Epithelial Tissues: Structure, Function, & Classification
advertisement

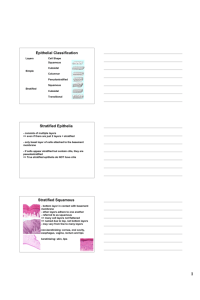
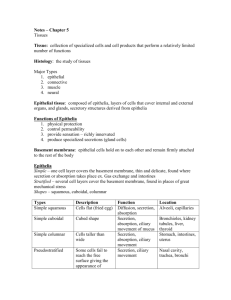
Objectives Chapter 3 Epithelial tissues Tissues • Groups of cells that are similar in structure and function • Four primary types – Epithelium – Connective – Nervous – Muscle 1. Name the four major tissue types and their subcategories (a. epithelial) 2. Explain the structure and function of each tissue 3. Give the primary locations of the tissue types in the body 4. Identify slides or pictures of each tissue EPITHELIA TISSUES •Location includes linings, coverings & glands • Functions include protection, absorption, filtration & secretion •http://www.stegen.k12.mo.us/tchrpges/sghs/ksulkowski/TissueS lides.htm •http://kcfac.kilgore.cc.tx.us/kcap1/practical_1_photos.htm Characteristics of Epithelia Tissues APICAL SURFACE • Form continuous sheets bound by cell junctions (p. 57) • Free surface or apical surface is exposed to body’s exterior or cavity of an organ • Basement membrane are underlining layers • Avascular – no blood vessels; rely on diffusion of gases & nutrients from underlying connective tissues • regenerates BASEMENT MEMBRANE 1 Classification of Tissue simple squamous stratified squamous Given two names: • Cell arrangement (layers) – Simple: one layer – Stratified: more than one layer • Cell shape simple columnar simple cuboidal cells – Squamous: flat – Cuboidal: cube shaped – Columnar: columns SIMPLE EPITHELIA Functions mainly to absorb, secrete & filtrate substances; too thin to protect 1. SIMPLE SQUAMOUS • Single, flat & scale like • Large central nucleus • Forms membranes where rapid diffusion occurs • Locations: air sacs of lungs, lining heart, blood vessels &kidneys, serous membranes 2. SIMPLE CUBOIDAL • Single, cube shaped • Large central nuclei • Locations: tubules of kidneys, ducts of glands & ovary 2 3. SIMPLE COLUMNAR • Single layer of tall cells with oval nuclei • May contain goblet cells that secrete mucus • Locations: lines digestive tract & gall bladder, mucous membranes STRATIFIED EPITHELIA Multiple layers of cells found in areas of protection 2. Stratified Cuboidal • 2 layers; cube shaped • Found in adult sweat glands, conjunctiva of eye, male urethra, pharynx & epiglottis 4. PSEUDOSTRATIFIED COLUMNAR • “false layers” • Some cells look shorter than others making it look stratified • Nuclei at various levels • Can be ciliated – respiratory tract • Nonciliated located in ducts of glands & male urethra 1. Stratified Squamous • Free surface looks squamous while lower layers are either cuboidal or columnar • Found in areas of friction – mouth, esophagus, skin or birth canal 3. Stratified Columnar • Multiple layers of column shaped cells • Lines tubules of kidneys 3 4. Transitional • Modified stratified squamous but large & more rounded • Ability to change shape allowing organs to stretch or distend • Lines urinary bladder, ureters & urethra GLANDULAR EPITHELIA • Consists of one or more cells that produce or secrete a product called a hormone 1. Endocrine • Ductless glands • Hormones diffuse directly into blood vessels that weave through the gland • Thyroid, pituitary, adrenal 2. Exocrine • Contains a duct through which secretions empty • Sebaceous (oil), sweat, mammary, pancreatic, liver 4 5