Document
advertisement

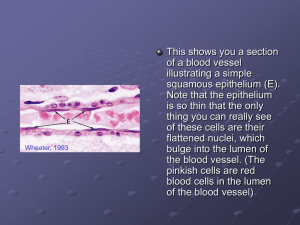
Lab # 6 T http://www.mhhe.com/bi osci/ap/histology_mh/ti smodov.html#connectiv e http://www.kumc.edu/inst ruction/medicine/anatom y/histoweb/epithel/epithel .htm http://www.lumen.luc.edu /lumen/MedEd/Histo/fram es/histo_frames.html Presented by Kami Dykes I S S U E S Melissa Epithelial Tissue • Consists of several layers of cube shaped, elongated, and irregular cells • Commonly possess cilia that move sex cells and mucus • Single layer flattened cells • Nuclei located at different levels within cells • Forms walls of capillaries and air sacs of lungs • Forms lining of trachea and bronchi • Younger cells cuboidal, older cells flattened Stratified squamous • Form inner lining of urinary bladder Epithelium • Lines kidney tubules and ducts of salivary glands Transitional epithelium • Forms lining of stomach and intestines • Nuclei located near basement membrane • Forms lining of oral cavity, anal canal, and vagina Simple columnar epithelium Simple cuboidal epithelium Simple squamous epithelium Pseudostratified columnar epithelium Simple cuboidal epithelium Transitional epithelium Simple columnar epithelium Stratified squamous epithelium Simple squamous epithelium Pseudostratified columnar epithelium with cilia Connective Tissue • Form framework of outer ear • Functions as heat insulator beneath skin • Contains large amounts of fluid and lacks fiber • Cells arranged around central canal • Binds skin to underlying organs • Provides stored enerdy supply in fat vacuoles Cartilage • Forms the flexible part of the nasal septum Elastic connective tissue • Pads between vertebrae that are shock absorbers • Forms supporting rings of respiratory passages • Cells greatly enlarged with nuclei pushed to sides • Matrix contains collagen fibers and mineral salts • Occurs in ligament attachments between vertebrae and artery walls • Hyaline, elastic, fibro Adipose tissue Blood Bone Dense connective tissue Loose (areolar)connective tissue Adipose Bone Hyaline cartilage Blood Loose (areolar) connective Reticular connective Dense connective Muscle and Nervous Tissue Cardiac muscle Nervous tissue Skeletal muscle Smooth muscle • Coordinates, regulates, and integrates body functions • Contains intercalated discs • Muscle that lacks striations • Striated and involuntary • Striated and voluntary • Contains neurons and neuroglial cells • Muscle attached to bones • Muscle that composes heart • Moves food through the digestive tract • Transmits impulses along cytoplasmic extensions Smooth muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Nervous tissue Labeling of bone tissue 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.