Court Cases 2 - Kenton County Schools
advertisement

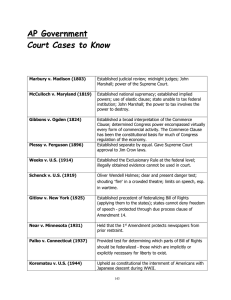
Brown v. Board of Education 1954 case that overturned Separate but Equal standard of discrimination in education. Gideon v. Wainwright 1963 ruling that a defendant in a felony trial must be provided a lawyer free of charge if the defendant cannot afford one. Griswold v. Connecticut 1965 decision that the Constitution implicitily guarantees citizens' right to privacy. Marbury v. Madison 1803 established the principle of judicial review Miranda v. Arizona 1966 ruling that upon arrest, a suspect has the right to remain silent and the right to consult with a lawyer. Plessy v. Ferguson 1896 ruling that separate but equal facilities for different races were not unconstitutional. Schenck v. United States 1919--Case involving limits on free speech. Established the "clear and present danger" principle. Roe v. Wade 1973 ruling that decriminalized abortion. Carig v. Boren 1976 ruling that classification of individuals based on gender must be related to an important government objective; replaced minimum rationality standard. Miler v. California 1973 ruling that determined the obscenity clause to related to works that lack literary, artisitic, political or scientific value. (LAPS test) Lemon v. Kurtzman 1971 defining government actionsin dealing with religion--must not inhibit or advance religion and does not entangle the goverment with religion. Fletcher v. Peck The decision stems from the Yazoo land cases, 1803, and upholds the sanctity of contracts. McCulloch v. Maryland 1819--The Court ruled that states cannot tax the federal government, i.e. the Bank of the United States; the phrase "the power to tax is the power to destroy"; confirmed the constitutionality of the Bank of the United States. Dartmouth College v. Woodward 1819--New Hampshire had attempted to take over Dartmouth College by revising its colonial charter. The Court ruled that the charter was protected under the contract clause of the U. S. Constitution; upholds the sanctity of contracts. Gibbons v. Ogden 1824--Clarified the commerce clause and affirmed Congressional power over interstate commerce. Korematsu v. U. S. T1941--he court upheld the constitutionality of detention camps for Japanese-Americans during World War 2. Escobedo v. Illinois 1964--Ruled that a defendant must be allowed access to a lawyer before questioning by police. U. S. v. Richard Nixon 1974--The court rejected Richard Nixon's claim to an absolutely unqualified privilege against any judicial process. Bakke v. Regents of the University of California 1978--Ambiguous ruling by a badly divided court that dealt with affirmative action programs that used race as a basis of selecting participants. The court general upheld affirmative action, but with a 4/4/1 split, it was a very weak decision. Brandenburg v. Ohio 1969--Determined that a law that proscribes advocacy of violence for political reform is constitutional if applied to speech that is not directed toward producing imminent lawlessness and is not likely to produce such action is not constitutional. Duncan v. Louisiana 1968 guarantees the right to a trial by jury where a sentence of at least two years is involved. Gitlow v. New York (1925) Anarchist calling for overthrow of the government. Established precedent of federalizing Bill of Rights (applying them to States); States cannot deny freedom of speech - protected through due process clause of Amendment 14 Palko v. Connecticut (1937) Provided test for determining which parts of Bill of Rights should be federalized - those which are implicitly or explicitly necessary for liberty to exist. Mapp v. Ohio (1961) Established exclusionary rule; illegally obtained evidence cannot be used in court; Warren Court's judicial activism. Engel v. Vitale (1962) Prohibited state-sponsored recitation of prayer in public schools by virtue of 1st Amendment's establishment clause and the 14th Amendment's due process clause; Warren Court's judicial activism. Baker v. Carr (1962) "One man, one vote." Ordered state legislative districts to be as near equal as possible in population; Warren Court's judicial activism. Abbington v. Schempp (1963) Prohibited devotional Bible reading in public schools by virtue of establishment clause and due process clause. Warren Court's judicial activism Wesberry v. Sanders (1963) Ordered House districts to be as near equal in population as possible (extension of Baker v. Carr to Congressional districts). Epperson v. Arkansas (1968) Prohibited states from banning the teaching of evolution. Tinker v. Des Moines (1969) Guaranteed a student's right to protest (wearing armbands). Furman v. Georgia (1972) State death penalties (as then applied) are arbitrary and violate equal protection of 14th Amendment. Gregg v. Georgia (1976) Upheld new Georgia death penalty laws requiring dual-phase trial and special circumstances; capital punishment does not constitute cruel & unusual punishment of 8th Amendment. Buckley v. Valeo (1976) 1st Amendment protects campaign spending; legislatures can limit contributions, but not how much one spends of his own money on campaigns. Webster v. Reproductive Health Services (1987) More leeway for states in regulation abortion, though no overturning of Roe v. Wade. Upholds MO law prohibiting abortion in public hospitals; shift in composition of court. (Later cases allow 24-hour waiting periods, parental consent for minors, etc.) Texas v. Johnson (1989) Flag-burning is symbolic speech with a political purpose and is protected by 1st Amendment. Shaw v. Reno (1993) NO racial gerrymandering; race cannot be the sole or predominant factor in redrawing legislative boundaries; majority-minority districts. U.S. v. Lopez (1995) Gun Free School Zones Act exceeded Congress' authority to regulate interstate commerce. Bush v. Gore (2000) Use of 14th Amendment's equal protection clause to stop the Florida recount in the election of 2000. Parker v. Gladden Right to an impartial jury Barron v Baltimore (1833) The guarantee in the 5th Amendment that private property shall not be taken "for public use, without just compensation" is not applicable to state governments as well as the federal government. Boy Scouts of America v. Dale The boy scouts were allowed to dismiss a leader after learning that he was gay, holding that freedom of association outweighed the New Jersey anti-discrimination statute. Near v Minnesota (1925) Case centered on censorship - government cannot censor something (newspapers) because that restricts freedom of the press. Main issue was government officials were being criticized and wanted to censor the criticism. Everson v Board of Education (1942) A New Jersey law allowing reimbursements of money to parents who sent their children to school (public and private) on buses operated by the public transportation system did not violate the establishment clause or the 1st and 14th Amendments. Palko v Connecticut (1937 Ruled a harsher sentence as a result of a new trial won on appeal does not violate double jeopardy.