The Legislative Branch: The Organization of Congress
advertisement

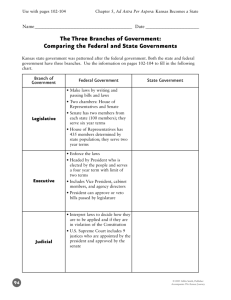
Bell Ringer • What age must one be to run for Congressperson? Senator? Congressperson – 25 years of age. Senate – 30 years of age. • What were Jim Crow Laws? The systematic practice of discriminating against and segregating Black people, especially as practiced in the American South from the end of Reconstruction to the mid-20th century. Fast Fact • The ZIP in Zip Code stands for “Zone Improvement Plan.” • What is the purpose of Zip Codes? They are used by the Post Office to deliver mail more efficiently. The Legislative Branch: The Organization of Congress Chapter 5 Congressional Membership Section 1 Congressional Organization • Bicameral Legislature: – House of Representatives – Senate • Congress’ purpose is to initiate and approve laws for the country. • Terms begin on January 3 of odd numbered years and last for two years. • Terms are divided into sessions, which last for one year and include time for holidays and vacations. The Current Session… How many members of the House of Representatives are there? • Plus 4 delegates in the House: – – – – – District of Columbia Guam American Samoa Virgin Islands NONE CAN VOTE! • Puerto Rico (resident commissioner). Membership in the House • Qualifications: – 25 years of age. – United States citizen for 7 years. – Legal resident of the state. • Terms of Office: – 2 year terms. – Elected in even-numbered years. • Salary and Benefits: – $174,000 (as of January 1, 2009) – Speaker of the House = $223,500 The First Census Membership in the House (cont.) • Representation and Reapportionment: – Based on census count. – Reapportionment - a reallotment of congressional seats in the United States on the basis of census results. – Reapportionment Act of 1929 set membership at 435. • Redistricting: – The redrawing of district lines based on reapportionment statistics. Membership in the House (cont.) • Abuses of redistricting power: – Creating congressional districts with very unequal populations. – Gerrymandering • Defined – the political party in control of the state government draws a district’s boundaries to gain an advantage in elections. • Term comes from Elbridge Gerry. – Packing – drawing the lines so they include as many of the opposing party’s voters as possible. – Cracking – dividing the opponent’s voters into other districts. Three Redistricting Cases • Baker v. Carr (1962). – Page 754. • Reynolds v. Sims (1964). – Page 764. • Wesberry v. Sanders (1964)Page 767. – “one-person, one vote” Membership in the Senate • Qualifications: – 30 years of age. – United States citizen for 9 years. – Legal resident of the state. • Terms of Office: – 6 year terms. – Elected in even-numbered years. – 1/3 elected every two years. • Salary and Benefits: – $174,000 (as of January 1, 2009) – President Pro Temp - $193,400. What prevents Congress from giving itself a pay raise? Membership in the Senate (cont.) • Senate Privileges: – Stationary – Franking Privileges • Postage for official business – Medical Care – Gymnasium – Allowances to pay for home-state offices and staff, trips home, and communication. – Tax deduction for maintaining two residences. A Huge Benefit… • Congresspersons have certain privileges that protect them in their official capacity. • Free from arrest “in all cases except treason, felony, and breach of the peace.” • Cannot be sued for anything they say on the House or Senate floor. – Does not apply to outside of chambers, news releases or newsletters. Congressional Judgment Calls • Exclusion – The refusal, by a majority vote, not to seat an elected member of Congress. • Expulsion – Only in most serious cases and by a 2/3 vote. • Censure – Formal disapproval of a member’s actions. – Reprimand published in official records. The House of Representatives And Lawmaking Section 2 Rules for Lawmaking • Article I, Section 5 orders each house to make their own rules. • Thomas Jefferson wrote the first rule book. • “It is much more material that there be a rule to go by, than what the rule is; that there may be a uniformity of proceeding in business not subject to the caprice [whims] of the Speaker or captiousness [criticism] of the members.” » Thomas Jefferson Rules of the House • Print the rules every two years. • Rules are aimed at defining the actions of the individual representatives while in the House Chambers and moving legislation along quickly. • Rule Committee serves as the “traffic officer”. Keeps the proper flow going. How??? • The House forms Committees, in which bills and/or legislation is assigned for further study and reporting. • Keeps the House, as a whole, from being overburdened with work. Responsibilities of House Leaders • Organizing and unifying party members. • Scheduling the work of the House. • Making certain that lawmakers are present for key floor votes. • Distributing and collecting information • Keeping the House in touch with the president. • Influencing lawmakers to support the policies of their political parties. House Leaders • Speaker of the House – Powerful position (elected by majority party). – Appoints some committee members. – Schedules bills for action. – Refers bills to proper House committee. Speaker of the House Rep. John Boehner, (OH) • Majority Leader – Help plan the party’s legislative program. – Steer important bills through. – Urge committee chairpersons to finish work on bills important to the party. Eric Cantor (VA) Majority Whip – – Whip - A member of a legislative body, such as the U.S. Congress charged by his or her party with enforcing party discipline and ensuring attendance. Assistant to the Majority leader. Kevin McCarthy (CA) Other Important People House Minority Leader Nancy Pelosi (CA) House Minority Whip Steny Hoyer (MD) How Bills are Scheduled… • Proposal is made… • Introduced in House and placed in hopper… • Speaker sends it to committee… • If it survives the committee it is placed on a calendar… • House votes and sends to Senate… House Calendars… • Union Calendar – bills dealing with money issues. • House Calendar – mostly public bills. • Private Calendar – bills that deal with individuals or places. • Consent Calendar – bills in which House has consented to debate out of order. • Discharge Calendar – used to petition bills be released from committee. The Senate Section 3 Informality • Smaller, more personal. • Ensure maximum freedom. • Unlimited debate (usually). The Senate Leaders President of the Senate • Is the Vice-President of the United States. • Mostly a “figure-head” • Limited abilities – cast a deciding vote. Joe Biden President Pro Tempore • Presides in absence of President of the Senate. • Usually most senior member of majority party. Daniel Inouye (D-HI) Majority and Minority Leaders • Most important officers in the Senate. • Job: steer the bills through!!! Harry Reid (NV) Majority Leader Mitch McConnell (KY) Minority Leader Majority and Minority Whips Richard Durbin (IL) Majority Whip Jon Kyl (AZ) Minority Whip The Filibuster… • Defined: Informal term for any attempt to block or delay Senate action on a bill or other matter by debating it at length, by offering numerous procedural motions, or by any other delaying or obstructive actions. • From the early 19th century Spanish and Portuguese pirates, "filibusteros", who held ships hostage for ransom. • Must stand and stick to subject for 3 hours, then it is free reign. • Can never stop or sit down. – Strom Thurmond hold’s the record. • 24 hours 18 minutes in 1957 over the Civil Rights Act. • Other famous filibusters’ – Huey Long – Wayne Morse Can a filibuster be broken? • Cloture - The only procedure by which the Senate can vote to place a time limit on consideration of a bill or other matter, and thereby overcome a filibuster. Under the cloture rule (Rule XXII), the Senate may limit consideration of a pending matter to 30 additional hours, but only by vote of three-fifths of the full Senate, normally 60 votes. Congressional Committees Section 4 Congressional Committees • Their purpose: – To help ease the workload by allowing Congressional members to divide their work. – They can become specialists. – To help select the bills that are most crucial to our government. – To hold public hearing and investigations. Kinds of Committees • Standing Committees – Permanent • Subcommittee – Specialized groups from the Standing Committees • Select Committees – Temporary – Study specialized interest • Joint Committees – Made up from both Houses • Conference Committees – Temporary – Formed when both Houses pass different versions of the same bill. Staff and Support Agencies Chapter 5, Section 5 Support Agencies • Library of Congress • Congressional Budget Office – Budget preparation • General Accounting Office – Watchdog of spending • Government Printing Office