Through the Eyes of Julius Caesar
advertisement

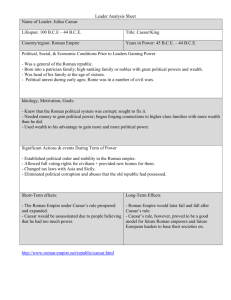
The Roman Republic: Decline and Fall Roman Expansion (p.17) 1. What groups threatened the security of Roman before the Punic Wars? 2. What types of losses did the Romans sustain during the Punic Wars? 3. How did the Conquest of Gaul make the city of Rome more secure? Punic Wars • Rome vs. Carthage (264-146BC) Julius Caesar (p.16) • Why was Caesar described as a man of contradictions? • What actions did Caesar take to help the common people of Rome? • Why did members of the Senate assassinate Caesar in 44 BC? Patricians? Plebeians? Left Out Men with lots of money and land Peasant farmers and craftsmen Women Slaves Citizens? Men who could: Vote, pay taxes, and fight Clients Allies Assembly? The two classes of citizens met here and voted for the following groups Two Consuls? •Governed the City. •One year term •Both had to agree to make a decision Magistrates? •Looked after Rome’s money. •Served as judges •Retired Magistrates •Gave advice to Consuls •Ended up controlling Rome Tribunes? Protected ordinary people against unfair treatment Senate? Adapted from schoolhistory.co.uk Key Words • Citizen: Roman adult men who could: vote, pay taxes, and fight in the legions. Key Words • Legion: a muster of 5,000 Roman citizens prepared to fight. Key Words • Dictator: An emergency leader elected for 6 months that has absolute power in military and government. Reasons the Roman Republic Declined and Fell • Demagogues • Wealth & Corruption • Expansionism • Evolution of Military Demagogues • Demagogue: an ambitious politician who appealed to the common people for support in order to increase their own power. Demagogues • Client: a Roman who is dependant on a wealthy and powerful politician. Clients could get loans, special political favors, business contracts, and legal defense from the politicians who supported them. In return, the clients would vote for their politician in elections. Patricians? Plebeians? Left Out Men with lots of money and land Peasant farmers and craftsmen Women Slaves Citizens? Men who could: Vote, pay taxes, and fight Clients Allies Assembly? The two classes of citizens met here and voted for the following groups Two Consuls? •Governed the City. •One year term •Both had to agree to make a decision Magistrates? •Looked after Rome’s money. •Served as judges •Retired Magistrates •Gave advice to Consuls •Ended up controlling Rome Tribunes? Protected ordinary people against unfair treatment Senate? Adapted from schoolhistory.co.uk Populares vs. Optimates Caesar Populares: Demagogues who look to the plebian s, or common citizens, for support. They built huge networks of clients among the plebeians, by trading favors and supporting popular reforms. Sulla Optimates: Conservative patrician politicians who supported government in the hands of the patricians (people who had a stake in the financial and political success of the Republic). They built networks of clients among young and ambitious politicians in order to maintain the status quo. Wealth & Corruption • The continuous military expansion of the Republic brought a continuous flood of slaves, plunder, and trade into Rome. • Whoever could control this flow of wealth could control the course of Roman politics. • Whoever controls the government can give out favors to build support. Wealth & Corruption • Way to control the flow of wealth: – Get a military command – Become governor of a province • The Roman Republic experiences a series of successful military commanders who seize control as dictators. Marius Sulla Caesar Wealth and Corruption • Wealth is used to breed political corruption in Roman politics. • Populares built networks of clients to put them in power • Optimates built networks of clients to protect their traditional power. • This leads to lots of political violence, riots, political gangs, assassinations, and civil wars. Roman Expansionism •Financing the politics of Roman is dependant on the continual flow of new wealth into Rome. •This leads to a tireless conquest and expansion of Roman power in the last century of the Roman Republic. Roman Expansionism Caesar as Governor of Gaul • After a decade of amazing military achievement, Caesar conquered all of Gaul • The Senate became scared by his growing power and recalled him as an outlaw Changes in the Military • Why were the soldiers ready to follow Caesar but not Pompey? Changes in the Military • Rome got too big to be governed effectively by a Republican government • It began using military governors to govern it’s provinces. This was a natural place for ambitious leader to come to power. • As the Roman legions expanded, there were not enough citizens. • The Roman soldier changed from a volunteer Roman citizen, to a paid career soldier. • Who are you loyal to? Some distant Republic? Or a commander that brings you glory and riches? Legacy of Julius Caesar • After victory became Dictator-for-Life • Assassinated by political rivals • Rome descends into 20 years of civil war. • Republic is dead • Roman Empire is founded bring 200 years of peace and 400 years of domination • • • • Caesar, Legions, and the Late Republic Interactive Video Lecture Using the Life of Julius Caesar to understand the following themes: Roman Expansionism Decline of Republic – – – – • • • • • Video Breakdown Intro (0:00-2:18) Demagogues (3:18-6:03 Wealth and Corruption in Politics (6:04-8:35) Roman Expansionism (9:00-9:38) – – • How big is Rome? How did it get so big? The Showdown – Evolution of the Military (36:11-38:04) – – • • • Demagogues Wealth & Corruption Expansionism Evolution of Military Roman Citizenship/Allies/Clients Why were the soldiers ready to follow Caesar but not Pompey? Death of the Republic (38:04-39:51) Skip beheading of Pompey Legacy of Caesar and Beginning of Empire(42:32-44:30) – – What legacy did Julius Caesar leave? What changed under the early empire?