Dependence potential
advertisement
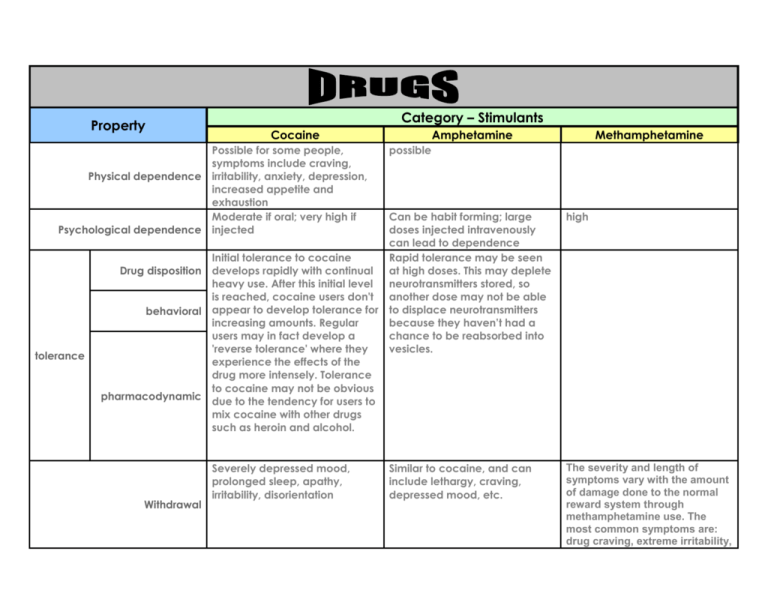
Property Category – Stimulants Cocaine Possible for some people, symptoms include craving, Physical dependence irritability, anxiety, depression, increased appetite and exhaustion Moderate if oral; very high if Psychological dependence injected tolerance Amphetamine possible Can be habit forming; large doses injected intravenously can lead to dependence Initial tolerance to cocaine Rapid tolerance may be seen Drug disposition develops rapidly with continual at high doses. This may deplete heavy use. After this initial level neurotransmitters stored, so is reached, cocaine users don't another dose may not be able behavioral appear to develop tolerance for to displace neurotransmitters increasing amounts. Regular because they haven’t had a users may in fact develop a chance to be reabsorbed into 'reverse tolerance' where they vesicles. experience the effects of the drug more intensely. Tolerance to cocaine may not be obvious pharmacodynamic due to the tendency for users to mix cocaine with other drugs such as heroin and alcohol. Withdrawal Severely depressed mood, prolonged sleep, apathy, irritability, disorientation Methamphetamine Similar to cocaine, and can include lethargy, craving, depressed mood, etc. high The severity and length of symptoms vary with the amount of damage done to the normal reward system through methamphetamine use. The most common symptoms are: drug craving, extreme irritability, loss of energy, depression, fearfulness, excessive drowsiness or difficulty in sleeping, shaking, nausea, palpitations, sweating, hyperventilation, and increased appetite Very high abuse potential Yes, can cause life problems, sleeplessness, moodiness, stop Abuse potential enjoying activities. high Very high high Very high Craving potential Addictive potential (disease) Small amounts no threat; increased amounts can lead to acute cocaine poisoning – convulsions, and respiratory or Acute Toxicity cardiac arrest; ventricular fibrillation, can trigger allergic reactions Irritant to nasal septum leading to chronically inflamed, runny nose Use in a binge can lead to irritability, restlessness, paranoia and paranoid psychosis Chronic toxicity Can lead to heart damage among chronic users because it briefly disrupts heart functioning ? 1. At higher doses, user panics easily and can become paranoid – coupled with increased feelings of power, this can lead to violence. 2. destruction of catecholamine neurons in rat studies 1. Could produce violent behavior, but risk is lower than that resulting from alcohol use 2. 2. contaminants from manufacture can produce toxic effects in brain cells It kills by causing heart failure 1. amphetamine psychosis (myocardial infarction), brain possibly caused by dream-sleep deprivation. damage, and stroke and it induces extreme, acute 2. also possible caused by psychiatric and psychological high dopamine stimulation in mesolimbic symptoms that may lead to suicide or murder. pathway. 3. compulsive and repetitive actions possibly due to affect on dopaminergic systems in basal ganglia Behavioral toxicity Very high reinforcement potential High doses injected intravenously can lead to dependence All addictive drugs have two things in common: they produce an initial pleasurable effect, followed by a rebound unpleasant effect. Methamphetamine, through its stimulant effects, produces a positive feeling, but later leaves a person feeling depressed. This is because it suppresses the normal production of dopamine, creating a chemical imbalance. The user physically demands more of the drug to return to normal. This pleasure/tension cycle leads to loss of control over the drug and addiction. Oral; intransasal, intravenous an smoked Snorted or smoked Peak effects occur 1.5 hours after ingestion; if snorted, peak effects occur between 15-30 minutes after ingestion; if smoked, peak effects occur within 5-10 minutes Effects felt within 5 seconds after snorting. Reinforcer Sniffed, injected, smoked – free base—extracting it into ether or Route of administration mixed with tobacco or mixed with baking soda to create crack and then smoked Effects felt within a couple of minutes; first there’s a rush and a freeze or numbing sensation; Time course after 5 minutes feelings of exhilaration and feelings of clarity Variable; 20-30 minutes followed by a comedown or How long effects last letdown. If injected, the rush occurs within seconds variable Effective dose Hard to determine because of Effects lasting anywhere from four to 24 hours. Variable Variable Variable variable Lethal dose individual differences in uptake and metabolism; Variable Safety margin With alcohol forms Drug interactions cocaethylene which is less potent than cocaine Variable How much needed One hour – another source says Half-life 40 minutes 7 to 14 hours (book says 10-12); full elimination is within two days after drug is taken 4-5 hours Amphetamine is recognized by catecholamine receptors; increased activity of dopamine, serotonin, and NE by stimulating their release from vesicles Nucleus accumbens Methamphetamine has methyl group added which makes it cross blood-brain barrier easier Metabolized by enzymes in How metabolized blood and liver Cocaine blocks reuptake of dopamine, serotonin, and Neurotransmitters affected norepinephrine Mesolimbic pathway Circuitry affected Coke, crack, snow Trade/street name Increased alertness, excitation, euphoria, increased pulse rate Possible effects and blood pressure, insomnia, loss of appetite Agitation, increased body Effects of overdose temperature, hallucinations, convulsions possible death Side Effects Same as cocaine Same as cocaine Elevated heart rate, increased blood pressure Originally thought to be safe and effective. Still used as a local anesthetic; still used in surgery in the nasal, laryngeal, and esophageal regions. Drug of high achievers in the Beneficial effects 80s because of increased energy and well-being 1. Amphetamines can cause excited feelings, but doesn’t eliminate depression – table 6.3 2. Weight control – can produce effects at first, but tolerance can occur after 4-6 weeks so weight loss stops 3. ADHD – but mechanism of action not understood. There may be deficits in the catecholamine-rich areas of the brain