Today we start Taxi Driver 1976 directed by Martin Scorcese starring
advertisement

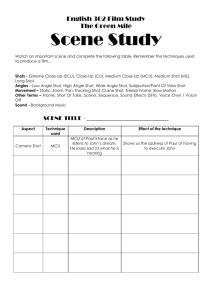
What do you think is the definitive scene from the Wizard of Oz? Follow the Yellow Brick Road We’re off to see the wizard She’s scary but remember the flying monkees? Poppies Somewhere over the rainbow There’s no place like home. A dream? I.B. Justify why it’s definitive When you do notes on a film write three paragraphs on the definitive scene. 1. Describe using Film vocabulary 2. Why it’s definitive a. tells same story as the film b. memorable c. a key turning point. 3. Give cultural, theoretical, and/or historical context Media Justify why it’s definitive When you do notes on a film write two paragraphs on the definitive scene. 1. Describe using Film vocabulary 2. Why it’s definitive a. tells same story as the film b. memorable c. a key turning point. d. a matter of opinion. Structure and Language of Film Vocabulary: shot, sequence, montage, types of shots, types of edits, types of camera movements Structure of a film • Shot – a simple run of the camera • Sequence– a group of shots depicting one action, or which seems to belong with or depend upon each other • Scene- A group of sequences or a group of shots which depict an event or occur in one place • Montage-a series of shots or sequences that are related by theme and not necessarily by time or place Shot • a simple run of the camera • The basic unit in film • Shot is to film as word is to text Types of shots long shot or wide shot medium shot close up extreme close up 2 shot over the shoulder shot Two shot Wide shot (w.s.) Description: Shows whole body or space. Purposes: Establish scene or setting, allow room for action. Description: Shows subject from waist up. Purposes: Allows connection with subject while providing room for gestures. Most frequently used shot. Medium Shot (m.s.) Description: Shows subject from waist up. Purposes: Allows connection with subject while providing room for gestures. Most frequently used shot. Close up (c.u.) Description: Shows enlarged view of part of subject. Purposes: Draws attention to details and adds emotion. CLOSE UP OF A FACE Extreme close up Medium shot (M.S.) of a person Another medium shot (M.S.) Long shot (L.S.) -to show action and/or perspective Aka “the establishing shot” Sequence- a group of shots depicting one action Scene- a series of shots in one setting or depicting an event Montage- series of shots connected by theme not necessarily by time and space Cut-the ending of a shot. If the cut is a jerky movement, which seems inconsistent with the next shot it’s called a jump cut Fade in or out-the image appears or disappears gradually. Often used as a division between scenes Dissolve-one image fades in while another fades out so that for a few seconds the two are super imposed An example of a dissolve edit Camera Movements • Pan-movement from side to side from a stationary position • Tilt- movement up or down from a stationary position • Tracking-camera itself moves to follow a moving object • Zoom-lens shortens or lengthens to make object closer or further • Dolly-moving camera in and out to make make subject appear larger or smaller in the frame Pan Description: Shows what's to the left or right of the screen. Purposes: Reveal setting, sweep across subject wider than screen, show relationship between two subjects . Tilt Description: Shows what's above or below the screen. Purposes: Reveal parts of vertical subject, useful for showing tall objects, show relationship between parts of a subject, can add suspense or surprise. Zoom Zoom Track or Truck Arc A variation on the tracking shot Dolly Camera Angles Normal camera angle is at the same level as the subject, but there could be cinematic reasons to move the camera up or down. High Angle—makes subject look small and vulnerable Low angle shot will tend to make subject look more powerful There are other reasons of course for high and low angle shots Bird’s eye angle Dutch Angle—used to communicate psychological imbalance among other things, now becoming overused perhaps. It’s actually a framing technique more than a camera angle Film noir—the femme fatale Film Noir—the cool loner Dark subject matter, shadowy photography, the white man’s blues SOUND Diegetic vs. Non Diegetic Diegetic = sound from the world of the film, that the characters can hear. Non Diegetic = sound, usually music and narration, that only the audience can hear Notes: it is possible for imagery to be non diegetic as well some directors as a matter of style have blurred the lines in diegeticism Establishing Shot from Truman’s P.O.V. Establishing Shot from Truman Mis en scene French for put in the scene Mis en scene Deep Focus 2nd Example Citizen Kane (1941) Orson Welles • • • One sentence synopsis 2 Paragraphs on Definitive Scene Questions 1. Is this the greatest movie of all time? Why or why not? 2. Explain some of the innovative film techniques in this film. 3. Describe how Kane is a tragic hero in the vein of Macbeth & Oedipus Do you know these script terms? EXT. INT. V.O. P.O.V Transitions DISSOLVE TO: CUT TO: FADE IN