PPT Accuracy, Precision, and Percent Error
advertisement

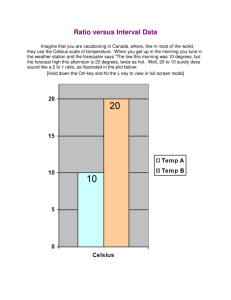
Accuracy, Precision, Percent Error, & Temperature Scales Accuracy • How close a measured value is to an accepted value -Accuracy can be determined by just on measurement -Depends on the quality of the measuring device The density of water is 1.00 g/mL 1.03 .98 1.01 1.00 .99 Precision •How close a series of measurements are to one another -Precision is determined by more than one measurement -Depends on the skill of the person measuring The density of water is 1.00 g/mL .89 .87 .89 .88 .88 Accuracy or Precision? The boiling point of water is 100°C The atomic mass of carbon is 12 amu’s 89°C 11.95 amu’s 91°C 12.01 amu’s 90°C 11.97 amu’s 91°C 11.98 amu’s 80°C 12.03 amu’s Accuracy or Precision? The electronegativity of Fluorine is 3.8 The evaporation temperature of isopropyl alcohol is 83°C 2.1 91°C 1.6 89°C 3.5 90°C 2.8 89°C 4.2 90°C Percent Error • Accepted Value (also known as theoretical value) - a quantity used by general agreement of the scientific community - “what you are supposed to get” • Experimental Value (also known as the actual value) - a quantitative value measured during an experiment - “what you got” Percent Error Error = the difference between the accepted value and the experimental value Percent Error = the percent that a measured value differs from an accepted value % Error = (What you got) – (What you were supposed to get) x 100 (What you were supposed to get) Percent Error Practice 1. The boiling point of water is 100°C. During an experiment, water came to a boil at 97°C according to the thermometer that was being used. What is the percent error of the thermometer? 2. An experiment was performed to determine the density of water. The results of the experiment showed that water had a density of 1.15 g/mL. What was the percent error in this experiment? Percent Error Practice 3. An experiment was conducted to find the mass of one mole of carbon atoms. The results of the experiment showed that a mole of carbon atoms had a mass of 15.78 g. The accepted value of a mole of carbon atoms is 16.00 grams. What is the percent error in this experiment? 4. An experiment performed to determine the density of lead yields a value of 10.95 g/cm3. The accepted value for the density of lead is 11.342 g/cm3. Find the percent error. Percent Error Practice 5. Find the percent error in a measurement of the boiling point of bromine if the laboratory figure is 40.6°C and the accepted value is 59.35°C. Temperature Scales Relationship between the Fahrenheit, Celsius, and Kelvin Scales The Fahrenheit Scale This is the temperature scale that you are probably most familiar with, living in the United States. When you listen to the weather report on TV, the Fahrenheit scale is used. The thermometers that you have in your house, for use as; swimming pools, cooking, bath tubs, or reading body temperature, are all likely to be in Fahrenheit. In Canada and most other countries, the news will report the temperature on the Celsius Scale. The Celsius Scale The Celsius scale is commonly used for scientific work. The thermometers we use in our lab are marked with the Celsius scale. The Celsius scale is also called the Centigrade scale because it was designed in such a way that there are 100 units or degrees between the freezing point and boiling point of water. One of the limitations of the Celsius scale is that negative temperatures are very common. Since temperature is a measure of the kinetic energy of molecules, this would also suggest that it is possible to have less than zero energy. This is why the Kelvin scale was necessary. The Kelvin Scale The International System of Measurements (SI) uses the Kelvin scale for measuring temperature. The Kelvin scale is based on the concept of absolute zero, the theoretical temperature at which molecules would have zero kinetic energy. Absolute zero, which is about 273.15°C, is set at zero on the Kelvin scale. A Comparison of Temperature Scales Set Points Fahrenheit Celsius Kelvin Water Boils 212 100 373 Body Temperature 98.6 37 310 Water Freezes 32 0 273 Absolute Zero -460 -273 0 Temperature Conversion Formulas Conversion Formula Example Celsius to Kelvin K = C + 273 21°C = 294K Kelvin to Celsius C = K – 273 313K = 40°C C =(F-32) x 5/9 89°F = 31.7°C Celsius to Fahrenheit F =(Cx9/5) + 32 50°C = 122°F Fahrenheit to Celsius

![Temperature Notes [9/22/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006907012_1-3fc2d93efdacd086a05519765259a482-300x300.png)