Minerals

107 Minerals Minerals
11/16/2015
EQ: How can comparing and contrasting help me to understand how matter physically or chemically changes?
Application:
Minerals WS
Starter:
108
11/16/2015
Connection:
Name some things that you have that are made of minerals
Exit : Summarize notes
Practice:
Notes : minerals
Starter
Gold
67.5
20 ml
1000 grams15
Because it expands when it freezes
Agenda
1. Starter
2. Minerals Notes
3.Minerals Ws
4. Exit
Table of Contents
Date Lecture/ Activity/ Lab Page
10/27 Writing Chemical Formulas 81-82
10/28 Ionic Bonding 83-84
10/29 ChemicalEquations and the Conservation of Mass 85-86
10/30 Balancing Act 87-88
11/02 Balancing Chemical Equations Activity 89-90
91-92 11/03 See Saw Poster
11/4 Law of Conservation of Mass Lab 93-94
11/5 Balancing Equations Review 95-96
11/6 Physical and Chemical Changes Notes 97-98
11/9 Physical and Chemical Properties Lab 99-100
11/10 Balancing Chemical Equations Writing 101-102
11/12 Signs of a Chemical change Video Quiz 103-104
11/13 Physical and Chemical Ws 105-106
11/16 Minerals 107-108
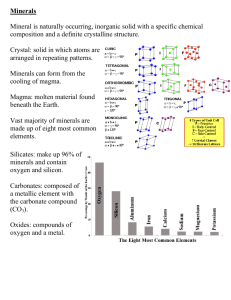
Minerals
What is a Mineral?
It must be inorganic – not formed from living things.
It must be found naturally.
It must have a definite chemical composition.
It must be formed of crystals.(# of faces and angles)
Must be a solid
Types of Minerals
Silicates
–
Minerals that contain silicon and oxygen
– 90% of the earth’s crust are made of these type of minerals
–
Ex. Quartz, mica
Non-silicates
–
Minerals that contain no silicon and oxygen
–
Ex. Halite, calcite
Properties of Minerals
Color
–
The color of a mineral is not the best way to identify it.
–
Color depends on many factors and can change from sample to sample .
Mineral Properties
Luster
–
Metallic luster; shiny, looks like a metal (gold, silver, copper)
–
Sub-metallic luster; dull metal finish(lead, hematite)
–
Non-metallic; waxy, glassy, dull, pearly(quartz, calcite, sulfur)
Types of Luster
Metallic
Sub Metallic
Non-Metallic
Mineral Properties
Streak
– color of a mineral in powdered form
– the streak is always the same for a mineral no matter what the surface color is.
– streak plates are used to determine the color
– some minerals leave no streak
Mineral Properties
Cleavage
–
The tendency of a mineral to break along specific planes.
Fracture
–
When a mineral breaks with no set planes.
Mineral Properties
Density
–
Each mineral has a specific density
–
Density is the amount of matter in a given space
–
The more matter in a smaller space the higher the density.
–
D=m/v
Mineral Properties
Hardness
–
Hardness is the ability of a mineral to resist being scratched.
–
Mohs scale of hardness developed by German mineralogist Friedrich
Mohs organizes minerals by hardness.
Mohs Scale of Hardness in order from softest to hardest
1 – Talc
2 – Gypsum
3 – Calcite
Mohs Scale of Hardness
4 – Fluorite
5 – Apatite
6 – Orthoclase
Mohs Scale of Hardness
7 – Quartz
8 – Topaz
9 – Corundum
10 – Diamond
Field Hardness Test
1
– easily scratched by fingernail
2
– scratched by fingernail
3
– easily scratched by nail, won’t scratch a copper penny
5
– Hard to scratch with a nail; won’t scratch glass
7
– scratches glass
8-10
– scratches steel
Special Properties of Some minerals
Fluorescence (glows)
Chemical reaction (produces bubbles)
Radioactivity (gives off energy)
Optical properties (can see through them)
Magnetism (attracts things)
Taste(You should never use taste to identify an unknown mineral)
Ore
Is a combination of minerals that has enough of one type of metal or mineral that it can be extracted.
–
Example: Galena is an ore for Lead
107 Minerals Minerals
11/16/2015
EQ: How can comparing and contrasting help me to understand how matter physically or chemically changes?
Application:
Minerals WS
Starter:
108
11/16/2015
Connection:
Name some things that you have that are made of minerals
Exit : Summarize notes
Practice:
Notes : minerals