Polyatomic Ions
advertisement

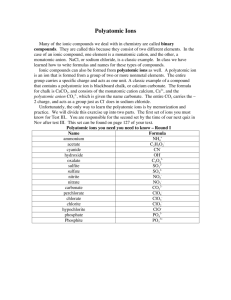
What are Polyatomic Ions? How do they form ionic compounds? Section 6.3b 6.4b Objective I 6.3b-4b know the difference of a polyatomic ion vs. a monatomic ion I can write formulas and names of polyatomic ionic compounds Monatomic Ions QUICK REVIEW…. Mono means “one” Monatomic ions are charged atoms. Monatomic cations are atoms that lose electrons to become positively charged: Monatomic anions are atoms that gain electrons to become negatively charged, their name ends in -ide Lithium ion Li+ Berllium ion Be2+ Oxide ion O2Bromide ion Br- They form ionic compounds like Li2O and BeBr2 Polyatomic Ions Polyatomic ions are charged molecules. The atoms within a polyatomic ion are usually very tightly bound together, and behave as a unit so the ion retains its identity within ionic compounds and over the course of many chemical reactions. N O O Nitrite = (NO2)- - O O N O Nitrate = (NO3)- Many polyatomic anions occur in –ite/-ate pairs. -ite / -ate pairs…….Do you see a pattern? -ite -ate sulfite, (SO3)2- sulfate, (SO4)2- nitrite, (NO2)- nitrate, (NO3)- chlorite, (ClO2)- chlorate, (ClO3)- The charge of each polyatomic ion –ite/-ate pair is the same. The –ite ending indicates less oxygen than the –ate ending. However, the ending does not tell you the actual number of oxygen atoms in the ion Most polyatomic ions are anions Polyatomic anion Naming Example monatomic anions end in -ide as you well know! Two less oxygens hypo-…-ite One less oxygen end in -ite The most common form ends in -ate One more oxygen per-…-ate The most common form of a polyatomic ion usually ends with…. A. B. C. -ide -ite -ate As you already know, monatomic anions always end with…. A. B. C. -ide -ite -ate The Common Polyatomic Ions Most common polyatomic ions are anions and have a negative charge There is one common cation… Ammonium NH4+ Most polyatomic anions end in –ate or –ite There are two name exceptions… Hydroxide OHCynide CN- Which of these is the correct formula and charge of a nitrate ion? A. B. C. D. NO2 NO3 NO2 NO3 charge = 1+ charge = 1+ charge = 1charge = 1- Which of these is the correct formula and charge of an amonium ion? A. B. C. D. NH3 NH4 NH3 NH4 charge = 1+ charge = 1+ charge = 1charge = 1- Which of these is the correct formula and charge of a sulfite ion? A. B. C. D. SO3 SO4 SO3 SO4 charge = +2 charge = +2 charge = -2 charge = -2 What is the name and charge of the CrO4 ion? A. B. C. D. E. F. Carbonate Chromate Dichromate Perchlorate Chromate Dichromate charge = -2 charge = 4 charge = -2 charge = -1 charge = -2 charge = 2 Writing Formulas with Polyatomic Ions Use the cross-cross method to find the formula for ionic compounds that contain polyatomic ions. Put (parentheses) around each polyatomic ion, and NEVER CHANGE THE IONS SUBSCRIPTS!!! (parenthesis) are usually dropped if the polyatomic ion’s subscript is 1. Formula Examples: a) calcium nitrate b) sodium hydroxide Writing Formulas with Polyatomic Ions Use the cross-cross method to find the formula for ionic compounds that contain polyatomic ions. Put (parentheses) around each polyatomic ion, and NEVER CHANGE THE IONS SUBSCRIPTS!!! (parenthesis) are usually dropped if the polyatomic ion’s subscript is 1. Formula Examples: a) calcium nitrate b) sodium hydroxide Ca2+ (NO3)Ca(NO3)2 Na+ OHNaOH Which of these is the formula for the compound formed from magnesium ions and hydroxide ions? A. B. C. D. Mg(OH)2 Mg2OH MgOH2 MgO2H2 Which of these is the formula for the compound formed from Al3+ and SO32-? A. B. C. D. Al3(SO3)2 Al2SO3 Al2(SO3)3 Al3(SO2)3 Which of these is the formula for potassium hypochlorite? A. B. C. D. P(ClO)2 K2CO PClO2 KClO Naming Ionic Compounds with Polyatomic Ions Naming examples: Simply name the cation and polyatomic anion with no change to either name. Examples Mg3(PO4)2 magnesium phosphate Li2SO4 lithium sulfate Name the compound….. LiCN A. B. C. D. lithium cyanate lithium cyanite lithium cyanide lithium nitride Name the compound….. (NH4)2SO3 A. B. C. D. E. ammonium sulfur trioxide hydro nitrogen sulfate ammonium sulfate ammonium sulfite diammonium sulfite Name the compound….. Fe(ClO3)2 A. B. C. D. iron(II) chlorate iron(III) chlorite iron(I) dichlorate iron(II) chloride What did we learn? Polyatomic ions are charged molecules that are very tightly bound together, so that they retain their identity within ionic compounds and over the course of many chemical reactions. Monoatomic ions end in –ide as we well know. Polyatomic ions add –ate, -ite or per- -ate Polyatomic ions behave as a unit and carry a charge as a group of atoms. In formulas, use (parenthesis) around polyatomic ions like: Ca(NO3)2 Additional Practice 1. Write the symbol and charge for the cation and anion then use criss-cross method to write the formula. a) potassium sulfate K2SO4 b) ammonium chloride NH4Cl Additional Practice Name these compounds a) Na2CO3 Sodium Carbonate b) AgNO3 Silver Nitrate