Stimulant Abuse Stimulants are drugs that affect the central nervous
advertisement

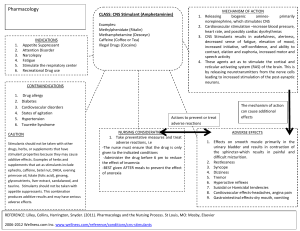
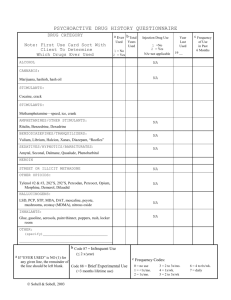
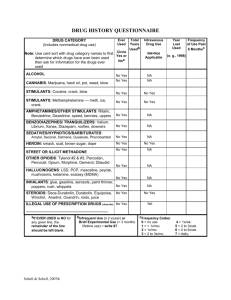
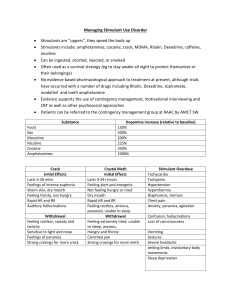
Stimulant Abuse Stimulants are drugs that affect the central nervous system by stimulating behaviour and agitation. This covers a huge range of drugs from mild stimulants such as caffeine, nicotine to amphetamines and cocaine. Other commonly used stimulants include amphetamines and methylphenidate and are often used to treat attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). They are effective to treat inattention and hyperactivity as well as other symptoms of the disorder. However, when abused and used in higher dosages than recommended, they can become addictive and cause problems. Other amphetamines such as methamphetamine are also often abused. People choose to use prescription stimulants to get high or for performance enhancement. They can suppress appetite causing weight loss, increase wakefulness, and increase focus and attention. The euphoric effects are caused when the tablets are crushed and snorted or injected. Cocaine is the most powerful stimulant derived from nature. In the U.S. cocaine is responsible for the most emergency room visits of any illegal drug. It harms the brain, lungs, blood vessels and heart. It can cause an increased heart rate or an abnormal beating of the heart known as arrhythmia, cause seizures or increase the risk of strokes. Snorting damages the lungs and sinuses. Crack cocaine irritates the lungs and can even cause permanent lung damage. It causes ulcers, kidney damage and when used chronically it can impair sexual function. Symptoms of stimulant overdose include: • Hallucinations • Convulsions • Respiration failure or pulmonary oedema (fluid in the lungs) • Heart attacks • Cardiac arrhythmias (irregular heartbeat), high blood pressure or fast heart beat • Headache • Convulsions • Coma or possible death