Tissues - Dickinson ISD
advertisement

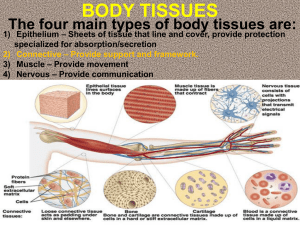
Tissues No, not that kind! BODY TISSUES!!! 4 Main Types Epithelial Connective Muscle Nervous Epithelial Tissues 2 main types: 1. Covering and Lining- includes mucosa, skin and serosae (moist membranes found in closed ventral body cavities.) Ex: pleura, pericardium, peritoneum 2. Glandular- endocrine and exocrine Connective Tissues Most abundant of the primary tissues. Most widely distributed, and varied type. It includes fibrous tissues, fat, cartilage, bone, bone marrow, and blood. often bind other organs together, hold organs in place, cushion them, and fill space. Characteristics: Common origin (mesenchyme) Varied degrees of vascularity Matrix- major component of connective tissue ○ Nonliving ○ Allows connective tissue to bear weight, withstand great tension and endure trauma. Types of Connective tissue Embryonic (mesenchyme) Connective tissue proper ○ Includes all mature connective tissue except bone, cartilage and blood. ○ Loose CT: areolar, adipose and reticular Reticular- liver, lymph nodes, marrow and spleen Adipose- fat in breasts, around eyes and kidneys and under skin. - Provides reserve food fuel, insulates against heat loss. Areaolar- packages organs, surrounds capillaries - Cushions organs, macrophages phagocytize bacteria, holds and transports tissue fluid Types of Connective Tissue, Cont. ○ Dense CT Elastic- provides durability with stretch - Walls of aorta, vocal cords, ligaments that connect vertebrae, parts of trachea and bronchi. Irregular- provides structural strength - Dermis, fascia, fibrous capsules of joints, etc. Regular- attaches muscles to bones and bones to bones - Tendons, ligaments and aponeuroses Types of Connective Tissue, Cont. Blood- transport of gases, nutrients and waists; immunity Cartilage ○ Hyaline cartilage: forms most of the embryonic skeleton, covers ends of long bones, costal cartilage of ribs, cartilage of nose trachea and larynx. ○ Fibrocartilage: intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, discs of knee joint ○ Elastic cartilage: epiglottis Bone (osseous tissue) ○ Very vascular. Has hard, calcified matrix w/ collagen. ○ Provides support and structure, calcium storage, and hematopoiesis. Muscle Tissues Highly cellular Well vascularized Responsible for body movement Types of Muscle Tissue: Voluntary: (skeletal) Long, cylindrical cells with many nuclei Striated Packaged by connective tissue sheets. Attached to bone Contract to pull on bone or skin. Involuntary: (cardiac and smooth) Cardiac ○ found only in heart. Smooth ○ has no visible external striation. ○ Spindle-shaped with one central nucleus. ○ Found in walls of hollow organs. ○ Propels substances through organs by contracting and relaxing. Nervous Tissues Found in brain, spinal cord and nerves. 2 major cell types Neurons- branching or stellate cells that generate & conduct nerve impulses. Neuroglial cellsnonconducting cells that support, insulate and protect neurons. Tissue Repair Most types of repair involve both regeneration and fibrosis. Regeneration- replacement of destroyed tissue by proliferation of the same type of cell. Fibrosis- proliferation of fibrous connective tissue. (scarring)