Aromatic Hydrocarbons - INAYA Medical College
advertisement

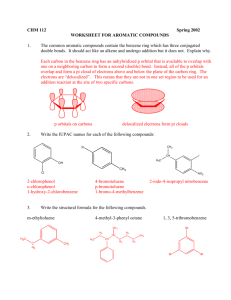
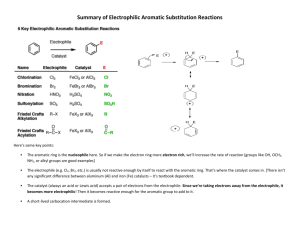
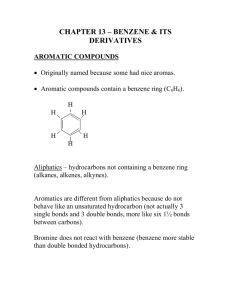
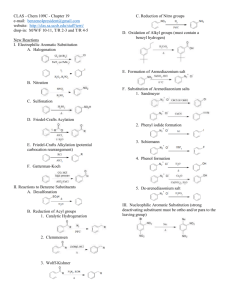
1 Hydrocarbons aromatic aliphatic Alkane alkene alkyne 2 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Some of them have pleasant odors. Aromatic compounds Aromatic hydrocarbons 1. Unsaturated ring compounds which contain a benzene ring in their molecules, C6H6 . 2. Compounds that are far more stable than they should be and resist the addition reactions typical of unsaturated aliphatic compounds. 4 H H Aromatic Compounds H C C C C Arene: A compound containing one or more benzene rings. C C H H benzene H ek ulé structure A Keku lé structu re w ing all atoms as a line-angle formula Aryl group: When we remove Naphthalene H C C C C C C H Phenyl C6H5H H Kek ulé structure A Keku lé structu re Phena a H atom from an arene (Ar-) H H Anthracene Benzene C6H6 Methylbenzene C7H8 Ethylbenzene C8H10 6 7 8 9 Many aromatic compounds are common in nature and in medicine. Aspirine 10 Six carbon atoms joined to form a hexagonal ring. Each carbon has four valence electrons One of these is used to form a bond with a hydrogen atom. Two other electrons are used to form sigma bonds with the carbon atoms on the either side. 11 Aromatic compounds are named with benzene as the parent chain. One side group is named in front of the name benzene. CH3 methylbenzene Cl chlorobenzene 12 • A benzene substituent is called a phenyl group, and it can be abbreviated in a structure as “Ph-”. • Therefore, benzene can be represented as PhH, and phenol would be PhOH. 13 • To name a benzene ring with one substituent, name the substituent and add the word benzene. • Many monosubstituted benzenes have common names which you must also learn. 14 OH n ol Some substituted benzenes have common names CH OH3 Toluene Phen ol OCH3 A nisole NH2 A niline OH OCH 3 NHOCH 2 3 O NH 2 C-H Phen ol A niline A nisoleBenAzaldehyde niline Ben A nisole O C-H Ben zaldehyde O C-OH Benzoic acid • There are three different ways that two groups can be attached to a benzene ring, so a ortho, meta, or para—can be used to designate the relative position of the two substituent. ortho-dibromobenzene or o-dibromobenzene or 1,2-dibromobenzene meta-dibromobenzene or m-dibromobenzene or 1,3-dibromobenzene para-dibromobenzene or p-dibromobenzene or 1,4-dibromobenzene 16 • If the two groups on the benzene ring are different, alphabetize the names of the substituents preceding the word benzene. • If one substituent is part of a common root, name the molecule as a derivative of that monosubstituted benzene. 17 For three or more substituents on a benzene ring: 1. Number to give the lowest possible numbers around the ring. 2. Alphabetize the substituent names. 3. When substituents are part of common roots, name the molecule as a derivative of that monosubstituted benzene. The substituent that comprises the common root is located at C1. 18 1 NO2 2 NO2 OH CH3 3 4 Cl 4-Ch loro-2nitrotoluen e Br 6 1 5 Br 2 3 4 Br 2,4,6-Trib romoph enol 4 3 2 Br CH2 CH3 1 2-Bromo-1-ethyl-4n itroben zene 19 Select the names for each structure: Cl 1. Chlorocyclohexane 2. Chlorobenzene 3. 1-chlorobenzene CH 3 1. Meta-methyltoluene 2. Meta-dimethylbenzene 3. 1,3-dimethylbenzene CH 3 20 Select the names for each structure: Cl 2. Chlorobenzene 1. Meta-methyltoluene 2. Meta-dimethylbenzene 3. 1,3-dimethylbenzene CH 3 CH 3 21 Write the structural formulas for each of the following: A. 1,3-dichlorobenzene B. Ortho-chlorotoluene 22 Write the structural formulas for each of the Cl following: A. 1,3-dichlorobenzene Cl B. Ortho-chlorotoluene CH3 Cl 23 Identify the organic family for each: A. CH3CH2CH3 B. C. 24 Identify the organic family for each: A. CH3CH2CH3alkane B. cycloalkane aromatic C. 25 Stability of Benzene • Benzene’s unusual behavior is not limited to hydrogenation. Benzene does not undergo addition reactions typical of other highly unsaturated compounds. • Benzene does not react with Br2 to yield an addition product. Bromine substitutes for a hydrogen atom, yielding a product that retains the benzene ring. 26 Physical state: Benzene, methylbenzene and ethylbenzene are liquids. Insoluble in water. Soluble in non-polar solvents such as cyclohexane. 27 28 29