blood types - Liberty Union High School District
advertisement

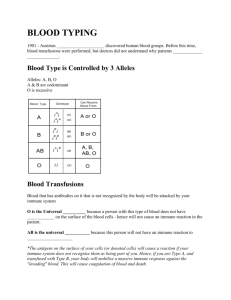
BLOOD TYPES On a cold day in 1667, a renegade physician named Jean Denis transfused calf's blood into one of Paris's most notorious madmen. In doing so, Denis angered not only the elite scientists who had hoped to perform the first animal-to-human transfusions themselves, but also a host of powerful conservatives who believed that the doctor was toying with forces of nature that he did not understand. Just days after the experiment, the madman was dead, and Denis was framed for murder. he ordeal resulted in the ban of human blood transfusions in France unless approved by the Paris Faculty of Medicine. Denis was ultimately cleared of the charges, but soon after ceased to practice medicine. 1901 - Austrian Karl Landsteiner discovered human blood groups Before this time, blood transfusions were performed, but doctors did not understand why patients would die. Even animals have blood types Blood Type is Controlled by 3 Alleles 4 Possible Blood Types Alleles: A, B, O A & B are codominant O is recessive Genotypes Consider Both Parents Type A (genotype AA) x Type O (genotype OO) Blood Type Antigens Blood that has antibodies on it that is not recognized by the body will be attacked by your immune system O is the Universal Donor because a person with this type of blood does not have antigens on the surface of the blood cells - hence will not cause an immune reaction in the patient. AB is the Universal Acceptor because this person will not have an immune reaction to A, B, AB, or O ----- AGGLUTINATION (the clumping of red blood cells following a transfusion reaction; likely fatal Rh Factor Rh Factor (Rh = rhesus monkey) A person can have surface Rh antigens (and be Rh +) or no antigens (and be Rh - ) Rh factor is caused by a dominant allele and is inherited like any other trait. Rh Factor A person can either be Rh + or Rh – (positive is dominant) Rh Factor and Pregnancy *Problem: When a fetus is Rh+ and the mother is Rh-, this can cause the mother’s immune system to attack the fetus. There are drugs that will suppress this reaction. *This condition is called Erythroblastosis fetalis . Doctors can prevent this reaction by giving the woman ( Rh - ) an injection that will suppress her immune reaction to an Rh + baby. *This condition is called Erythroblastosis fetalis . Doctors can prevent this reaction by giving the woman ( Rh - ) an injection that will suppress her immune reaction to an Rh + baby. Blood Type Test Blood can carry diseases and health care professionals must be careful when working with blood. A bloodborne pathogen is any disease causing agent that is present in the blood and can be transferred from one person to another. Examples of blood borne pathogens: Hepatitis B and C, HIV, and Malaria Blood Safety EXAMPLES OF BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS ●HEPATITIS B (HBV) ●HEPATITIS C (HCV) ●Other NON A, NON B HEPATITIS ●HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS (HIV) ●MALARIA ●OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS TRANSMISSION HIV, hepatitis B virus, and hepatitis C virus are the viruses most likely to be transmitted via the following routes in an occupational setting: needle stick / sharps injuries skin or eye contact mucous membrane and non-intact skin exposure to contaminated blood or other potentially infectious materials ( scratches, cuts, bites, or wounds ) Avoid Contact With Blood ●Wear gloves ●Dispose of items that have been contaminated (tissues, needles, bandaids) in biohazard containers ●Do not “horse around” ●Treat every person as if they may be carrying an infectious disease