Chap 11 -- Industry
advertisement

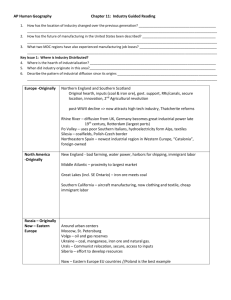
Chap 11: Industry Envs 204 Industry -- Defined INDUSTRY -- Production of goods, especially through manufacturing techniques, and a group of firms with similar technical structures for production. a. Method of adding value such as man-made value, from motive force,or other outside source to create a final product b. Includes factory system, limited stock companies, integrated activities, specialization, scale economies,... 11.1 Industrial Revolution • “The root of the Industrial Revolution was technology involving several inventions that transformed the way in which goods were manufactured” – Unprecedented expansion of output and productivity – Substantial increase in standard of living – Resulted in a Demographic Boom and Transition (In the Western World) Good 2 minute overviews http://www.history.com/topics/industrial-revolution/videos/the-industrial-revolition?m=528e394da93ae&s=undefined&f=1&free=false http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aO3AW0JAHmU – 2minute overview http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E_tFFQyEu_Q&feature=related – 2 minute view of child labor with musical background http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JhF_zVrZ3RQ BBC 1 hour documentary Industrial Revolution • Resulted in and from new social, economic, and political inventions/organization and developments – not just industrial ones • Changes were gradual • Diffused outward across the globe from England after 1750 • Diffusion continues today Change & Impacts 1. Industrial Revolution -- completely changed a) b) c) d) How goods were produced. How economy was organized How people worked & organized How goods were consumed - formerly “folk” based activities became “economic” based (much like the change from folk to popular customs) Hearth Areas 2. Hearth Area - England after 1750's a. Key Invention Steam Engine -non-natural power source Diffusion Diffusion to and impact on other industries Coal -- key new input, why??? Hint birth of the “energy slave” Iron Production -- vastly increased why??? Transportation & Spatial Interaction -- both infrastructure and technology changes the world’s spatial geography (resulted in a time-space compression – speeds up diffusion) Textiles – becomes first leading industry Engineering – emerges from the inventors of these new technologies Food Processing – necessary input to support urban labor concentration Diffusion of Railroad Technology – Time-Space Compression • Hierarchical diffusion – note nodes from which it spreads • Contagious diffusion – spaces in between nodes Diffusion • Relocation – immigration brought new technologies to distant locations – Also the British attempted to limit this by forbidding skilled textile “engineers” from emigrating • Hierarchical – between Major centers of commerce like London, Paris, Berlin, NYC • Contagious – exponential outward expansion as everyone wants to participate – both production & consump. 11.2 Distribution of Industry Tools • Hearth Area • Diffusion – Relocation – follows immigration – Hierarchical – transferred between major metro areas – Contagious – acceptance expotential – Stimulous – principles most easily shared 11.2 Distribution of Industry Tools cont… • Pattern – High clustering in few countries at first – Clustering apparent even at present • High density concentration = efficiency • Spatial Interaction – Space-Time compresion results from process 11.2 Distribution of Industry Tools cont… Site & Situation – both key to eventual sitting of activities • Site Factors include: resources, labor, capital (human and monetary), land, and markets – China today focuses on cheap Labor • Situation Factors focus mainly on long distance transportation routes – Coastal China today 11.2 Distribution of Industry Tools cont… • Resources & Markets – Each exerts influence on locating industry Major Centers in Europe Major Centers in East Asia Manufacturing Zones in China Click here Major Centers in US & Canada Turning to Robots for Manufacturing click here http://tlc.discovery.com/videos/understandingrobots-mass-customization.html 11.3 Situation – Transport Costs Think Networks for Trade • Bulk Reducing Activities – Locate near raw material – By reducing bulk final cost reduced – Example Copper smelting • Bulk Gaining Activities – Locate near final market – Add bulk at last minute – less trans cost – Example Beer production 11.3 Situation Factors Bulk Gaining 11.4 Changes in Steel Location • 1770s Near Energy Source – locate iron/steel forges in mountain valleys and use wood/charcoal • 1850s Near Energy Source – coalfields because greatest bulk – Pittsburgh favored • 1890s In between coal and iron ore – Lake Erie sites favored • 1910s Move closer to markets as coal requirements drop – South Lake Michigan favored • 1950s Move closer to East Coast – More dependent on foreign iron inputs & local markets • Today – foreign sites & major US Market sites – – Foreign producers lower labor cost in integrated mills Major markets switch to scrap iron as input and mini-mills Steel has changed from bulk reducing to market sensitive locations in the USA while moving to Labor sensitive locations internationally 11.4 Changes in Steel Location • 1770s Near Energy Source – locate iron/steel forges in mountain valleys and use wood/charcoal • 1850s Near Energy Source – coalfields because greatest bulk – Pittsburgh favored • 1890s In between coal and iron ore – Lake Erie sites favored • 1910s Move closer to markets as coal requirements drop – South Lake Michigan favored • Today – foreign sites & major US Market sites – – Foreign producers lower labor cost in integrated mills Major markets switch to scrap iron as input and mini-mills http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_hlfqggGOZw&feature=related Steel has changed from bulk reducing to market sensitive locations in the USA while moving to Labor sensitive locations internationally Creative Destruction? http://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=V-wRygi2PaQ http://www.youtube.com/w atch?v=7O3ye1h60qU http://www.youtube.com/watc h?v=Pr3EJ-I1vaU Site vs Situation for Steel • 1770s Near Energy Source – Site condition dominates – Energy & Bog Iron very close – site – Transport of output to market -- situation • 1850s Near Energy Source – Site condition dominates – What Site conditions favored Pittsburgh? • 1890s In between coal and iron ore – Situation condition dominates – What Situation conditions favored Lake Erie ports? • 1910s Move closer to markets as coal requirements drop & iron increases – Site conditions dominate – What Site condition favored South Lake Michigan? Favored • 1950s Move closer to East Coast change to foreign supplies – Situation conditions dominate – More dependent on foreign iron inputs & local markets • Today – foreign mills & major US Market sites – Site conditions dominate – What Site conditions favors LDC Foreign producers for integrated mills? – What Site conditions favor large urban markets like Seattle for mini-mills? Migration to lower cost developing nations Side note: ownership of mills even in MDCs also migrates to LDCs like China and India Modern Mini Mill http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v0F5ITivFzo Some Mini Mills in US & Mexico Tend to favor Site Conditions – Locate close to markets and scrap iron/steel sources 11.5 Auto Production Situation Sensitive – Why? Changing pattern of plants to reflect just-intime system & unionization Situation based Network of assembly Site based lower cost Southern Labor Auto Alley: Focused on I65 and I75 Example of Just-in-time delivery and assembly 70% of the value in a car comes from independent suppliers Situation: Over time auto suppliers and assemblers have migrated to the center of the country to minimize distribution cost of final products Site: Suppliers and assemblers have also migrated south to lower cost labor New Car Plant Locates in Indiana 11.6 Transport Modes Break of Bulk Point • Place where move from one mode of transport to another – good place to process goods – Seaport, airport, rail yard… – Opportunity for further processing before sending on – Example wheat from farms may be assembled at a port for export and milled there into flour Just-In-Time Production • Low stockpiles at assembly plant • Multiple suppliers concentrate in same region • Japanese automakers developed this system due to small land area for factories James Rubenstein talks about Auto Production – video 30 12:15 minutes “Just in time” example – truck seats click here http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JTJLhWGVQQs Mode of Transport • Variations based on cost & speed • • • • High Cost High Speed Air Truck Rail Boat Just in time possible Low Cost Low Speed Just in case or large stockpiles 11.7 Site Factors Site: Three of most important Factors • Labor – currently most important in labor intensive industries like textiles • Land – causes industry to migrate to the edge of urban areas – looking for “green field” sites encouraging sprawling single floor factories • Capital – can either be locally available or from outside – FDI – foreign direct investment – such as capital flows to China – Venture Capital – readily available in Silicon Valley Textile & Apparel Spinning: Labor intensive mainly done in LDCs Woven Cotton: Dominated by low cost labor and readily available raw materials in China and India 11.8 Textile & Apparel Production Production of Men’s & Boy’s Trousers: Higher skill then weaving, currently migrating to LDCs Labor-Intensive Industries Labor-intensive Industries • Consideration – Balance of lowest cost per hour of labor versus skills embodied in labor – And transportation cost versus timeliness of delivery – Example cheap to make Christmas toys in China, but if early supplies sell out difficult to restock due to the distance Decline in Labor Intensive Clothing in USA Migration of “skilled” textile jobs abroad Comparative Labor Costs for Clothing Manufacturing Note how Indonesia could be the next large textile producer Notice where Pakistan falls 11.9 Emerging Industrial Regions • US Shifts – From high labor cost/protection areas to low areas • Movement out of US – Outsourcing – China as workshop of the world – BRICS as possible future manufacturing centers Santa’s Helpers http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MQh2CZZK1YU