Middle east respiratory syndrome( MERS)
advertisement

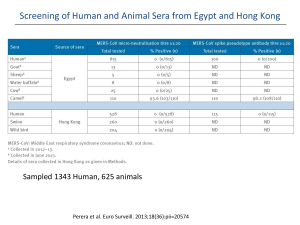
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS-COV) Done by : Fatimah Al-Shehri Intern pharmacist Supervised by : Dr . Sahal Khoshhal Infectious disease clinical pharmacy specialist Outline: • Case review . • • • • • • Definition Signs and symptoms Transmission pathway Epidemiology Complications Treatment. • Case follow up . • Prevention and control. Case review : • 28 years old male admitted to the hospital on 30/3/2014 complaining of productive cough , generalized body pain , nausea , vomiting , sever headache, high grade fever, dysphasia and sever respiratory failure . • • • • • PMH: Hx of glucose 6 phosphate deficiency (G6PD) . Mild sulpha drugs allergy . Medically free. The patient is an orthopedic resident and he has a history of working in environment (KFH ) in which CORONA virus was detected. • After admission: • pneumonia was suspected since the X-ray was done that day and showed right middle zone infiltration and right middle lob pneumonia but then PCR was done and the viral DNA of CORONA VIRUS was extracted from the patient’s plasma so MERS-coV was confirmed . • The patient developed acute kidney injury , rhabdomyolysis , sever respiratory distress ,liver injury , increase in cardiac enzymes . X-ray on 3/4/2014 FINDINGS: Examination compared with 28 March 2014. Interval development of bilateral air-space disease involving both middle lungs and the left lower lung likely related to chest infection, for clinical correlation and follow-up.. X-ray 4/4/2014 . FINDINGS: -Comparison was made to the previous study done yesterday. -Appearance of airspace opacity is noted in the middle zone of the right lung and middle zone of left lung. X-ray 16/4/2014 • FINDINGS: -Comparison was made to the previous study dated April 16, 2014. Redemonstration of the previously seen bilateral diffuse scattered consolidation with better aeration of both lungs. -Bilateral interval decrease of pleural effusion. Tubes and lines are noted in satisfactory position. The laboratory value and vital signs since confirmation of MERS COV : Items 6/4 7/4 8/4 9/4 10/4 13/4 14/4 Temp 38.6 38.2 37.5 39.1 36.3 36.3 36.8 BP 110/48 100/58 133/85 128/63 112/56 107/51 130/70 99/32 116/23 109/38 88/14 83/16 89/13 HR/RR 44/23 BUN 2.4 2.3 5.7 9 7.1 2.8 Na 135 133 135 138 146 143 K 3.4 4.3 5.2 5.1 3.6 3.7 Cl 104 102 100 103 109 107 Co2 20 23 21 21 26 25 G 7.4 5 5.2 8 7 5.5 Cr 72 76 136 103 79 71 CrCl 183.17 164.69 96.97 128.04 156.54 183.53 200.66 The laboratory value and vital signs since confirmation of MERS COV : Items 6/4 7/4 Ca 2.10 2.17 phos 1.31 Mg 0.7 Bili 11.6 22.1 ALK 63 Alb 8/4 9/4 10/4 13/4 2.31 2.32 2.24 0.96 0.41 0.84 1.12 0.8 29.9 61.2 82.4 66 107 81 66 26 25 20 23 25 AST 82 104 124 147 120 103 ALT 56 61 61 50 35 46 WBC 2.5 7 11.6 12.3 7 7.3 9.8 HGB 16 14.5 14.6 12.3 11 9.4 10.1 087 38.6 14/4 The laboratory value and vital signs since confirmation of MERS COV : Items 6/4 CPK 7/4 8/4 9/4 10/4 13/4 126 883 2553 933 LDH 747 1548 1792 797 HCT 48.3 45.6 46.4 39.9 PLT 203 257 217 14/4 32.8% 28.8 31.0 207 207 212 Medications: Anesthesia : Analgesia : Ulcer prophylaxix -Midazolam HCl 10mg IV -Morphine 50 IV push Push. -Acetaminophen 1000mg IV push. -Esomprazole 80mg IV push. Corticosteroides: Antibiotics : Antivirals: -Dexamethasone 8mg IV -Ribavirin (600mg susp q push. 8hrs). -peginterferon 190mcg subcut q1w. -Oseltamivir 75mg cap BID. -Linezolid 600mg IV BID -Augmentin 1200mg IV push -Meropenem 1g IV push q 8 -Vancomycin Hcl 1g IV push Duretics : Muscles relaxants: Thrompolytic: -Albumin 100ml IV push. -Heparin 5000 Units IV Push. -Furosemide40mg IV Push. -Cistatracurium besyalate 20mg IV push. Respiration aid: Inotrops: Prokinetics: -Salbutamol. -ECMO. -NE 15mg/250ml. -Metoclopramide 10mg IV Q8hrs. CORONAVIRUSIS : • MERS (middle east respiratory syndrome): It’s a viral respiratory illness first reported in Saudi Arabia in 2012. • SARS ( Severe acute respiratory syndrome): It’s caused by a virus that was first identified in 2003. It causes acute respiratory distress and sometimes death. Signs and symptoms : • • • • • • • Fever Cough Sneezing Shortness of breath Generalized body pain Vomiting Mayalgia Transmission pathway: Viruses classification Classification of corona viruses: Distribution of cases of MERS-CoV reported worldwide by month of disease onset, outcome and place of infection, as of 14 May 2013. Distribution of cases of MERS-CoV by gender and age, April 2012 – 13 May 2013. MERS- coV cases in KSA June 2012-June2013 Cases of MERS-CoV reported in the Arabian Peninsula and Jordan, April 2012 to 15 May 2013 . Distribution of confirmed cases of MERS-CoV byreporting country, 1 – 30 April 2014 . Distribution of confirmed cases of MERS-CoV by age and sex, March 2012 – 31 March 2014 (n=206*) and 01 April - 30 April 2014. Distribution of confirmed cases of MERS-CoV by month of onset* and place of reporting, March 2012 – 30 April 2014 . Distribution of confirmed cases of MERS-CoV by reporting country, March 2012 – 30 April 2014 (n=424) Middle East: Europe: -UK: 4 cases / 3 deaths -Germany: 2 cases / 1 death -France: 2 cases / 1 death -Italy: 1 case / 0 deaths -Greece: 1 case/ 0 deaths -Saudi Arabia: 342 cases / 105 deaths -UAE: 49 cases / 9 deaths -Qatar: 7 cases / 4 deaths -Jordan: 5 cases / 3 deaths -Oman: 2 cases / 2 deaths -Kuwait: 3 cases / 1 death -Egypt: 1 case/ 0 deaths Africa: -Tunisia: 3 cases / 1 death Complications: • Multi-organ damage . Treatment: Treatment : • Supportive care . • Chloroquine: • which has potent antiviral activity against the SARS-CoV (HCoV-229E and against HCoV-OC43 both in cultured cells and in a mouse model). Treatment: • • • • Respiratory aids. Antivirals . Patients in ICU (FAST HUG MAIDENS). Monitoring of the kidney, liver, heart functions. • Monitoring of myoglobin ?? Respiratory aids: • Mechanical ventilation . • ECMO. ECMO: Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Indications: • Respiratory distress syndrome. • Primary pulmonary hypertension in newborn. • Congenital diaphragmatic hernia(CDH). Antivirals : • Ribavirin : Antihepaciviral, Nucleoside (Anti-HCV) • Mechanism of action: Ribavirin Ribavirin • Doses : - Recommended therapy duration: - Genotype 1: 48 weeks. - Genotypes 2,3: 24 weeks. - <66 kg: 800 mg daily (400 mg in the morning and evening) - 66-80 kg: 1000 mg daily (400 mg in the morning, 600 mg in the evening) - 81-105 kg: 1200 mg daily (600 mg in the morning, 600 mg in the evening) - >105 kg: 1400 mg daily (600 mg in the morning, 800 mg in the evening). Ribavirin • • • • Ribavirin : 2000 mg as loading dose then: 1200mg q 8 hrs for 4 days . 600 mg po q 8hrs for 4-6 days . • Peginterferon : • 1.5 mg/kg once /w for 2 doses. Ribavirin: • Use : - Treatment of hospitalized infants and young children with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) specially indicated for treatment of severe lower respiratory tract RSV infections in patients with an underlying compromising condition. - In combination with interferon alfa 2b (pegylated or nonpegylated) injection for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C . • Use - Unlabeled: - Treatment for RSV in adult hematopoietic stem cell or heart/lung transplant recipients. - Used in other viral infections including influenza A and B and adenovirus. Interferon alpha: Interferons (IFNs): proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of pathogens such as viruses ,bacteria, parasites or tumor cells. Interferon alpha: Mechanism of action : Treatment: Replication of novel human corona virus hCoV-EMC/2012 in response to combined treatment with interferon alpha and Ribavirin in vetro cells. Results : Effects of (a) mycophenolic acid, (b) ribavirin, and (c) interferons (Intron A, Avonex, Rebif, and Betaferon) on MERS-CoV replication in Vero cells. Effects of (a) mycophenolic acid, (b) ribavirin, and (c) interferons (Intron A, Avonex, Rebif, and Betaferon) on MERS-CoV replication in Vero cells. Conclusion: • Compared with ribavirin and interferons, mycophenolic acid exhibits a number of attributes that support its practical use in MERS-CoV infection. • Interferon beta 1b with mycophenolic acid should be cosidered in the treatmern trials of MERS . Follow-up: Items : 5/5 8/5 BUN 3.7 3.6 Na 137 136 K 3.7 3.5 Cl 101 100 Co2 27 26 G 5 5 Cr 59 60 211.34 211 WBCs 7.4 7 HGB 9.4 9 PLT 265 265 HCT 30.7% 30.7% CrCl MERS PCR Negative (not detdected) Negative (not detdected) Follow-up FINDINGS: No significant interval changes noted since the previous examination dated May 1, 2014. Prevention and control Prevention and control: • Health‐care workers apply standard precautions consistently with all patients regardless of their diagnosis in all work practices all the time. Prevention and control: • Avoid contact with camels, good hand hygiene, and avoiding drinking raw milk or eating food that may be contaminated with animal secretions or products unless they are properly washed, peeled, or cooked. Prevention and control: • For the general public, when visiting a farm or a barn, general hygiene measures, such as regular hand washing before and after touching animals, avoiding contact with sick animals, and following food hygiene practices, should be adhered to. Prevention and control: • WHO recommends increasing efforts to raise awareness of MERS among travelers going to and travelling from MERS‐affected countries. References :