiplier One person in town decides not to buy a product Creates a ripple effect of people not spending, following the first decision Ultimately the entire town experiences an economic downturn 27-16 Homework Tonight • Questions (6-9) p565 & Problems (6-7,9) p.566. • Begin Reading Ch#29 Economics 10/22/14 http://mrmilewski.com • OBJECTIVE: Complete examination of Chapter#27 AP Macro-II.B • Language objective: Talk about basic macroeconomic relationships. • I. Review last nights homework • Homework: Look over Ch#29 Economics 10/23/14 http://mrmilewski.com • OBJECTIVE: Begin examination of aggregate demand & aggregate supply Chapter#29 AP Macro-II.B • Language objective: Talk about basic macroeconomic relationships. • I. Journal#24 -notes on basic AD & AS • Homework: Questions on Learnsmart Aggregate Demand • Real GDP desired at each price level • Inverse relationship • Real balances effect • Interest effect • Foreign purchases effect LO1 29-20 Price level Aggregate Demand AD 0 LO1 Real domestic output, GDP 29-21 Changes in Aggregate Demand • Determinants of aggregate demand • Shift factors affecting C, I, G, Xn • 2 components involved • Change in one of the determinants • Multiplier effect LO1 29-22 Price level Changes in Aggregate Demand AD2 AD3 AD1 0 Real domestic output, GDP LO1 29-23 Consumer Spending • Consumer wealth • Household borrowing • Consumer expectations • Personal taxes LO1 29-24 Investment Spending • Real interest rates • Expected returns • Expectations about future business conditions • Technology • Degree of excess capacity • Business taxes LO1 29-25 Government Spending • • LO1 Government spending increases • Aggregate demand increases (as long as interest rates and tax rates do not change) • More transportation projects Government spending decreases • Aggregate demand decreases • Less military spending 29-26 Net Export Spending • National income abroad • Exchange rates • Dollar depreciation • Dollar appreciation LO1 29-27 Aggregate Supply • Total real output produced at each price • LO2 level Relationship depends on time horizon • Immediate short run • Short run • Long run 29-28 AS: Immediate Short Run Price level Immediate-short-run aggregate supply P1 0 ASISR Qf Real domestic output, GDP LO2 29-29 Aggregate Supply: Short Run AS Price level Aggregate supply (short run) 0 Qf Real domestic output, GDP LO2 29-30 Aggregate Supply: Long Run Price level ASLR Long-run aggregate supply 0 Qf Real domestic output, GDP LO2 29-31 Economics 10/24/14 http://mrmilewski.com • OBJECTIVE: Continue examination of aggregate demand & aggregate supply Chapter#29 AP Macro-II.B • Language objective: Talk about basic macroeconomic relationships. • I. Journal#25 -notes on interest, & continue AD & AS • Homework: Finish Questions on Learnsmart Changes in Aggregate Supply • Determinants of aggregate supply • Shift factors • Collectively position the AS curve • Changes raise or lower per-unit production costs LO2 29-33 Changes in Aggregate Supply AS3 AS1 Price level AS2 0 Real domestic output, GDP LO2 29-34 Input Prices • Domestic resource prices • Labor • Capital • Land • Prices of imported resources • Imported oil • Exchange rates LO2 29-35 Productivity • Real output per unit of input • Increases in productivity reduce costs • Decreases in productivity increase costs Productivity = Per-unit production cost LO2 total output total inputs = total input cost total output 29-36 Legal-Institutional Environment • Legal changes alter per-unit costs of output • Taxes and subsidies • Extent of government regulation LO2 29-37 Price level (index numbers) Equilibrium AS 100 a 92 b Real Output Demanded (Billions) Price Level (Index Number) Real Output Supplied (Billions) $506 108 $513 508 104 512 510 100 510 512 96 507 514 92 502 AD 0 502 510 514 Real domestic output, GDP (billions of dollars) LO3 29-38 Decreases in AD: Recession • Prices are downwardly inflexible • Fear of price wars • Menu costs • Wage contracts • Efficiency wages • Minimum wage law LO4 29-39 Decreases in AS: Cost-Push Inflation Price level AS2 AS1 b P2 P1 a AD 0 Q1 Qf Real domestic output, GDP LO4 29-40 Increases in AS: Full-Employment Price level AS1 P3 P2 P1 AS2 b c a AD2 AD1 0 Q1 Q2 Q3 Real domestic output, GDP LO4 29-41 Impact of Oil Prices Diminished? • 1970’s • Reduced AS and negative GDP gap • Cost-push inflation • Rising unemployment • 2000’s • Core inflation steady • Use 50% less oil and gas today • Federal Reserve more vigilant 29-42