7. Digestion and absorbtion of vitamins and minerals
advertisement

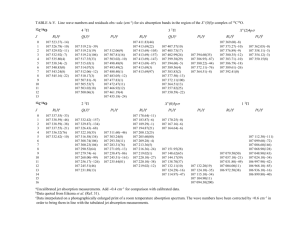
Digestion and Absorbtion of vitamins Cellular Biochemistry and metabolism 1 CLS 331 Dr. Samah Kotb Lecturer of Biochemistry 2015 DIGESTION & ABSORPTION OF VITAMINS & MINERALS Dr Samah Kotb 2 Dr Samah Kotb 3 Objectives In the end of the lecture, you should know 1. Definition of vitamins. 2. Digestion and absorption of vitamins and minerals. 3. Some important definitions in metabolism Vitamins are organic nutrients that are required in small quantities for a variety of biochemical functions and which generally cannot be synthesized in the body and must be supplied by the diet DIGESTION & ABSORPTION OF VITAMINS & MINERALS Dr Samah Kotb 6 Vitamins and minerals are released from food during digestion. Dr Samah Kotb 7 The fat-soluble vitamins are absorbed in the lipid micelles that result from fat digestion. Water-soluble vitamins and most mineral salts are absorbed from the small intestine either by active transport or by carrier-mediated diffusion. Dr Samah Kotb 8 Vitamin B12 absorption requires a specific transport protein, intrinsic factor. Calcium absorption is dependent on vitamin D. Zinc absorption probably requires a zinc-binding ligand secreted by the exocrine pancreas. Dr Samah Kotb 9 Dr Samah Kotb 10 Vitamin D regulates calcium homeostasis and is required for the intestinal absorption of calcium. Dr Samah Kotb 11 Synthesis of the intracellular calcium binding protein, calbindin, required for calcium absorption, is induced by vitamin D, which also affects the permeability of the mucosal cells to calcium, an effect that is rapid and independent of protein synthesis. Dr Samah Kotb 12 Phytic acid (inositol hexaphosphate) in cereals binds calcium in the intestinal lumen, preventing its absorption. Dr Samah Kotb 13 Other minerals, including zinc, are also chelated by phytate. Dr Samah Kotb 14 High concentrations of fatty acids in the intestinal lumen as a result of impaired fat absorption can also reduce calcium absorption by forming insoluble calcium salts; a high intake of oxalate can sometimes cause deficiency. Dr Samah Kotb 15 IRON ABSORPTION Dr Samah Kotb 16 Dr Samah Kotb 17 Iron Absorption It is limited & strictly controlled but is enhanced by vitamin C. Inorganic iron is accumulated in intestinal mucosal cells bound to an intracellular protein, ferritin. Once the ferritin in the cell is saturated with iron, no more can enter. Dr Samah Kotb 18 Iron Absorption The most effective compound is vitamin C, and while intakes of 40–60 mg of vitamin C per day are more than adequate to meet requirements. Dr Samah Kotb 19 Iron Absorption An intake of 25–50 mg of vitamin C per meal will enhance iron absorption, especially when iron salts are used to treat iron deficiency anemia. fructose also absorption. enhance Dr Samah Kotb iron 20 Iron Absorption Heme iron from meat is absorbed separately and is considerably more available than inorganic iron. However, the absorption of both inorganic and heme iron is impaired by calcium a glass of milk with a meal significantly reduces availability. Dr Samah Kotb 21 body mass index (BMI) The body mass index, defined weight in kilograms divided height in meters squared, commonly used as a way expressing relative obesity height. Dr Samah Kotb as by is of to 23 Basal metabolic rate (BMR) Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the energy expenditure by the body when at rest , but not asleep, under controlled conditions of thermal neutrality, measured at about 12 hours after the last meal, and depends on weight, age, and gender. Dr Samah Kotb 24 Basal metabolic rate (BMR) Body weight affects BMR because there is a greater amount of active tissue in a larger body. Dr Samah Kotb 25 Basal metabolic rate (BMR) The decrease in BMR with increasing age, even when body weight remains constant, is due to muscle tissue replacement by adipose tissue, which is metabolically much less active. Dr Samah Kotb 26 Basal metabolic rate (BMR) Similarly, women have a significantly lower BMR than do men of the same body weight because women’s bodies have proportionately more adipose tissue than men. Dr Samah Kotb 27 Basal metabolic rate (BMR) Undernutrition occurs in two extreme forms: marasmus- a form of severe malnutrition characterized by energy deficiency in adults and children and kwashiorkor is a form of severe protein -energy malnutrition characterized by edema in children. Dr Samah Kotb 28 Basal metabolic rate (BMR) Overnutrition from excess energy intake is associated with diseases such as obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis, cancer, and hypertension. Dr Samah Kotb 29 Dr Samah Kotb 30