Mexico - Doral Academy Preparatory
advertisement

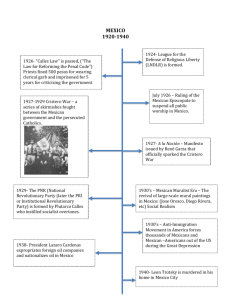
By: Alex Lopez Population of about 100.2 Million Territory 761,602 sq Miles Independent since 1810 from Spain Religion Mainly Roman Catholic Languages: Spanish, Various Mayan, Mahuatl, etc. Currency: Peso Climate: varies from tropical to desert Natural Resources: petroleum, silver, copper, gold, lead, zinc, natural gas, timber. Revolution of 1917 Constitution The Era Cardenas Upheaval of Hegemonic Party Rule Federal (Federal, State, Municipal) Legislative Branch Executive Branch Judicial Modeled Branch after the US Government on Paper Constitutional Citizen President of the United Mexican States Felipe Caldron Six-year presidential term Basic Election requirements, some based off US presidential Requirements Can not be re-elected Elected by direct vote Number of Seats: 128 senators Length of Term: 6 years Power: Foreign Affairs and Impeachment, Enacting all public policy Election Process: Each party nominates two candidates who run and are elected together by direct vote. The party of the two candidates that won the second highest vote within the state or the Federal District then assigns a senator to occupy the third seat. Number of Seats: 500 deputies Length of Term: 3 years Power: Fiscal Legislation, Enacting all public policy Election Process: -300 "majority deputies" are directly elected by plurality from single-member districts -200 "party deputies" are assigned through rules of proportional representation Selection Process: Proposed by the president and approved by the senate Several Powers broken down by the different courts. Current Head: Juan Nepomuceno Silva Meza: Supreme Justice/Liberal The president confers broad powers on cabinet secretaries, although the cabinet rarely meets as a single body. There is a hierarchy of influence among the different cabinet posts, and the power of a minister or secretary varies, depending on the priorities set by a particular president as well as the resources available at the time. Three PRI: Main Parties Run Mexico centrist or even neoliberal party and Centre-Left. PAN: Conservative and Centre-Right in the Mexican political spectrum PRD: Left wing, democratic socialist party Political Elite Recruitment: From middle class, mainly born in Mexico city with secondary education and a degree in economics or public administration Voting, attending campaign rallies, and petitioning public officials. Media is the source of legitimacy Used to be fined for speaking out against the government Now has full freedom, informs the public on all issues. Is a First world country Industrialized Several Factors lead to it being an Industrialized country Free Market Economy State-Owned Industries Part of Several International Organizations Power of the international Organizations Influence of such organizations on Mexico Current Pressing Political Issue: Illicit Drugs: Drug tracking through Mexico to the US, and cultivation of drugs in Mexico. Recent Policies: North Atlantic Free Trade Agreement, National Solidarity Program, UN. Corporatist system Divided into 3 sectors; labor, peasant and popular Several Key interest groups; CTM,CNC, CNOP, Roman Catholic Church Work the same as the US Lobbying, political pressure on leaders to in act laws for supporters, political campaigns rallies, pushing for social reforms Originally the Mexican people put up with corruption to extract benefits, but after the horrible corruption with the Lopez Portillo and Salinas administration, people no longer wanted to put up with what they said was drug money politics. Most people vote, though it is not mandatory Mestizo (Amerindian-Spanish) 60%, Amerindian or predominantly Amerindian 30%, white 9%, other 1% Roman Catholic 76.5%, Protestant 6.3% (Pentecostal 1.4%, Jehovah's Witnesses 1.1%, other 3.8%), other 0.3%, unspecified 13.8%, none 3.1% (2000 census) No real ethnic clashes THE BOOK CIA FACTBOOK