Simple squamous
advertisement

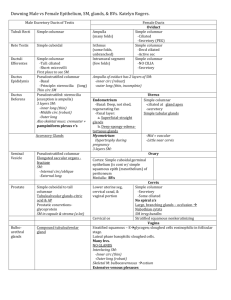
Chapter 5 Tissues Intercellular Connections • Individual cells connect to form tissues 3 ways: – Tight junctions- prevents permeability of ions through junction. – Desmosome- adhesion between cells in spots. Allows from some permeability. – Gap junctions- cytoplasms of adjacent cells are connected through transport proteins. • Ions can pass freely through cells. Intercellular Connections Tissue Types A tissue is a group of cells with a common structure & function The human body is composed of four main tissue types: 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Connective Muscle Nerve Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Characteristics Always has a free (apical) surface exposed to outside or open space. Lacks blood vessels Readily divide and replicate Has a basement membrane to anchor underlying tissue Between epithelial and connective tissue Functions Covers body surfaces Makes up glands Protects Absorbs Secretes Excretes Classified by Shape Squamous – flattened cells Cuboidal – cube-shaped Columnar – tall, column-shaped Classified by Shape May occur in layers: Simple – 1 layer of cells Stratified – 2 or more layers Pseudostratified – appears to be layered, but is not Example – simple cuboidal Example – stratified columnar Examples of Epithelial Tissue s Simple Squamous- Thin, flattened cells. Allow for diffusion and filtration. Line air sacs of lungs and walls of capillaries. Simple cuboidal-single layer of cube shaped cells. Lines follicles of thyroid gland, kidneys and ducts of certain glands. Used for secretion and absorption Simple columnar- single layer of elongated cells. Can contain cilia, used for protection and absorption in digestive tract. Can contain goblet cells. Stratified squamous- Layers of squamous cells. Make up epidermis and line cavities exposed to external environment. Outer layer die and accumulate keratin. Stratified columnar- Several layers of columnar cells overlying cuboidal cells near the basement membrane. Found in male reprod. System and pharynx Pseudostratified ciliated columnar- Appear stratified but are not. Often contain cilia and goblet cells which secrete mucus. Line respiratory passages. Pseudostratified ciliated columnar w/goblet cells- Line Respiratory passages to trap unwanted particles Transitional tissue- Changes in response to change in tension (stretching). Line urinary bladder and urethra. Larger cells at surface, smaller cells deeper. Glandular Epithelium • Specialized to secrete substances • Usually glands are lined w/cuboidal or columnar epithelium • Those that secrete substances into ducts that open onto a surface are exocrine glands (salivary, oil glands, etc.) • Those that secrete into tissues or blood are endocrine glands (pituitary) Classifying Glands by Structure • Simple- does not branch off before reaching secretory portion • Compound- duct that does branch before secretory portion. Classifying Glands by Type of Secretions 3 types: • • • • • No loss of cytoplasm in secretions • Ex. – pancreas Small portions of cells in secretions Ex. – mammary glands Classifying by Secretions • Secretions w/entire cells filled w/secretory products; ex. – sebaceous (oil) glands Connective Tissue Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. connects supports protects provides framework fills spaces Functions 6. stores fat 7. produces blood cells 8. protects against infection 9. transports nutrients 10.helps repair damaged tissue Characteristics 1. Consists of cells in a matrix (intercellular material) 2. Cells some distance apart 3. Most can divide 4. Good blood supply Types of Fibers: 1. collagenous – composed of collagen (protein); have great tensile strength; slightly elastic; compose bones, tendons & ligaments Types of Fibers - continued elastic – composed of elastin (protein); very elastic but weaker; compose vocal cords & air passages of lungs Types of Fibers - continued Reticular – composed of very fine collagenous fibers. Form support network. Types of Cells 1. Fixed cells – stay in one place & have stable numbers; 2 types: fibroblasts – large & star-shaped; most prevalent Types of Cells - continued mast cells – may release heparin (for blood clotting) & histamines (promotes allergic reactions & inflammation); usually located near blood vessel walls Types of Cells - continued 2. Wandering cells – macrophages – travel through body; numbers change in response to infection; scavengers (Purple cells – macrophages, Green cells – T-lymphocytes) Examples of Connective Tissue Areolar tissue- binds the skin to underlying organs and under epithelium to provide bloodflow. Binds and protects. A- fibroblast, Bcollagen, C- elastin Adipose tissue- connective tissue composed of fats, cushion joints and provide insulation. A- nuclei, B- fat globules Regular dense connectivestrong fibers bind body parts together. Found in ligaments and tendons. Poor blood supply so slow healing. A- fibroblasts. B- collagen and elastin Irregular dense connectivedisorganized and strong. Found in the dermis Hyaline cartilage- Most common, found on ends of bones, nose cavity and supporting rings of resp. system. A- chondrocytes, B- Matrix (fine collagen fibers), C- Lacunae Fibrocartilage- tough tissue containing collagenous fibers. Shock absorbers between vertebrae and pubic girdle. A- Chondrocyte, BCollagen fibers Elastic cartilage- flexible cartilage make up ears and larynx. Used for flexible support. Achondrocytes, B- elastin, C- Lacunae Blood – platelets, found in plasma. Used for blood clotting Blood – red cells & white cell Red- used for transport, white- immunity Elastic connective- allows for stretching, found in attachments between vertebrae. Aelastic fibers Reticular connective- walls of liver and spleen. Used for support. Bone- A- central canal (contains blood vessels) B- Canaliculi- minute tubes allow for movement between cells. Bone- D- Lamellae (layers of osetocytes), Costeocytes (Bone Cells) Muscle & Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue 3 types: Skeletal- Attached to bone and controlled by conscious effort (Voluntary). Used for movement Striated Long and thin with multiple nuclei Muscle Tissue Cont. Smooth- lacks striations found in skeletal, used for involuntary movements Ex- move food through digestive tract Cardiac- striated muscle found only in the heart At intercellular junction contain intercalated discs. Allows for heart to contract as one unit 3 Types of Muscle Tissue Smooth muscle- B- nucleus Skeletal muscle- A- striations, B- nucleus Cardiac muscle- A- Intercalated discs, Bcell Nervous Tissue • Found in the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves. • Cells called neurons – Responsible for transmitting nervous impulses to muscles and glands. • Also include neuroglia cells (support cells) – Support the function of the neurons Nerve tissue – A- neuron, B- Axon, Cneuroglia