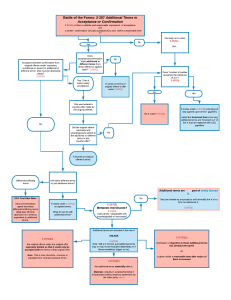
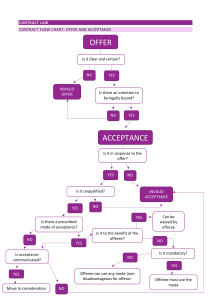
FORMATION Acceptance Terminate before acceptance? (R.2d 36) If offer do not specify, then either returned promise or return performance (R.2d 32) Is there a Promise Lapse of Time Unilateral Bilateral a. Majority approach: Returned does not bound offeree to promise complete performance (Cook v. Coldwell Banker) (R.2d 45) Create an option Silence (R.2d 69) contract Generally not acceptance unless (check outline) b. Minority approach: 1. Specific offeree 2. Definite terms 3. Intention to be bound No Can he revoke? Yes, unless: Revocation Is there an offer? Yes Rejection 1. Option Contract (Kmoch) 2. Mere recital* (§ 87(1)a) 3. Estoppel Counter-offer Did he revoke? 1. Offeror acted inconsistently 2. Offeree learned through reliable source (§ 43) (Kmoch) Ads* (Lonergan) Is there Consideration? 1. Benefit/DetrimentTest 2. Bargained-for Exchange (R. 71) * Charitable Cause a. Maj: still need consideration (King v. BU) b. Min: waive consideration (R.2d 90b) Mailbox Rule (R.63) i. Bilateral (§ 87(2)) - Drennan ii. Unilateral (§ 45) - Cook Death/Incapacity No Beginning performance bound offeree to complete performance (R.2d 62) unless it is rewards (Sateriele v. R.J. Reynolds) Did he revoke in time before acceptance was sent? Yes Terminate power of acceptance Invalid Consideration 1. Sham/nominal/recital consideration 2. Past performance / Preexisting Legal Duty 3. Inadequacy 4. Illusory Promise 5. Gift / "prize" Promissory Estoppel (R.2d 90) If not 1. Promise 2. Reasonable Expected Reliance 3. Actual Reliance 4. Injustice Promissory Restitution Non-Promissory Restitution 1. Renewed promise 2. Promise to perform a voidable obligation 3. Promise to pay a debt discharged by bankruptcy 4. Material benefit rule (R. 86) - Webb v. Gowin Pop's Cone / Harvey v. Dow 1. Benefit received 2. D has knowledge of that benefit 3. D has accepted or retained that benefit 4. It would be inequitable for D to retain benefit without paying value TERM INTERPRETATION Plain Meaning Rule Do parties agree on the terms? Patent ambiguity Is the word ambiguous on its face?Yes, go to Parol Evidence for extrinsic evidence Partially Integrated Yes No Do both parties know / did not know? That meaning governs R.2d 201 Yes No Gap Filler Parol Evidence What is the level of integration? Add or explain only Cannot contradict terms Completely Integrate No contract Who has reason to know? Explain only Cannot add or contradict terms (Thompson v. Libby) (R.2d 215) R.2d 201(3) The meaning of innocent party prevails R.2d 201(2) Context Latent ambiguity Review extrinsic evidence through Parol Evidence then decide if there is ambiguity (R.2d 210) Exception 1. Explain ambiguity 2. Subsequent agreement (modification) 3. Oral conditions 4. Illegality (fraud in execution only) 5. Equitable remedy/Restitution 6. Collateral Agreement TERM CONSTRUCTION determine legal effects independent of parties' assent Covenant of Good Faith and Fair Dealing (R.2d 205) / UCC 1-304 Agreement to Agree (what if there are missing terms?) Different/Additional terms from offer to acceptance Appropriateness of a party's Minority Majority R.2d 27 / Quake Constructionv.AA (Walker v. Keith) Business Efficacy Finding a breach / bad exercise of discretion (reasonable effort/obligation) faith when no express term (Morin Bldg. v. Baystone) (Wood v. Lucy, Lady McDuff) has been violated (Locke v. Warner Bros.) Battle of the Form Min: subjective Yes Gap Filler UCC Mirror Image Rule (Seidenberg) Maj: objective Common Law No No Contract Contract Term Rejection / Counter-offer Parol Evidence If both parties performed to reveal parties' expectation Last Shot Rule Changed Circumstance DEFENSES TO CONTRACT FORMATION Capacity Duress (R.2d 175(1)) 1. Improper/wrongful/coercive acts 2. Inducing involuntary assent 3. Circumstances permitting no alternative Is the contract "within" the statute? No Yes Unexpected and important event that upset "basic assumption?" Yes No Yes Undue Influence (R.2d 177) No The party seeking relief bears the risk? 1. Unfair persuasion 2. Domination; OR 3. Confidential/special relationship Statute of Fraud Yes Is the contract written and signed by D? R.2d 132 - 133 Yes No Is K in one document? Yes No Are exceptions available? Part performance (land only) Yes No Beaver v. Brumlow R.2d 129 Promissory Estoppel (general issue) Rice v. Alaska Dem. Others Impossibility Modification More demanding than R.2d 90 Event makes that party’s performance impracticable? Event substantially destroy value of other party’s performance? Nondisclosure (R.2d 161) 1. 2. 3. 4. Impracticability Is there a nondisclosure? Of material fact or fraudulent in nature? Justifiable reliance That induces recipient's assent Unconscionability (R.2d 208) Parol Evidence Crabtree v. Elizabeth 1. Fraudulent OR material in character 2. Justifiable reliance 3. That induces recipient's assent R.2d 139 Seeking specific performance No Fraud / Misrepresentation No Yes Are pieces refer to same transaction? Satisfied SofF Was event fault of party seeking relief? 1. Procedural unconscionability 2. Substantive unconscionability Unilateral Mistake (R.2d 153, 154) Mistake 1. A unilateral mistake 2. About "basic assumption" of contract 3. "Material effect" on mistaken party 4. The adversely affected party was not assigned the risk 5. Enforcement would be unconscionable OR non-mistaken party had reason to know of the mistake Frustration of Purpose Mutual Mistake (R.2d 152, 154) 1. 2. 3. 4. A mutual mistake About "basic assumption" of contract "Material effect" on exchange of performance Who bears the risk? Is there a condition to a party’s performance ripen in the contract? BREACH No Yes Is there Anticipatory Repudiation? Is the condition unambiguous? (i.e. contains "if") No Yes Yes No Has it been rescinded in time? (R.2d 256) Truman&Sons v. Schupf Constructive condition Express condition Yes No Has the condition been discharged or excused? Contract defenses Disproportionate forfeiture Waiver Prevention No Rest 234(2): if performance cannot be rendered at the same time, the performance requiring the longer period of time must be rendered before the other performance. a. Simultaneous performance: sale of goods / land b. Longer performance goes first: construction / employment Yes BREACH Constructive condition / Anticipatory Breach Express condition Is it material? (R.2d 241) Total Breach (R.2d 242) Non-breaching party can terminate Yes No 1) Would the delay prevent the making of substitute arrangements by the nonbreaching party? / 2) Does the contract emphasize the importance of performing without delay? / 3) Is the breacher's conduct unreasonable? Yes Non-breaching party can suspend performance (R.2d 242) Non-breaching party terminate. Can seek both Reliance Damage (past damages) & Expectation Damages (future damages) (R.2d 236(1)) Sackett v. Spindler In Partial Breach, only include [loss value + other loss] when calculating Expectation Damages Jacob&Young v. Kent No Total Breach Material Breach (R.2d 241) Partial Breach (R.2d 235) Non-breaching party must continue performing. Can only seek Reliance Damage (actual harm resulted to date) (R.2d 243(4)) In Total Breach, when the contract is terminated, must include [cost avoided - loss avoided] when calculating Expectation Damages Acceptance Same Term Different / Additional Term Does it fall under UCC? Battle of the Form (UCC 2-207) Proceed to next step analysis Yes No Is acceptance expressly condition on add-terms? Yes No Common Law Mirror Image Rule A contract is formed There is no contract. Look to Conduct (2-207(3)) 2-207(1) Look to conduct to see if the terms are consistent with the intention of having a contract when both parties intend so Are terms different or additional? Different Inclusive Evaluate but usually excluded Additional (2-207(2)) Exclusive Knock-out New terms are proposal UCC fills gap based on common practice Non-merchant Merchant Additional terms are proposal Do the additional terms: The offer expressly limits acceptance to the terms of the offer Materially alter the offer Objection raised to the additional terms Yes Proposals that can be accepted/rejected No New terms become part of the contract Electronic T&C Who is the offeror? Buyer Seller Easterbrook approach Klocek approach Offer/Invite acceptance: click to buy / place an order Offer Invite acceptance: shipping with all the terms Offer 2-204 Does consumer have an opportunity to review? shipping / accept payment: seller 's acceptance Acceptance Yes Does consumer expressly consent to ADDITIONAL TERMS (proposals)? Yes No Contract Proposals New proposals Acceptance 2-207 No Does consumer keep after specified time? Yes No Contract No contract No contract DAMAGES Limitations to Recovery 1. Causation 2. Foreseeability Hadley 3. Certainty Floralfax v. GTE 4. When Justice so requires 5. Contract allocation of risk 6. Losing contract AA v. Schectman / Handicapped Children J&Y v. Kent Wartzman v. Hightower Walser v. Toyota US Coastal Steel v. Blair Specific Performance 1. Adequacy of remedy at law 2. Lack suitable substitute 3. Collectability 4. Definiteness 5. Hardship in supervision City Stores v. Ammerman