Ch 8- Photosynthesis
advertisement

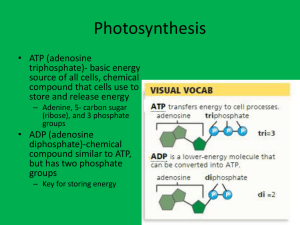
Ch 8- Photosynthesis • • • • Animation Quiz - Calvin Cycle Photosynthesis Visualizing Electron Transport Where do plants get the energy they need to produce food? • What type of organism makes their own food? • What type of organism obtains energy from foods they consume? • ATP (adenosine triphosphate)- basic energy source of all cells, chemical compound that cells use to store and release energy – Adenine, 5- carbon sugar called ribose, and three phosphate groups • ADP (adenosine diphosphatte)- chemical compound similar to ATP, but has two phosphate groups – Key for storing energy • How is the energy that is stored in ATP released? – Chemical bond between second and third phosphate group is broken • Because of the characteristics of ATP, it is an exceptional source of energy Sec 2- Photosynthesis: An Overview • Photosynthesis- series of reactions that uses light energy from sun to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars and oxygen • 6 CO₂ + 6 H₂O→ C₆H₁₂O₆+ 6 O₂ • Plants use the sugars to produce complex carbohydrates- starches • In addition to water and carbon dioxide, it requires light and chlorophyll, molecule in chloroplasts • Plants gather the sun’s energy with light absorbing molecules called pigments • Several types of pigments which include; chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, carotenoids, xanothophylls • Chlorophyll- principal light absorbing pigment – Chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b – Absorbs light very well in certain regions of visible spectrum, green light is reflected • Carotene- red and orange pigments, absorbs light • Chlorophyll b is an accessory pigment that assists in capturing light • Carotenoids are also a accessory pigment that absorbs colors the chlorophylls do not Sec 3- Reactions in Photosynthesis • Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts • Thylakoids- sac-like photosynthetic membranes inside chloroplasts – Arrange in stacks known as grana – Proteins in thylakoids organize chlorophyll into photosystems – 2 types of photosystems – 2 types of reactions in photosystems- light dependent reactions and light independent reactions= Calvin cycle – Light dependent reactions-thylakoid membranes – Calvin cycle= stroma, a region outside thylakoid membranes Electron Carriers • Sunlight excites electrons in chlorophyll= great deal of energy • Electron carriers transport high energy electrons from chlorophyll to other molecules • NADPᶧ- carrier molecule that accepts and holds 2 high energy electrons along with hydrogen ion – Converts NADPᶧ into NADPH – Allows energy of sunlight to be trapped in chemical form • High energy electrons used to build molecules for cell Light Dependent Reactions • Requires light • Converts ADP and NADPᶧ into ATP and NADPH and produces oxygen • Steps of light dependent reaction – Light is absorbed by electrons in photosystem II Are electrons ever used up? Where do the electrons come from? – High energy electrons move through electron transport chain to photosystem I – Photosystem I reenergizes electrons released. Electrons are used to form NADPH – Positively charged hydrogen ions fill up thylakoid membrane – Hydrogen ions pass through ATP synthase, ADP is converted into ATP Calvin Cycle • Plants use energy that ATP and NADPH contain to build high energy compounds • Does not require light, known as light- independent reactions • Steps of Calvin cycle – CO₂ enters the cycle, 6 carbon dioxide molecules combined with six 5 carbon molecules to form twelve 3- carbon molecules – ATP and NADPH are used to convert twelve carbon molecules into higher energy forms – Two 3 carbon molecules removed from cycle to form sugars, lipids, amino acids – 10 remaining 3- carbon molecules converted into six 5- carbon molecules- used in next cycle • Plants use sugars to build cellulose Factors Affecting Photosynthesis • Factors include water, temperature, and intensity of light • How are plants found in Arizona different from plants in Kansas? • Photosynthesis functions best between 0° and 35° C • Increasing the light intensity increase the rate of photosynthesis, the level of intensity varies among plants