CNS Stimulants - AODAResourceCenter
advertisement

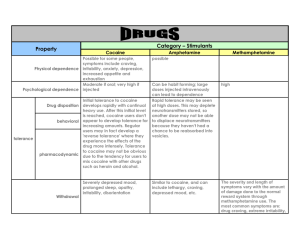
CNS STIMULANTS JENNA WASHULESKI AUDIENCE You may be suffering from an addiction, or maybe you are an occasional user. You could be a family member or friend of an addict, or you could just be a curious individual. No matter who you are, you are welcome to view this power point on CNS Stimulants, health related symptoms, street slang terms, withdrawal symptoms, and more. Addiction is a serious issue. Become aware of what CNS Stimulants are and how they effect our bodies in this 20 minute presentation. Enjoy. WHAT ARE CNS STIMULANTS Central Nervous System Stimulants increase alertness, euphoria, and cause the user to feel more energized • Also known as an “Upper” • Reason for Dependence and Misuse Stimulants are classified in two categories • Schedule I • “Designer” Amphetamines • Schedule II • Amphetamine, Cocaine, Methylphenidate (Ritalin) Hanson, Glen R., Peter, Venturelli J., and Fleckenstein, Annette E. "Chapter 10: Stimulants." Drugs and Society. 11th ed. Burlington, MA: Jones and Bartlett, 2012. 285-321. Print. CNS STIMULATES Can be • Prescribed by a doctor • Over-the-counter (OTC) • In small doses such as in chocolate and coffee Abuse can occur to individuals who use stimulants for legitimate reasons or for illicit reasons. Hanson, Glen R., Peter, Venturelli J., and Fleckenstein, Annette E. "Chapter 10: Stimulants." Drugs and Society. 11th ed. Burlington, MA: Jones and Bartlett, 2012. 285-321. Print. AMPHETAMINES Video on Amphetamines (End video at 1:36) Amphetamines are a sympathomimetic drug • Similar to neurotransmitters like dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine, and serotonin Amphetamines increase the production of neurotransmitters (like dopamine) and prevent it from being recycled which creates a longer high feeling BlueBelly. "How Stimulant Drugs Work." How Stimulant Drugs Work. BlueBelly, 09 June 2009. Web. 16 Apr. 2014. APPROVED USES OF AMPHETAMINES In 1932, inhalers were used to treat nasal congestion • The first therapeutic use of amphetamine Originally sold for obesity, alcoholism bed-wetting, depression, schizophrenia, morphine and codeine addiction, heart block, head injuries, seasickness, persistent hiccups, and caffeine mania. “In 1967, some 31 million prescriptions were written for anorexiants (diet pills) alone.” Hanson, Glen R., Peter, Venturelli J., and Fleckenstein, Annette E. "Chapter 10: Stimulants." Drugs and Society. 11th ed. Burlington, MA: Jones and Bartlett, 2012. 285-321. Print. APPROVED USES OF AMPHETAMINES (CONTINUED) In 1970, the Food And Drug Administration restricted legal use of amphetamines to three medical conditions 1. Narcolepsy 2. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) 3. Short term weight reduction programs Hanson, Glen R., Peter, Venturelli J., and Fleckenstein, Annette E. "Chapter 10: Stimulants." Drugs and Society. 11th ed. Burlington, MA: Jones and Bartlett, 2012. 285-321. Print. TYPES OF AMPHETAMINES Designer drugs are a product of amphetamine and methamphetamine that have prominent psychedelic effects in addition to their CNS stimulatory action. Some designer drugs are… Methcathinone (“Cat”) • Properties similar to methamphetamine and cocaine Methylenedioxy-n-methylamphetamine (MDMA, Ecstasy) • Stimulant and Hallucinogen Methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA) Hanson, Glen R., Peter, Venturelli J., and Fleckenstein, Annette E. "Chapter 10: Stimulants." Drugs and Society. 11th ed. Burlington, MA: Jones and Bartlett, 2012. 285-321. Print. TYPES OF AMPHETAMINES (CONTINUED) Methamphetamine Dextrostat Adderall Methylphenidate (Ritalin) Adderall XR Concerta Dexedrine Detroamphetamine Vyvanse • Used for ADHD and narcolepsy Levoamphetamine • A psychostimulant used to increase alertness Procentra Focalin Strattera Lisdexamfetamine • Used for ADHD "Lists of Amphetamines." Amphetamines.com. N.p., 2014. Web. 11 Apr. 2014. COMMON SLANG TERMS FOR AMPHETAMINES Speed Crystal Meth Bennies Dexies Uppers Pep pills Ice Whiz Diet pills Jolly beans Copilots Hearts Footballs White crosses Crank Chalk Glass "Amphetamine Facts." Amphetamines. Australian Drug Foundation, 27 Jan. 2013. Web. 10 Apr. 2014. WHAT DO AMPHETAMINES LOOK LIKE? Powder • Can vary in color, most common in white to brown Tablets And Capsules • Varies in color Crystal • Most potent form of amphetamine • Large sheet like crystals or crystalline powder "Amphetamine Facts." Amphetamines. Australian Drug Foundation, 27 Jan. 2013. Web. 10 Apr. 2014. METHOD OF ADMINISTRATION Oral Insufflation (Snorting) Injection Rectal "Amphetamine." Drugs Forum RSS. SIN Foundation, 2012. Web. 11 Apr. 2014. AMPHETAMINE EFFECTS Decreases appetite • Weight loss Increases Energy Insomnia Euphoria Increases Motivation Irritability Dry mouth Alertness Anxiety and panic Headache Increased heart rate and blood pressure Increased body temperature and sweating Increased breathing rate Mood swings Depression Increases concentration Behavioral stereotypy •Meaningless repetition of single activity "Amphetamine." Drugs Forum RSS. SIN Foundation, 2012. Web. 11 Apr. 2014. METHYLPHENIDATE (RITALIN) “A Special Amphetamine” Mild stimulant Schedule II drug Blocks the reuptake of dopamine and noradrenaline into their receptive neurons Treats narcolepsy and ADHD Intended to be used orally • Can be abused by snorting or when used as a performance enhancer Hanson, Glen R., Peter, Venturelli J., and Fleckenstein, Annette E. "Chapter 10: Stimulants." Drugs and Society. 11th ed. Burlington, MA: Jones and Bartlett, 2012. 285-321. Print. OTHER STIMULANT PRODUCTS Caffeine Caffeine-like drugs (Xanthines) • Stay-Awake Products • Picker-Uppers Herbal stimulants • Contain ephedrine, ephedra, or guarana OTC Sympathomimetics • Cold, allergic, and diet aid medications Performance Enhancers • Drugs taken to increase physical or mental performance to achieve a more positive result (Adderall for tests in school) Methamphetamine Cocaine Crack cocaine Daughtery, R., & O'Bryan, T. (2014). Prime for life. (8.0 ed.). Lexington, Kentucky, USA: Prevention Research Institute. CAFFEINE The worlds most frequently used and potentially the most popular drug. “Almost 80% of the world’s population consumes caffeine daily.” “30% of Americans consume 600mg or more per day.” • Most commonly consumed are methylxanthines (also known as Xanthines) Hanson, Glen R., Peter, Venturelli J., and Fleckenstein, Annette E. "Chapter 10: Stimulants." Drugs and Society. 11th ed. Burlington, MA: Jones and Bartlett, 2012. 285-321. Print. XANTHINE Consumed in beverages and foods • • • • • • Coffee beans Tea plants Kola nuts Mate leaves Guarana paste Yoco bark • Herbal “natural products” • Energy Drinks • Chocolate • Cocoa • Soft Drinks (Mountain Dew, Pepsi, Coca-Cola, etc.) OTC Medication • NoDoz • Excedrin • Vivarin Hanson, Glen R., Peter, Venturelli J., and Fleckenstein, Annette E. "Chapter 10: Stimulants." Drugs and Society. 11th ed. Burlington, MA: Jones and Bartlett, 2012. 285-321. Print. PHARMACOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF XANTHINE CNS Effects • • • • 100-200 mg/day - Alertness, arousal, and reduces tiredness 300+ mg/day – Insomnia, increased tension, anxiety, and muscle twitches 500+ mg/day – panic sensations, chills, nausea, and clumsiness Extreme doses/day – May result in seizures, respiratory failure, and even death Cardiovascular and Respiratory Effects • • 500+ mg leads to increased heart activity Can help with asthma-related respiratory problems Caffeine Intoxication • Caffeinism: frequent high does of caffeine Caffeine Dependence • Not likely to be an issue. Individual may experience headaches when not consuming caffeine, but it shouldn’t interfere with daily activity. Hanson, Glen R., Peter, Venturelli J., and Fleckenstein, Annette E. "Chapter 10: Stimulants." Drugs and Society. 11th ed. Burlington, MA: Jones and Bartlett, 2012. 285-321. Print. MDMA (ECSTASY) In late 1970s and early 1980s MDMA was used for psychotherapy Schedule I Drug Illegally manufactured Causes user to feel sensory enhancement, psychedelic effects, hallucinations, and extreme euphoria Often used at raves, clubs, and bars Video on what MDMA does to your brain “MDMA (Ecstasy or Molly)” NIDA for Teens. National Institute on Drug Abuse, 24 Mar. 2014. Web. 12 Apr. 2014. MDMA (ECSTASY) STREET SLANG NAMES Molly E X XTC Adam Hug Beans Clarity Lover’s Speed Love Drug Taking more than one pill at once is called “Bumping” “MDMA (Ecstasy or Molly)” NIDA for Teens. National Institute on Drug Abuse, 24 Mar. 2014. Web. 12 Apr. 2014. MDMA (ECSTASY) Form • Pill, tablet, or capsule • Varies in colors • Often have cartoon-like images on them Takes 15 minutes to enter bloodstream and reach brain Takes 45 minutes to feel “high” Last for 3 to 6 hours “MDMA (Ecstasy or Molly)” NIDA for Teens. National Institute on Drug Abuse, 24 Mar. 2014. Web. 12 Apr. 2014. MDMA (ECSTASY) NEGATIVE EFFECTS Anxiousness Sweating and chills Dizziness Muscle tension Nausea Blurred Vision Increased heart rate Increased blood pressure Intense clenching of the teeth Sadness and depression • Can last for several days to a week Memory difficulties • Can become permanent Dehydration that leads to hyperthermia • Lead to heart and kidney problems • Could lead to death High levels in blood stream can lead to seizures “MDMA (Ecstasy or Molly)” NIDA for Teens. National Institute on Drug Abuse, 24 Mar. 2014. Web. 12 Apr. 2014. METHAMPHETAMINE “More than 12 Million Americans have abused methamphetamine and 1.5 million of these uses are addicted to this potent stimulant.” “In 2009 approximately 500,000 people were using this potent stimulant monthly.” Hanson, Glen R., Peter, Venturelli J., and Fleckenstein, Annette E. "Chapter 10: Stimulants." Drugs and Society. 11th ed. Burlington, MA: Jones and Bartlett, 2012. 285-321. Print. METHAMPHETAMINE STREET SLANG NAMES Meth Speed Chalk Tina Ice Crystal Crank Glass Fire Go fast “Methamphetamine (Meth)." NIDA for Teens. National Institute on Drug Abuse, 24 Mar. 2014. Web. 12 Apr. 2014. METHAMPHETAMINE Chemically similar to amphetamines Increase mood and happiness Increase energy and alertness “Methamphetamine (Meth)." NIDA for Teens. National Institute on Drug Abuse, 24 Mar. 2014. Web. 12 Apr. 2014. METHAMPHETAMINE Is a synthetic drug • Made with over-the-counter, toxic ingredients • Drain cleaner, battery acid, antifreeze, and more Illegally man-made in… • Small laboratories • “Superlabs” • Big illegal laboratories that make large quantities of meth “Methamphetamine (Meth)." NIDA for Teens. National Institute on Drug Abuse, 24 Mar. 2014. Web. 12 Apr. 2014. METHAMPHETAMINE Forms • Powder • Pill • Rock called crystal • Shiny, white or clear Method of Administration • • • • Snorted Smoked Oral Ingestion Sometimes mixed with alcohol or marijuana “Methamphetamine (Meth)." NIDA for Teens. National Institute on Drug Abuse, 24 Mar. 2014. Web. 12 Apr. 2014. Consumption of Methamphetamine can lead to overdose and death. STAY AWAY FROM METH! COCAINE Schedule II Drug “Cocaine has been used as a stimulant for thousands of years.” Derived from the leaves of the Erthroxlon coca plant Then produced into coca paste (80% cocaine) Paste is processed at laboratories to form powder Before Cocaine is sold on the streets, it is often mixed with other substances like powdered sugar, arsenic, methamphetami ne, etc. • Purity can be from 10% to 85% "Cocaine." NIDA for Teens. National Institute on Drug Abuse, 24 Mar. 2014. Web. 12 Apr. 2014. STREET SLANG FOR COCAINE Blow Coke Tornado Snow Flake C Toot White lady Nuggets Rock(s) Fat Bags Nose Candy "Cocaine." NIDA for Teens. National Institute on Drug Abuse, 24 Mar. 2014. Web. 12 Apr. 2014. FORMS OF COCAINE Little Pellets also known as rocks • Must be crushed before use Flakes or Powder Speedball: cocaine typically mixed with heroin and smoked "Cocaine." NIDA for Teens. National Institute on Drug Abuse, 24 Mar. 2014. Web. 12 Apr. 2014. METHOD OF ADMINISTRATION Sometimes powder cocaine is rubbed onto tissues such as gums. Orally Injected Inhaled (snorted) Smoked Freebasing: conversion of cocaine into its alkaline form for smoking "Cocaine." NIDA for Teens. National Institute on Drug Abuse, 24 Mar. 2014. Web. 12 Apr. 2014. PHARMACOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF COCAINE Enhanced activity of dopamine, noradrenaline, adrenaline and serotonin transmitters Blocks the reuptake and inactivation of these elements following their release from neurons CNS Effects • Creates increased strength, energy, and performance • Increases euphoria, self-confidence, well-being, and sociability Cardiovascular System Effects • Increases the levels of adrenaline, increases heart rate, raises blood pressure Local Anesthetic Effects • Reduces bleeding • Topical numbing effects Hanson, Glen R., Peter, Venturelli J., and Fleckenstein, Annette E. "Chapter 10: Stimulants." Drugs and Society. 11th ed. Burlington, MA: Jones and Bartlett, 2012. 285-321. Print. EFFECTS OF COCAINE Increased happiness and excitement Talk, move, and think quickly Alertness, wakefulness, restlessness Heart beats faster Nervousness and anxiety Mood swings Aggressiveness Paranoia Twitching and shaking of the body Increased Blood Pressure Could lead to heart attack or stroke Suppressed appetite Possible weight loss "Cocaine." NIDA for Teens. National Institute on Drug Abuse, 24 Mar. 2014. Web. 12 Apr. 2014. EFFECTS OF COCAINE If Individuals inject cocaine with dirty/shared needles, they are at higher risk for HIV/AIDS and hepatitis Repeated snorting of cocaine can result in nosebleeds, constant runny nose, hoarseness, and sense of smell • Cocaine user developed a hole in their nose over a period of time. Oral consumption may lead to bowel problems and reduce blood flow in the intestines Overdose • Death When the “high” wears off • • • • • “Crash” feeling Fatigue Sadness Cravings to do more cocaine Feeling of sickness, stomach pain, headaches "Cocaine." NIDA for Teens. National Institute on Drug Abuse, 24 Mar. 2014. Web. 12 Apr. 2014. COCAINE ABSTINENCE PHASES Phase 1: “Crash” • 28-48 hours since last binge • Depression, anorexia, suicidal thoughts, fatigue, no craving, insomnia, and exhaustion Phase 2: Withdrawal • 1-10 weeks since last binge • Mood swings, sleep returns, some craving, little anxiety, intense craving, and obsessed with drug seeking Phase 3: Extinction • Indefinite since last binge • Normal pleasure, mood swings, cues trigger craving Hanson, Glen R., Peter, Venturelli J., and Fleckenstein, Annette E. "Chapter 10: Stimulants." Drugs and Society. 11th ed. Burlington, MA: Jones and Bartlett, 2012. 285-321. Print. CRACK COCAINE Cocaine Hydrochloride Baking soda Water Paste which dries into hard rock pieces Already processed cocaine and making it pure again is crack cocaine • Could contain as much as 90% pure cocaine Inexpensive Typically smoked in a glass water pipe • A rush or high happens within 8 to 10 seconds • The high can last about 3 to 5 minutes • “Crash” occurs for 10 to 40 minutes • Extreme state of depression "Cocaine." NIDA for Teens. National Institute on Drug Abuse, 24 Mar. 2014. Web. 12 Apr. 2014. WITHDRAWALS FROM CNS STIMULANTS Hunger Anxiety Irritability Aggression Radical mood swings Depression Paranoia Extreme fatigue Long but restless sleep Nightmares Severe distress and panic "Amphetamine Facts." Amphetamines. Australian Drug Foundation, 27 Jan. 2013. Web. 10 Apr. 2014. CSN STIMULANTS AND PREGNANCY Research done on CNS Stimulants and pregnancy is not fully understood and is not always clear because either there aren’t enough studies, or the current studies do not have well defined or properly matched pregnancy populations. Studies can also be contaminated there are poor nutrition, living conditions, and lifestyles, and other drug use such as alcohol was present during pregnancy. These symptoms are what may happen… Daughtery, R., & O'Bryan, T. (2014). Prime for life. (8.0 ed.). Lexington, Kentucky, USA: Prevention Research Institute. Amphetamines – If a pregnant mother are taking prescription medicine, she should talk to her doctor about further taking medication. "Amphetamine Facts." Amphetamines. Australian Drug Foundation, 27 Jan. 2013. Web. 10 Apr. 2014. Caffeine - Pregnant mothers should have less than 200 mg/day. Mothers who chose to drink caffeine are at higher risk of miscarriage and stillbirth. There can be slight reduction in weight of baby at birth. "Caffeine during Pregnancy." BabyCenter. BabyCenter, L.L.C., Apr. 2012. Web. 15 Apr. 2014. MDMA (Ecstasy) - There has not been enough research in this area. Pappas, Stephanie. "Ecstasy in Pregnancy Is Bad for Baby, Study Finds."LiveScience. TechMedia Network, 08 Mar. 2012. Web. 15 Apr. 2014. Methamphetamine – Low birth weight, Cleft palates, Premature birth, Mental and physical birth defects, Increased risk of miscarriage Chait, Jennifer. "What Are the Effects of Crystal Meth on Pregnancy?"LoveToKnow. Love To Know Corp., 24 Mar. 2014. Web. 15 Apr. 2014. Cocaine “Cocaine Babies” - Low birth weight, Premature birth, Small head, Increased irritability, Cognitive defects, Problems with motor skills and language development, Problems gathering info, short attention span. There is a high rate of mother’s abandoning their babies after birth. Crack Cocaine “Crack Babies” – Similar defects to Cocaine Babies "Cocaine." NIDA for Teens. National Institute on Drug Abuse, 24 Mar. 2014. Web. 12 Apr. 2014. TREATMENT FOR DEPENDENCE ON CNS STIMULANTS Inpatient and outpatient programs AODA Counseling Psychological counseling Motivation Goals Recovery Story, 15 Reasons to Overcome Addiction IN THE APPROPRIATE BOX, WRITE DOWN THE PROS AND CONS BASED ON YOUR LOW RISK CHOICES TOWARDS CNS STIMULANTS. THEN WRITE DOWN THE PROS AND CONS OF CONTINUED HIGH RISK CHOICES. High Risk Choices Daughtery, R., & O'Bryan, T. (2014). Prime for life. (8.0 ed.). Lexington, Kentucky, USA: Prevention Research Institute Low Risk Choices PROS CONS In the video from the previous slide, Jessica listed 15 reasons to stay sober. What reasons can you think of? This chart will help you decide. CONCLUSION If you or someone you know has an addiction, take action today!