Contracts PPT
advertisement

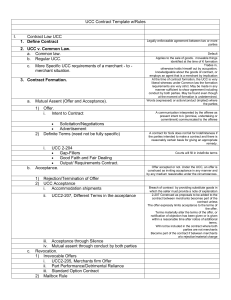
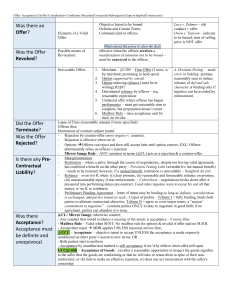
An Overview of Contracts By Tom Weygandt Contracts - Today’s Lesson What is a contract and how is it made? What must be included in a contract? What are the consequences of breaching a contract? Are there any special rules a farmer should follow? Other related issues. What Is a Contract? A legally enforceable agreement between two or more persons which creates an obligation to do or not to do something Promises or sets of promises Legal remedy for breach Bad deals are OK May not be against public policy or illegal Some Types of Contracts Sale of goods Sale of land Exculpatory agreements Insurance Requirement Unilateral / bilateral Under seal Production Open-end Negotiable instruments Employment / non-compete Prenuptial Adhesion Input / output Glossary Acceptance Performance Assignor/assignee Privity Breach Remedy Cognovit judgment Repudiation Consideration Rescission Contractor Severability Damages Unconscionable Mutuality Accord & satisfaction Elements of a Contract Offer Acceptance Capacity Consideration Legality Offer A manifestation of intent to contract by A reasonable person Serious intent Complete and definite terms Offer – complete and definite terms Parties Subject matter Price Time for performance Communication Offer – UCC exceptions Allows some terms to be omitted Policy is to encourage free flow of trade Course of dealings Course of performance Trade usage Offer - Revocation Termination by offeror statement or conduct offeree must be aware Lapse of time Revocation sent via mail is not effective until received Offer - Always Irrevocable Options contract promise to keep offer open must have consideration Merchant under UCC rules Detrimental reliance Unilateral if performance has begun Acceptance Agreement to the terms of the offer By a person who knows of the offer By the person to whom it is made Acceptance - Methods Completion of performance Promise to perform Mailbox Rule unilateral effective when mailed, unless the contract provides otherwise Silence is not acceptance UCC Acceptance - UCC Acceptance then breach shipped the wrong goods Accommodation offeror may accept and pay list price reject the shipment Acceptance – Other Issues Mirror Image Rule Any change from the original = a new offer Unordered merchandise Mail = offer to sell Other delivery = reasonable care for a reasonable time Rejection Termination by the offeree Counter-offer v. bargaining Conditional acceptance final, can’t later accept by mail is effective when received direct or indirect = rejection Death Rejection - UCC Exceptions Both parties are merchants Offer not limited to its terms Must be rejected within a reasonable time Any additional terms are not material Revocation Communication Automatic Passage of time Incapacity Destruction of subject matter Subsequent illegality Mutuality Freely made by contracting parties “Meeting of Minds” No reason for courts to interfere unless there’s a problem The court will try to determine the intent of the parties Mutuality – Destruction Fraud Misrepresentation Mutual mistake Duress Undue influence Mutuality – Fraud Fraud in the factum Intended wrongful statement Concealment of facts Knows will materially affect the contract Contract is void Fraud in the inducement Problem in the creation Contract is voidable Mutuality Misrepresentation Wrong facts, without intent Mutual mistake of material fact Both parties make the mistake Basic assumption Description, existence, price, no excuse for mistake of law Exc. = law of other states Material to the contract Mutuality Unilateral mistake Usually the contract will be valid, unless The other party knows of the mistake And could have avoided significant reliance Mutuality Duress Physical or emotional Economic or business compulsion Undue influence Dominant party Confidential relationship Mutuality – Effects of Destruction Voidable contracts Rescission By the innocent party Wrongdoer is liable Fraud Damages Mutual mistake Capacity Rebuttable presumption of capacity Incapacity may result in: Voidable contract Repudiation Radification Capacity Minor Until the day before the 18th birthday Not voidable for necessities Minority ends with: Emancipation Abandonment Marriage Enlistment Capacity Mental impairments Intoxication Insanity Consideration Bargained for legal detriment Forebearance Money or property Services Promise not to sue Settlement of claims Charitable pledges Promissory estoppel What’s not Consideration Past consideration Unless expressly requested & expectation of payment Pre-existing legal duty Part payment to forgive balance of debt Illusory promises Gifts Illegality Criminal or tortious acts By statute Usury Gambling Unconscionable Unlicensed Blue laws By public policy Obstruction of justice or public services Defraud creditors Exculpatory agreements Restraint of trade Restrictive employment agreements Form of the Agreement Oral Written Difference is in the enforceability Statute of Frauds, 1677 Requires a written document for: Performance not to be completed within one year Sale of land Sale of goods over $500 Executors and administrators Guaranty the debts of third parties Contracts in consideration of marriage Elements of the Writing Names and identification of the parties All material terms Identification of the subject matter Statement of the consideration Signature of the party to be charged Parol Evidence Rule Four Corners Doctrine Requires Written contract Terms are integrated No contemporaneous agreements may be added, no outside evidence Exception is statement of collateral Other exceptions defect in formation, typos explanations may supplement but not contradict Modification Under common law requires consideration usually included in original contract terms Under UCC good faith Third Parties in Contracts Beneficiaries Intended Insurance Donees Incidental Obligor, Obligee Assignor, Assignee Assignments Transfer of rights under a contract Consideration is not required May not substantially change the duties of the obligor Warranty of assignment if consideration given Must give written notice of subsequent assignments Assignments Most are revocable Restrictions Delegation = transfer of duties May not delegate special skills or special reputation Don’t need consent of obligor Novation, substitution Releases assignor of all liability How does a contract end? Discharge Performance Complete Substantial Satisfactory Nonperformance Tender of performance Conditions Breach Contract is usually an economic transaction so the decision to breach is also an economic decision Remedies Damages compensatory, incidental, punitive, Quantum Meruit Doctrine Specific performance Injunctive Damages Usually nominal if no actual damages Liquidated damages are determined when the contract is made For difficult to estimate circumstances Reasonable forecast of costs Use an expectation analysis What would it take to make me whole? What is avoidable? Foreseeable? Excuse for nonperformance Destruction of subject matter Casualty to identified goods Incapacity of a necessary person Supervening illegality Extreme and unreasonable increase in cost Frustration of purpose Excuse by Unforeseen Event After the contract was formed but before completed Unforeseen Affects the ability to perform or the value of the contract Impossibility Impracticability extreme hardship Uniform Commercial Code Provides exceptions to the Statue of Frauds Defines how business people work Streamlines the flow of commerce National system enacted by state legislatures UCC 1, General 2, Sales 2A, Leases 3, Negotiable Instruments 4, Bank Deposits 4A, Funds Transfers 5, Letters of Credit 6, Bulk Transfers 7, Documents of Title 8, Investment Securities 9, Secured Transactions 10 Administrative UCC Merchants are held to a higher standard of knowledge of commercial law Written conformations only 10 days to object Relaxes rules for acceptance Court will fill in terms of the contract Course of dealings Course of performance Trade usage The Cautious Farm Manager READ and UNDERSTAND! Know what is expected of you. Know the consequences for breach. Preprinted contracts ARE negotiable! DON’T RELY ON ORAL REPRESENTATIONS! DON’T SIGN IF YOU’RE UNCOMFORTABLE!








![1 I. Introduction to Contracts [1-2, 27-32]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/015272080_1-d365479c16074871a5e2ab79d2fc22c9-300x300.png)
