Carbohydrates & Lipids
advertisement

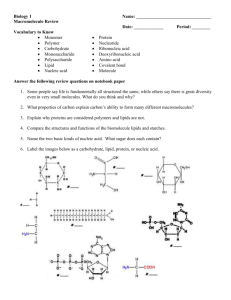
The Chemistry of Life Turn your cartoons in to the box Chemistry Review Atom Element Compound Mixture Chemistry Electrons Octet Rule Valence electrons Ions Bonding Properties of water Polar~ opposite ends, opposite charges Water Cohesion~ H+ bonds holding molecules together Adhesion~ H+ bonds holding molecules to another substance Capillary Action ~ Cohesion PLUS Adhesion… how water moves UP a plant Surface tension~ measurement of the difficulty to break or stretch the surface of a liquid That’s strange… Density: Ice is LESS DENSE than liquid water… why ice floats! Due to H bonding (high) Specific heat~ amount of heat absorbed or lost to change temperature by 1°C (high) Heat of vaporization~ quantity of heat required to convert 1g from liquid to gas states Hydrogen bonding Today Water Lab! 8 stations – get as far as you can, but don’t rush. CLEAN UP after each station – everything liquid can go down the sink. Everything solid goes in the trash. LAB GOGGLES! Latex allergy? Do not touch balloons at station 8 Warm Up 9/8 1. 2. 3. Attractions between different water molecules are known as _____________ bonds. True or False: Water cools rapidly. What is the difference between an ionic bond and a covalent bond? Homework Work on/ review organic compounds chart (due Thursday) Work on Unit 1 Review Sheet (DUE 9/17) Have you read 2.1-2.3 yet? If not, add that to your HW!!! Today Go over Water Lab – then turn it in to the box Notes: Organic compounds (Carbohydrates and lipids) Crashcourse Video: Carbs and Lipids Organic Compounds Carbohydrates 1. • • • Sugars, grains Contain simple energy Found in plants, sugary foods 3. Proteins • • 4. Nucleic Acid • Lipids 2. • • • Fats Contain the most energy Found in meats, dairy Meat, certain vegetables Bodies produce proteins to function • • DNA/RNA Genetic information storage Found in all cells, not much energy Organic Compounds Contain CARBON In science terms, organic means carbon-containing Are POLYMERS Polymers are composed of monomers Organic Compounds Carbon containing compounds Form covalent bonds with (usually) other carbon or hydrogen atoms By virtue of its 4 valence electrons: Can form single, double, or triple covalent bonds with itself (and other atoms) Can form a variety of shapes (chains, rings, branches sheets, etc.) Carbon Molecules Polymer Poly = many Mono = one Polymers are to macaroni necklaces as monomers are to macaroni polymer monomer Huh? Carbs, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids are all made up of repeating subunits. CrashCourse: Biomolecules Biomolecule = macromolecule = organic compound Also… I have Ch’s 1 & 2 to check out! 1. Carbohydrates Examples: Sugars (simple carbs) and starches (complex carbs) Glucose, fructose, sucrose, ribose, deoxyribose, cellulose, potatoes, pastas, glycogen (how animals store energy) Carbohydrates structure = Rings or long chains of rings Carbohydrates Elements: Carbon, Hydrogen ,Oxygen – CHO H:O ratio = 2:1 For every 2 H’s, there is one O Glucose = C6H12O6… 12:6 = 2:1 Cellulose = (C6H10O5)n… 10:5 = 2:1 Carbohydrates Monomer: monosaccharide Mono = ONE Di = TWO Poly = MANY Sucrose is a disaccharide made of glucose PLUS fructose Cellulose is a polysaccharide made of up to 10,000 connected D-glucose molecules Carbohydrates FUNCTION: quick energy Sugars = simple very quick energy Ex: OJ if blood sugar is low Starches = complex carbohydrate takes longer for body to break down… longer term energy source Ex: Before a football game, eat pasta or cereal 2. Lipids Examples: Fats, oils, waxes, steroids, fatsoluble vitamins (A, D, K, E), triglycerides, cholesterol Butter, olive oil, cell membranes (phospholipids) Lipids Structure: 2 or 3 long Hydro-Carbon tails Lipids Elements: CHO Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen H:O ratio is >2:1 Ex: Vitamin E (tocopherol) = C29H50O2 so the H:O ratio = 50:2 = 25:1 which is GREATER THAN 2:1 Lipids Can look like a simple hydrocarbon (CHO) Lipids Monomer: glycerol + fatty acids* *Technically, there are many types of lipids, BUT: Most lipids have a glycerol or carboxylic acid “head” and fatty acid “tails” Lipids Function: Long term energy storage Ex: The human body converts excess glucose (sugar) into fat. What’s wrong with this picture? Carbs vs. Lipids BOTH have CHO BOTH store energy Carbs: quick energy Lipids: long term energy storage Excess carbs get turned into fat for storage How can you differentiate between carbs and lipids??? Carbohydrate or Lipid? Formula: C18H34O2 Carbohydrate or Lipid? Formula = C12H22O11 Carbohydrate or Lipid? Formula: C27H46O Carbohydrate or Lipid? Formula: C12H24O2 Carbohydrate or Lipid? Formula: C6H10O5 Warm Up 9/19 1. 2. A molecule that end in –ose can be categorized as a ______________. What kind of molecule is this and how do you know: HW Work on Unit 1 Review Sheet Today Crashcourse: Carbs, Lipids Notes: Proteins, Nucleic Acids 3. Proteins Examples: Insulin, keratin, casein, ENZYMES (catalase, amylase, lactase…) Found in meats, dairy products, eggs, and some plants (nuts, lentils, and legumes such as beans, peas, soy…) Proteins Structure: complex chain of linked amino acids (peptide bond links AA’s) polypeptide = precursor to protein Proteins Elements: CHON (sometimes S) Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, NITROGEN (complex proteins have disulfide bridges… hence Sulfur) H:O ratio – N/A Proteins Monomer: AMINO ACIDS A long chain of AA’s = a polypeptide… why? Peptide bonds connect AA’s Proteins are just folded polypeptides Proteins are made of… 20 essential amino acids AA’s connected by peptide bond Peptide bond Proteins Function: structure (pectin; chitin), catalyzing reactions (enzymes lower activation energy), repair and maintenance, Immune System (antibodies) 4. Nucleic Acids Examples: DNA, RNA (tRNA, mRNA, rRNA)… NA stands for Nucleic Acid Found in ALL LIVING THINGS!! In the NUCLEUS of eukaryotes (protists, fungi, plants, animals) Free-floating in prokaryotes (bacteria) Nucleic Acids Structure: single stranded (RNA) or double stranded (DNA) DNA: ATCG RNA: AUCG Nucleic Acids Elements: CHONP Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, PHOSPHORUS H:O ratio: N/A Nucleic Acids Monomer: Nucleotide Nucleic Acids Nucleotide 1. 2. 3. = phosphate group (P) nitrogen base (N) 5-carbon sugar (CHO) is a carb… CHO Deoxyribose or ribose Sugar Nucleic Acids ATP is the energy currency of the cell It is a close relative of the nucleotide Adenine Nucleic Acids Function: Heredity; storage of genetic information Stores ALL genetic information Codes for proteins responsible for expressed traits Carb, Lipid, Protein, or Nucleic Acid? Provides rigid structure for plant cells Made of long chain of monosaccharides Carb, Lipid, Protein, or Nucleic Acid? Genes are made of this Long, complex molecule containing CHONP Carb, Lipid, Protein, or Nucleic Acid? Main component of cell membranes Carb, Lipid, Protein, or Nucleic Acid? Monomer: nucleotide Carb, Lipid, Protein, or Nucleic Acid? Amino Acids are connected by peptide bonds This macromolecule is HUGE and complex Carb, Lipid, Protein, or Nucleic Acid? Simple ones end in –ose Complex ones are broken down to simple ones to power cellular respiration (and make ATP) That’s why you eat!!! Carb, Lipid, Protein, or Nucleic Acid? Elements: CHO H:O ratio is >2:1 Crashcourse: Nucleic Acids Notes: Enzymes Vocab for Enzyme Activity enzyme – catalyst – chemical reaction – activation energy – substrate – active site – denatured – Enzymes Enzymes are PROTEINS Biological catalysts Speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy Substrate-specific (like a lock and a key) Reusable Ends in –ase Affected by temperature and pH Enzymes Proteins Enzymes Speed up rxns (catalyze rxns) by lowering activation energy Higher concentration of enzyme = faster reaction Enzymes Substrate-specific (like a lock and key) Reusable End in -ase Denaturation Vocab for Enzyme Activity enzyme – catalyst – chemical reaction – activation energy – substrate – active site – denatured –