HST_Overview
advertisement

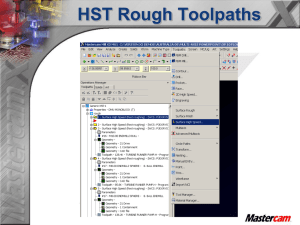
HST Toolpaths Enhancements Summary 10 HST Toolpaths Smooth Entry and Exit Motions Reduced Retracts Toolholder Definition and Collision Check Rest Machining and Slope Angles in HST Toolpaths Tool Inspection Toolpath Fillets What’s different with HST Toolpaths New Parameter Tabs Operations can now be copied with current settings and then change toolpath type (Core Roughing to a Waterline toolpath) What’s different with HST Toolpaths New Parameter Tabs When changing toolpath type any parameters that can be kept from the copied operation are kept. What’s different with HST Toolpaths Quick View Settings Quick View Setting keep info in sight through all parameter tabs so there’s no need to change tabs to get information. Toolpaths Area Clearance Area Clearance: Is a roughing toolpath for clearing out material in cavities, cutting from inside out. Toolpaths Area Clearance Notice that the toolpath starts from the inside out Toolpaths Core Roughing Core Roughing: Is a roughing toolpath for clearing out material that changes strategies from outside in for bosses and inside out for cavities. Toolpaths Core Roughing Notice the tool starts on the inside and works its way out for the cavity Toolpaths Core Roughing Rapid Cut direction Notice the tool starts on the outside and works its way in on bosses. Toolpaths Core Roughing Backplot of tool cutting outside and working its way in. Cut Parameters Note: The cut parameters will change based on the toolpath type. When possible the same settings will be brought into the new toolpath type. Cut Parameters Turn on the “Add cuts” option Stepdown – Determines the Z spacing between adjacent cutting passes Add cuts- Activates the adaptive stepdown feature, which add cuts at the shallow areas of the profile so that the toolpath does not have excessively large horizontal spacing between cutting passes Min stepdown – Specifies the minimum stepdown value when Add cuts is activated. Passes will be no less than this distance from each other – in the z axis Cut Parameters Max profile stepover – Determines the maximum change in the surface profiles for two adjacent cutting passes. This represents the maximum value of the shortest horizontal distance between adjacent points on the two profiles. Max profile stepover – is the thickness of the scallop. If the thickness exceeds the .250 setting then a z cut is added to bring the thickness under the .250 setting. Cut Parameters Notice the scallop thickness Cut Parameters Max profile stepover Cut Parameters Turn on the “Smoothing” option Smoothing – Replaces sharp corners with an arc for faster and smoother transitions in the tool direction. Cut Parameters Max Radius – Enter the radius of the largest arc that you will allow Mastercam to insert to replace the corner. Larger arcs will result in a smoother toolpath but with greater deviation from the originally programmed toolpath Profile Tolerance – The maximum distance that the outermost profile of the smoothed toolpath that will deviate from the original toolpath Offset tolerance – This is the same measurement as the profile tolerance but is applied to all of the profiles except the outermost one. This lets you maintain different tolerances for the subsequent profiles. Cut Parameters Possible to leave different amounts of stock for floor and wall surfaces. Note: Can’t leave less stock on the walls than the floor Cut Parameters Toolpaths Rest Roughing Rest roughing toolpath is used when you want to calculate the cutting passes from the stock left over from one or more previous roughing operations, similar to Restmill Toolpaths Rest Roughing Rest Roughing Rest Material Rest Material All previous operations - Calculates the remaining stock using all operations in the Toolpath Manager. This method determines the areas of stock where the tool did not go. One other operation - Calculates the remaining stock using all operations in the Toolpath Manager. This method determines the areas of stock where the tool did not go. Roughing tool - Calculates the remaining stock based on the diameter and corner radius of a tool. Cad file – Uses an STL file to calculate where the tool can remove material Rest Material Lists the current operations in the operation manager Rest Material Stock resolution - Use a smaller value to tighten up the stock model and create a smoother restmill toolpath. Use a larger value to loosen the stock model and create a faster but rougher restmill toolpath. Rest Material Adjustments to remaining stock Use remaining stock as computed – No adjustment to the stock model Adjust remaining stock to ignore small cusps – Use this setting to set the adjustment distance to reduce the stock model, this setting will find less material to machine Adjust remaining stock to mill small cusps – Use this setting to set the adjustment distance to increase the stock model, this setting will find more material to machine Rest Material Adjustments to remaining stock Adjustment distance - Enter a value to expand or reduce the calculated stock model Rest Material Roughing tool is a theoretical calculation. Note: With the “Skip pocket” setting its possible to have the tool plunge into material with the “Roughing Tool” setting Rest Material An STL file can be used to calculate remaining stock. Verifying a toolpath and then saving the stock as an STL may give a more accurate results. Rest Material Rest Material machining in finish toolpaths Rest Material Rest Material machining in finish toolpaths All Finish toolpaths except Horizontal Area have a Rest Material option Rest Material Toolpath without Rest Material off Rest Material Toolpath with Rest Passes on Rest Passes: The toolpath is calculated as a normal toolpath and only the areas that the Roughing Tool can’t reach are kept. Toolpaths Waterline Waterline is a constant Z finish toolpath (similar to contour) Toolpaths Waterline Toolpaths Scallop Scallop is a 3D toolpath Toolpaths Scallop Notice the smooth entry and rapid motion Toolpaths Horizontal Area Horizontal is a finish toolpath for flat surfaces Toolpaths Horizontal Area Toolpaths Raster Raster is a finish toolpath that cuts in one direction (like parallel) Toolpaths Raster Toolpaths Pencil Pencil is a finish toolpath for cleaning up radii Toolpaths Pencil Toolpath motion Toolpaths Spiral Spiral toolpath is used to create cutting passes where the tool feeds into the part in a continuous spiral motion. Toolpaths Spiral Toolpaths Radial Radial creates cutting passes that radiate outwards from a central point, used mostly on round parts. Toolpaths Radial What’s different with HST Toolpaths Smooth Stepovers between passes are automatically generated Constant Z toolpath (Core Roughing) What’s different with HST Toolpaths Stepovers Between Passes Constant Z toolpath What’s different with HST Toolpaths Smooth Stepdowns are automatically generated Between Z cuts ` Top View Constant Z toolpath (waterline) What’s different with HST Toolpaths Step downs Between Z cuts ` Front View Constant Z toolpath (waterline) What’s different with HST Toolpaths Stepdowns Between Z cuts ` Constant Z toolpath (waterline) Tool Tool Inspection Tool Tool Inspection When toolpath reaches the liner distance or time the tool will retract Note: The time is based on the feedrate Holder Toolholder Definition & Collision Protection 3 Toolholder Libraries www.CommandTool.com Holder Toolholder Definition & Collision Protection Over 50 pre-defined tool holders Holder Toolholder Definition & Collision Protection Holder Toolpath without Collision Check Holder Toolpath with Collision Check Front View The toolpath only cuts where the tool can reach Holder Toolpath without Collision Check Toolpath with Collision Check Front View Cut Parameters Option to leave different amounts of stock on the walls and floors in all HST toolpaths Cut Parameters Scallop Each toolpath has its own settings, so a Raster toolpath with have different parameters Cut Parameters Raster Down Milling: Helps inserted cutters keep the inserts in the holders UP Milling: Better finish in soft steels Cut Parameters Raster Scallop Height Calculator was added to Raster and Pencil toolpaths Cut Parameters Pencil Cut Parameters Pencil Unlimited Step Over Cut Parameters Pencil Unlimited Step Over First part of toolpath Unlimited Step Over: The toolpath will first cut the outside passes then finish the pencil trace working towards the corner. Cut Parameters Pencil Unlimited Step Over Second section of toolpath Cut Parameters Pencil Unlimited Step Over 3rd section of toolpath 4th section of toolpath Cut Parameters Pencil Unlimited Step Over Completed Toolpath Transitions Two Entry Options, Helix and Profile Transitions Smooth Entry and Exit Motion Helix Entry Transitions Smooth Entry and Exit Motion Transitions Smooth Entry and Exit Motion Radius value is calculated automatically from the cutter diameter Helical Entry Transitions If the helix can’t fit then the profile ramp is automatically used Transitions Core Roughing Ramp Entry Helical Entry Two entry methods with same setting Transitions Smooth Entry and Exit Motion Since the helix couldn’t fit, the profile entry is being used Transitions Smooth Entry and Exit Motion Transitions Smooth Entry and Exit Motion “Skip pockets smaller than” this solves the problem where a pocket is large enough to accommodate the tool, but the entry move is so compressed that the tool is effectively plunging into the part. Transitions Smooth Entry and Exit Motion Toolpath with no “Skip pockets smaller than” Transitions Smooth Entry and Exit Motion Toolpath with “Skip pockets set to .600” Steep / Shallow Steep / Shallow Defined Slope Angle for all High Speed Toolpaths Angle options is used to only create cutting passes on those areas of the part that fall in the angle setting. Steep / Shallow Slope Angle Slope Angle Note: Notice that entire part is being cut Steep / Shallow Slope Angle The cutting passes are being restricted to the angle settings Linking Parameters Linking Parameters: Control the toolpaths air cuts. Linking Parameters Waterline Linking Parameters Minimum distance Retract Minimum Distance: The cutter takes a direct route from one pass to another clearing the surface by the part clearance distance Linking Parameters Minimum distance Retract Minimum Distance: The cutter takes a direct route from one pass to another clearing the surface by the part clearance. Linking Parameters Part Clearance Linking Parameters Minimum Distance setting Linking Parameters Leads Finish Waterline Linking Parameters Smooth Entry and Exit Motion Front View Horizontal arc entry .250 Setting Linking Parameters Smooth Entry and Exit Motion Horizontal arc exit Top View Arc filter / Tolerance Toolpath Fillets Toolpath Fillets: Theoretical fillets are created in sharp corners to keep the tool motion smooth and allow flat cutters to be used in roughing where fillets weren’t created in the model. Arc filter / Tolerance Toolpath Fillets No Toolpath Fillets used Notice the sharp corner Arc filter / Tolerance Toolpath Fillets Notice the transition Arc filter / Tolerance Toolpath Fillets Notice the sharp corner Arc filter / Tolerance Toolpath Fillets Notice the stock that is left Arc filter / Tolerance Toolpath Fillets Notice the stock that is left Tools Supported All Toolpaths Support 3 +2 Axis Cutters Flat Ball Bullnose Taper Flat Ball Enhancements Summary of what’s in HST Toolpaths Smooth Entry and Exit Motions Reduced Retracts and Rapid Motion Toolholder Definition and Collision Check Rest Passes and Slope Angles in all HST Toolpaths Tool Inspection Toolpath Fillets