The Chemistry of Life - Willimon-PHS

Good Morning 9/23
Pass out syllabus
Set up note book
Take notes over biomolecules and enzymes
Practice for quiz over biomolecules next class.
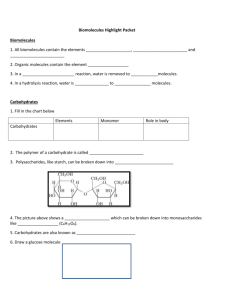
BIOMOLECULES
Objective
9A Compare the structure and functions of different types of biomolecules including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
Why are we studying Chemistry?
All living organisms are formed from atoms.
◦ we need some basic chemistry to understand the living world around us.
8 Common Elements in Living Organisms
◦ C, H, N, O, P, S, K, Ca
◦ 20 other trace elements
What are the 2 types of Chemical
Compounds?
Organic – We will focus on these, organic compounds contain mainly Carbon to
Hydrogen bonds.
Inorganic – Do not contain Carbon to
Hydrogen bonds.
What makes Carbon special?
THE single element common to all molecules that make up life.
electron configuration allows C to form up to 4 covalent bonds.
Carbon MOST commonly bonds with H.
Also, often bonds with N,O,P,S.
What are Biomolecules made from?
Small molecules are called monomers
◦ MONO = ONE
◦ Subunits of bio/macromolecules
Monomers link together in rings, straight or branched chains to form polymers
◦ POLY = MANY
◦ Polymers = macromolecules
Objective
9A Compare the structure and functions of different types of biomolecules including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
What are Biomolecules?
4 groups of organic macromolecules
◦ Carbohydrates
◦ Proteins
◦ Nucleic Acids
◦ Lipids
sometimes called biomolecules because all 4 compounds are required for life to exist.
What are
Carbohydrates?
Glucose is the monomer of carbohydrates
Made up of C-H-O in 1:2:1 Ratio(ex. C
6
H
12
O
6
)
Examples
◦ Monosaccharides (glucose - monomer)
◦ Disaccharides (sucrose)
◦ Polysaccharides (starch)
Primary source of energy for animals and in plants supports cell wall structure.
What are
Proteins?
Made up of C-H-O-N(sometimes S)
Amino acids are monomers that attach via peptide bonds to form proteins.
Responsible for building structures and assisting with metabolism.
What are
Nucleic Acids?
Polymers made up of C,H,O, N,P
◦ DNA is the master code for an organism (genetic and sequencing info)
◦ RNA reads instructions and helps build proteins.
Nucleotides are the monomers.
Store information for cellular activity that is then carried out by proteins. Also carry codes for making proteins.
What are
Lipids?
Made up of C-H-O in different ratio than in carbohydrates. More C,H, less O
Non-polar = insoluble (ex. Oil, wax, fat, steroids, phospholipids)
Serves as energy storage as well as secondary energy source(2.5x the energy of sugars). Also provide insulation and protection for internal organs.
Objective
9A Compare the structure and functions of different types of biomolecules including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
Work with your group to sort the items in your baggie into the correct category.
Use you notes as a resource.
Get out a clean sheet of paper.
Using your notes,
Complete the following questions on your own.
Check for Understanding
Answer on a clean sheet of paper (keep because there are more questions!!
Identify which biomolecule is used by living organisms as their primary source of energy.
Indicate which element most commonly bonds with Carbon.
Distinguish between monomers and polymers?
Provide 3 examples of a monomer and identify which macromolecules they corresponds to.
Enzymes
Objective:
9C Identify and investigate the role of enzymes
What is a catalyst?
A substance that speeds up a chemical reaction
What is an enzyme?
Proteins that act as biological catalysts. All chemical reactions in your body require enzymes
Why are enzymes important?
Chemical reactions take a long time to happen OR require too much energy.
Enzymes help speed up the time it takes for reactions to happen OR
Allow the reaction to happen without using up too much energy
What is activation energy?
In chemical reactions, energy is either released or absorbed.
In order to get the chemical reaction started, it requires a certain amount of
“Activation Energy”
Graph of energy of activation
How do enzymes speed up chemical reactions?
1.
Chemical compounds attach to the
ACTIVE SITE of an enzymes
2.
3.
The SUBSTRATE are the specific substances that can bind to enzymes
Enzymes hold the substrate in place so the chemical reaction can happen
4.
After reaction is finished, enzyme releases the PRODUCTS and helps another substrate.
Do enzymes need a specific environment?
YES
They are sensitive to pH and temperature
Ex. Human body is 37 C so most enzymes function best at this temperature
Different organs have different pH (like the stomach) so enzymes “adapt” to their specific environments
Write in your journal…
Draw and Describe what is happening in this picture.
How do we name enzymes?
They are named for the reaction the catalyze and have the suffix –ase attached to the end
Ex. Lipase – breaks down lipids
Protease – breaks down proteins
Amylase – breaks down starch or amylum
On a clean sheet of paper answer the following questions in complete sentences.
1.
Why are enzymes necessary for life?
2.
What is the active site of an enzyme?
3.
How do enzymes catalyze chemical reactions?