Tissue Level of Organization
advertisement
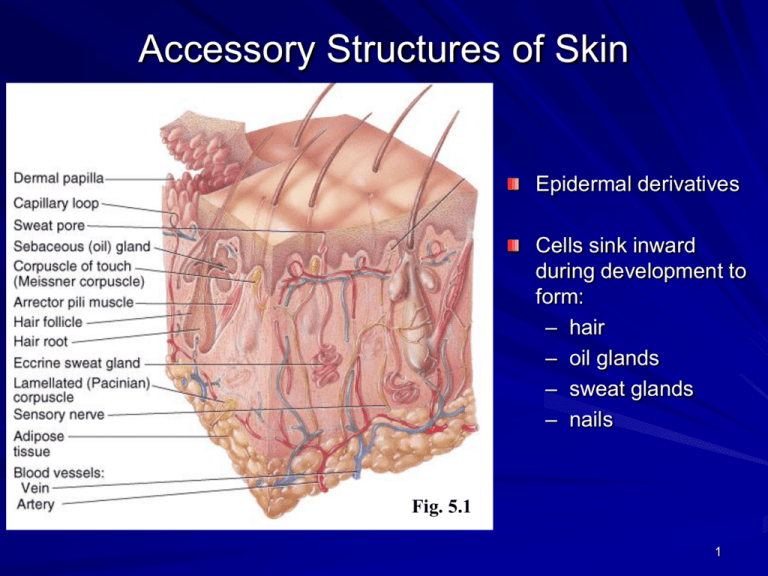
Accessory Structures of Skin Epidermal derivatives Cells sink inward during development to form: – hair – oil glands – sweat glands – nails Fig. 5.1 1 Structure & Fxn. of Hair Shaft -- visible – medulla, cortex & cuticle – straight hair Xsec round – wavy hair X-sec oval – curly hair x-sec kidney shaped Root -- below the surface Fig. 5.5 Follicle surrounds root – external root sheath – internal root sheath – base of follicle is bulb blood vessels germinal cell layer 2 Hair Growth Growth cycle = growth stage & resting stage Growth stage – lasts 2 - 6 yrs. – matrix cells @ base of hair root produce length Resting stage – lasts 3 mths. – matrix cells inactive & follicle atrophies Old hair falls out as growth stage begins again – normal hair loss = 70 100 hairs/day 3 Hair Related Structures Arrector pili muscle – smooth muscle in dermis contracts w/ cold or fear. – forms goosebumps as hair is pulled vertically Hair root plexus – detect hair movement Fig. 5.5 4 Glands of the Skin Specialized exocrine glands found in dermis Sebaceous (oil) Sudiferous (sweat) Ceruminous (wax) Mammary (milk) Fig. 5.1 5 Sebaceous (oil) glands Fig. 5.6 Secretory portion in the dermis Most open onto hair shafts Sebum – Comb. of cholesterol, proteins, fats & salts – keeps hair & skin soft & pliable – inhibits growth of bacteria & fungi (ringworm) Acne – bacterial inflammation of glands – secretions stimulated by hormones @ puberty 6 Sudoriferous (sweat) glands Fig. 5.6 Eccrine (sweat) glands – most areas of skin – secretory portion in dermis with duct to surface – regulate body temperature – H2O, NaCl, urea, uric acid, A.A., glucose, & lactic acid Apocrine (sweat) glands – Armpit & pubic regions – Also around areolae & bearded regions of adult males – Secretory portion in dermis w/ duct that opens onto hair follicle – Secretions more viscous & milky (lipids & protein) 7 Ceruminous glands Fig. 22.10 Modified sweat glands produce waxy secretion in ear canal Cerumin contains secretions of oil & wax glands Helps form barrier for entrance of foreign bodies Impacted cerumen may reduce hearing 8 Structure of Nails Fig. 5.7 Tightly packed keratinized cells Nail body – visible portion pink due to underlying capillaries – free edge appears white Nail root – buried under skin layers – lunula is white due to thickened stratum basale Eponychium (cuticle) – stratum corneum layer 9 Thin Skin vs. Thick Skin Thick skin – only on palms and soles – thick epidermis (.6 to 4.5 mm.) with distinct stratum lucidum & thick stratum corneum – lacks hair follicles and sebaceous glands 10 Thin Skin vs. Thick Skin Thin skin – covers most of body – thin epidermis (.1 to .15 mm.) that lacks stratum lucidum – lacks epidermal ridges, has fewer sweat glands & sensory receptors 11 Photodamage UVA & UVB light can damage skin Acute overexposure causes sunburn UVA produces oxygen free radicals that damage collagen & elastic fibers leads to wrinkling DNA damage in epidermal cells can lead to skin cancer 12 Skin Cancer 1 million cases diagnosed per year 3 common forms of skin cancer – basal cell carcinoma (rarely metastasize) – squamous cell carcinoma (may metastasize) – malignant melanomas (metastasize rapidly) most common cancer in young women arise from melanocytes ----life threatening key to treatment is early detection watch for changes in symmetry, border, color and size risks factors include-skin color, sun exposure, family history, age & immunological status 13 Epidermal Wound Healing Abrasion or minor burn Basal cells migrate across the wound Contact inhibition w/ other cells stops migration Epidermal growth factor stimulates cell division Full thickness of epidermis results from further cell division 14 Deep Wound Healing 4 phases: – Inflammatory – Migratory – Proliferative – Maturation Scar formation – Hypertrophic – Keloid Which phases have been left out of this illustration? 15 Burns Types of burns: – 1st – 2nd – 3rd Destruction of proteins of the skin – chemicals, electricity, heat Problems that result – shock due to water, plasma & plasma protein loss – circulatory & kidney problems from loss of plasma – bacterial infection 16 Skin Grafts New skin can not regenerate if stratum basale and its stem cells are destroyed Skin graft is covering of wound with piece of healthy skin To ensure no tissue rejection occurs transplantations are: – Autografts (from self) – Isografts (from twin) – Autologous skin used transplantation of patients skin grown in culture http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/0 02982.htm for more info. Serial documentation of healing skin grafts following burns in an 18 month old child. Photographer: Gigi William's 17 Pressure Sores Decubitus ulcers Caused by constant deficiency of blood flow to tissue Areas affected is skin over bony prominence in bedridden patients Preventable w/ proper care 18








