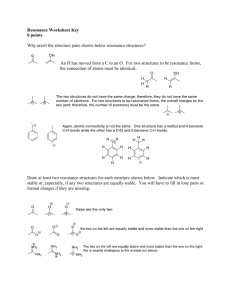
resonance.
advertisement

Resonance A molecule or polyatomic ion for which 2 or more dot formulas with the same arrangement of atoms can be drawn is said to exhibit RESONANCE. Resonance Example CO32- 3 resonance structures can be drawn for CO32the relationship among them is indicated by the double arrow. the true structure is an average of the 3. Resonance Example CO32- 3 resonance structures can be drawn for CO32the relationship among them is indicated by the double arrow. the true structure is an average of the 3. Resonance Example CO32- 3 resonance structures can be drawn for CO32the relationship among them is indicated by the double arrow. the true structure is an average of the 3 Resonance Structures Another way to represent this is by delocalization of bonding electrons: (the dashed lines indicate the 4 pairs of bonding electrons are equally distributed among 3 C-O bonds; unshared electron pairs are not shown) See p. 256 VSEPR valence shell electron pair repulsion Molecular Shape Lewis structures (electron dot structures) show the structure of molecules…but only in 2 dimensions (flat). BUT, molecules are 3 dimensional! for example, CH4 is: Molecular Shape Lewis structures (electron dot structures) show the structure of molecules…but only in 2 dimensions (flat). BUT, molecules are 3 dimensional! but in 3D it is: a tetrahedron! = coming out of page = going into page = flat on page Why do molecules take on 3D shapes instead of being flat? Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory “because electron pairs repel one another, molecules adjust their shapes so that the valence electron pairs are as far apart from another as possible.” Why do molecules take on 3D shapes instead of being flat? Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory Remember: both shared and unshared electron pairs will repel one another. Non-Bonding Pairs H—N — H H Bonding Pairs 5 Basic Molecule Shapes Linear Example: CO2 5 Basic Molecule Shapes Bent or angular Example: H2O Notice electron pair repulsion 5 Basic Molecule Shapes tetrahedral example: CH4 5 Basic Molecule Shapes Pyramidal Example: NH3 (note: unshared pair of electron repels, but is not considered part of overall shape; no atom there to contribute to the shape) 5 Basic Molecule Shapes Trigonal planar or planar triangular Example: BF3 Geometry and polarity Three shapes will cancel out polarity. Shape One: Linear Geometry and polarity Three shapes will cancel out polarity. Planar triangles 120º Geometry and polarity Three shapes will cancel out polarity. Tetrahedral Geometry and polarity Others don’t cancel Bent Geometry and polarity Others don’t cancel Trigonal Pyramidal