Understanding, Creating, and Implementing Contracts
advertisement

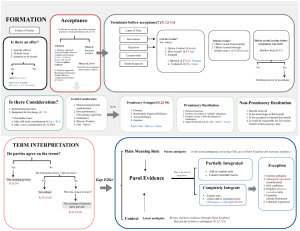
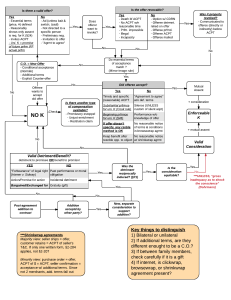
Week 2 Agreement Invalid Assent Agreement The manifestation (or indication) of mutual assent by the parties. Objective Standard An objective standard is used to determine whether parties had a “meeting of the minds”. Looks to what a reasonable person would believe, based on the circumstances. Offer An indication of current willingness to enter into a contract, communicated by the person making the offer. Consideration Something promised, given, refrained-from, or done that has the effect of making an agreement a legally enforceable contract. Open Terms Under the UCC a contract may form despite a failure to specify certain terms Also called “gap-filling” Revocation Under common law, an offer that is not, in itself, a contract, can be revoked at any time before acceptance (unless promissory estoppel applies). Firm Offer A UCC rule under which no consideration is required to hold offer open between merchants. Rejection Offeree terminates offer If an offeree rejects an offer, the rejection terminates the offer and any subsequent attempt to accept is an offer. Counter Offer Offeree responds to offer with an offer. Acceptance Acceptance is compliance or agreement by one party with the terms and of another’s offer so that a contract forms. Implied Acceptance Normally, “pure” silence does not operate as acceptance Acceptance can be implied based on behavior, partial performance, or past dealings Mailbox Rule Common law rule Acceptance occurs when dispatched by appropriate means Mirror Image Rule Common law rule Acceptance must be identical to offer Battle-of-the-Forms Rule UCC rule Overrides mirror image rule when merchants use forms Invalid Agreements When does offer plus acceptance not equal a contract? Apparent agreements may be invalid because of duress, fraud, mistake, or misrepresentation Fraud Fraud is a false statement of material fact, made with intent to deceive, on which another reasonably relies, to his or her detriment. Misrepresentation Misrepresentation is a false statement made without intent to deceive, upon which a party justifiably relies to his or her detriment. Mistake The concept of mistake is generally limited to mutual mistakes about the “basic assumptions” of fact in cases where the parties have not specifically allocated risk with respect to assumptions. Duress Duress is a wrongful threat, intended to induce action by the other party. Undue Influence A special relationship can give one person undue influence over another. If the dominant party takes advantage of that position in entering a contract, the agreement may be voidable. Often, undue influence involves a fiduciary relationship —a relationship in which one party is obliged to act in the best interest of the other party. Unconscionable A contract that is so unreasonable that it is “shocking”.