Tissue 2
advertisement

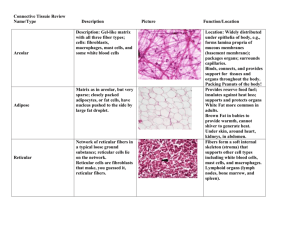
Connective Tissue Connective Tissue Support and attachment for various organs, fills body spaces giving body form and maintenance Composed of 3 main elements – cells, fibers and ground substance (fiber and ground substance = extracellular matrix or ECM) Derived from the embryonic tissue, mesenchyme Classification Classified based on the nature of the matrix Ground substance – amorphous (unstructured) material that fills the space between cells Fibers – 3 types Cells – 2 types 3 Types of Fibers Collagen fibers (white fivers in fresh tissue, pink on slide) – strong, non-elastic with great tensile strength and flexibility Elastic fibers (yellow fibers, dark purple on slide) – thinner, not as strong as collagen fibers, randomly coiled, wavy look Reticular fibers (dark purple on slide) – very thin, fine fibers that branch extensively and form a network Reticular Collagen Fibroblasts Elastic Cell Types Cells – 2 types –blast cells – immature, actively mitotic cells, used to build matrix –cyte cells – mature, non-mitotic cells, maintain matrix CT-Proper Fibroblast Fibrocyte Cartilage Chondroblast Chondrocyte Bone Osteoblast Osteocyte Blood Hemocytoblast Various types (erythrocyte, thrombocyte, leukocyte) Classification of Connective Tissue Subtypes Mesenchyme (Common embryonic tissue) Connective tissue Proper Loose – 3 specific types: Areolar, Adipose, Reticular Connective tissue Proper Dense – 3 specific types: Regular Dense, Irregular Dense, Elastic Cartilage – 3 specific types: Hyaline Cartilage, Fibrocartilage, Elastic Cartilage Osseous (Bone) – 2 specific types: Compact Bone, Spongy (cancellous) Bone Blood – Cell types: Erythrocytes (red blood cells), Leukocytes (white blood cells), Thrombocytes (platelets) Subtype: Mesenchyme Forms the undifferentiated “filling” of the early embryo Forms CT between and within developing tissues and organs In adults, only found in dental pulp Consists of mesenchymal cells with stem cell properties (able to give rise to other cells) Subtype: Loose CT Proper, Specific Type: Areolar Loosely organized matrix with all 3 fiber types Fibrocytes most common cells (flat or spindle shaped), although mast cells and macrophages (immune cells) present Ground substance – semifluid Functions: widespread flexible framework within and between organs. Contain blood vessels that nourish surrounding tissue and is site of immune reactions Location: beneath epithelial tissues, around and within muscles and nerves and in come serous membranes, composes superficial fascia Subtype: Loose CT Proper, Specific Type: Adipose Cytoplasm and nucleus compressed to edge of cell by large lipid droplet Adipocytes (“signet cells”) filled with fat Ground substance - very little Fibers – none Function: protective cushion and insulation throughout body Location: buttocks, breasts, surrounding kidneys, eye sockets Subtype: Loose CT Proper, Specific Type: Reticular Network of fine (reticular) fibers Ground substance – semifluid Cells - reticular cell (type of fibroblast that produces reticular fibers) Function: provides supporting framework for many vascular organs, hematopoietic tissue and lymph nodes Location: spleen, bone marrow, lymph nodes Subtype: Dense CT Proper, Specific Type: Regular Closely packed collagen fiber bundles in parallel arrangement Ground substance - very little Fibers - mostly parallel collagen fibers Cells – Fibrocyte Function: tensile strength Location: Tendons, aponeurosis, ligaments. Forms the deep fascia Subtype: Dense CT Proper, Specific Type: Irregular Bundles of collagen fibers (and a few elastic fibers) randomly interwoven Ground substance - very little Cells – fibrocyte Function – strength from many directions Locations: most of skin dermis, sheaths around nerves and tendons Subtype: Dense CT Proper, Specific Type: Elastic Bundles of parallel elastic fibers that branch and unite with one another Ground substance - very little Fibers – elastic Cells – fibrocyte Function – great elasticity (flexibility) Location: ligaments of vertebral column and walls of large arteries Subtype: Cartilage Surrounded by a fibrous membrane called the perichondrium Mature cells, called chondrocytes, lie in lacunae Lack blood vessels Cells derive nourishment by diffusion from capillaries in the perichondrium Subtype: Cartilage, Specific Type: Hyaline Matrix - firm with an imperceptible fibers (collagen) (i.e. fibers not routinely visible) Most common type of cartilage Cells - chondrocyte in lacunae (mature) Function: provides smooth surface so tissues may move easily over one another. Also provides flexibility and support Location: composes much of fetal skeleton prior to ossification, covers ends of long bones in adults, cartilaginous part of nasal septum, trachea and costal cartilage Subtype: Cartilage, Specific Type: Fibrocartilage Alternating bundles of collagen fibers and rows of chondrocytes, lack perichondrium Matrix - semi-firm thick collagen fibers Cells - chondrocyte in lacunae Function: provide support and rigidity to surrounding structures, strongest of the 3 types of cartilage Location: intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, meniscus of knee joint Subtype: Cartilage, Specific Type: Elastic More flexible and elastic than hyaline cartilage Matrix - firm with obvious elastic fibers Cells - chondrocyte in lacunae Function: provide support to surrounding structures and to define and shape area in which it is present Location: external ear (auricle), auditory tubes, epiglottis Subtype: Osseous (Bone) Hard, strong and lightweight Bone is continually modified and reconstructed (remodeling) Subtype: Osseous (Bone), Specific Type: Compact Compact bone (Ground Bone and decalcified bone slides) Composed of functional units called osteons (concentric circles with central canal) Matrix - hard and calcified with many collagen fibers Cells - osteocytes in lacunae within matrix Function: protection, support, and storage of minerals Location: skeleton Subtype: Osseous (Bone), Specific Type: Spongy Spongy (Cancellous) bone Interior to and continuous with compact bone Numerous trabeculae (branching bony plates) with interconnecting spaces. The space are filled with marrow Matrix - hard and calcified with many collagen fibers but lacks bone lamellas. Cells - osteocytes in lacunae within matrix Function – protection, support, storage of bone marrow Subtype: Blood Make up of formed element (blood cells) and plasma (fluid) Matrix - plasma- fluid Cells - Blood cells –erythrocytes (red blood cells), leukocytes (white blood cells), thrombocytes (platelets, cell fragments) Fibers are only present during clotting Function: transport of oxygen, waste, nutrients and hormones, aids in regulation of body temp, maintains homeostasis by buffering tissue Nervous Tissue Nervous System Transmit information Cells Neurons - nerve cell bodies (soma) with dendrite and axon processes, major cell type Supporting cells - non-conducting support cells