Notes from today's class Powerpoint
advertisement

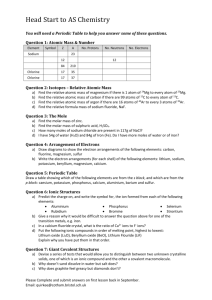
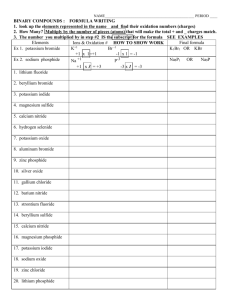
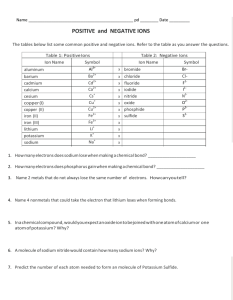
Sponge Give the ionic compound for the following: 1. K+ + O22. Sr2+ + Cl3. Na+ + F4. Fe3+ + Cl- IONIC BONDING PART 2 Chemistry Unit 3, Day 2 Properties of Ionic Compounds • Crystal Lattice Structure • Each positive ion is surrounded by negatives • Each negative ion is surrounded by positives • Strong Bonds • Require large amounts of energy to break apart • High melting points • High boiling points • Hard, Rigid, Brittle solids Strength of the Bond • Energy required to separate one mole of the ions of an ionic compound is referred to as Lattice Energy • The more negative the energy, the stronger the force of attraction, the harder to separate ions Compound Lattice Energy (kJ/mol) KBr -671 NaBr -732 AgCl -910 SrCl2 -2142 RECALL: Writing Formula Units • The formula unit (product) • Li+ and O2- must be neutral (zero charge) • Add the ions involved • The cation is written first, then the anion +1 -2 = -1 charge, need + • Li+ + O2- + Li+ +1 -2 +1 = 0 charge, check! • Li2O Oxidation Numbers • The charge on the ion is called its oxidation number or oxidation state • Atoms can have more than one oxidation number Naming Monatomic Ionic Compounds • Monatomic- an ion made up of one type of atom (Li+, Na+, O2-, etc.) • The cation is given its full name • The anion uses the suffix –ide • For example, Li+ and O2• Lithium Oxide • For example, Na+ and Cl• Sodium Chloride Think-Pair-Share: complete the chart by creating the formula unit. Leave room to also include the name of the compound. Na+ F- O2- N3- S2- 1 NaF 2 Na2O 3 Na N 3 4 Na2S Sodium Fluoride Li+ Mg2+ Be2+ 5 LiF Lithium Fluoride 9 MgF2 Magnesium Fluoride 13 BeF2 Beryllium Fluoride Sodium Oxide 6 Li2O Lithium Oxide 10 MgO Magnesium Oxide 14 BeO Beryllium Oxide Sodium Sulfide Sodium Nitride 7 Li3N Lithium Nitride 11 Mg3N2 Magnesium Nitride 15 Be3N2 Beryllium Nitride 8 Li2S Lithium Sulfide 12 MgS Magnesium Sulfide 16 BeS Beryllium Sulfide Guided Practice – reading charts Compound KI Lattice Energy (kJ/mol) -632 Melting Point (˚C) 681 KF -808 858 • Which is a stronger bond? Why? • KF, more negative energy • Which has a higher melting point? • KF • What is the relationship between ionic bond strength and melting point? • The stronger the bond, the higher the melting point!