Exam - WordPress.com
advertisement

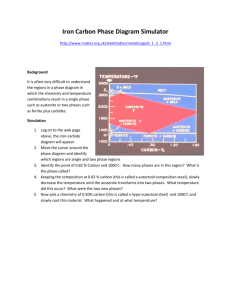
Saskatchewan Institute of Applied Science and Technology Kelsey Campus ENGM 180 – Materials of Engineering For FCP Evaluation Midterm Examination Exam Date?? Time Allowed: 2 Hours Calculator required NAME: ____________________________ PART A: TRUE/FALSE (1 mark each) – Circle either True of False for each of the following statements. 1 There are dislocations in pure metals. T F 2 Austenitic stainless steels are ferromagnetic. T F 3 Corrosion is likely to occur in metals that exhibit a passive surface film. T F 4 Hardness tests done on carbon steels are a good indication of their ultimate strength. T 5 F Hot finished products are processed at a temperature above the recrystallization temperature. T F T F 6 Eutectoid transformation occurs entirely in solid state. 7 AISI 316L stainless steel contains a higher percentage of carbon than AISI 316 stainless steel. T F 1 PART B: MULTIPLE CHOICE (1 mark each) – Circle the correct answer. 1 What is the unit cell structure of untempered martensite? a. b. c. d. e. 2 FCC BCC Fe3C BCT HCP Compared to carbon steels, the modulus of elasticity (E) for aluminum alloys is: a. lower. b. slightly higher. c. about the same. 3 Which of the following does not cause internal stresses in metals? a. b. c. d. 4 cold working welding casting heating The steel that is the least expensive from the list below is: a. b. c. d. high alloy steels. ultra high strength steels. high strength, low alloy steels. alloy steels. 5 What is the role of aluminum as an alloying element in steel? a. Aids nitriding. b. Adds dissolved oxygen. c. Increases strength. 6 The presence of chromium in carbon steel: a. b. c. d. 7 decreases hardness due to alloying effect. decreases high temperature strength. decreases the resistance to corrosion decreases the ability of steel to remain austenite at room temperature. Which of the statements is not true in the case of HSLA steels? a. The purpose of these steels is weight reduction through increased strength. b. These steels are commonly made into sheet, strip, and structural shapes. c. These steels are difficult to weld. 2 8 One of the most important differences between crystalline substances and amorphous substances is that crystalline substances: a. b. c. d. 9 are water soluble. readily ionize in solutions. have better optical properties than the amorphous materials. have structure formed by repeating units of atomic cells of similar geometric patterns. Duplex stainless steels have a microstructure that is both: a. b. c. d. austenite and martensite. ferrite and PH. ferrite and martensite. austenite and ferrite. 10 The alloying element that can be substituted for nickel in austenitic stainless steels is: a. b. c. d. manganese. magnesium. molybdenum. polonium. 11 The most popular type of stainless steel in the chemical industry is: a. b. c. d. duplex. martensitic. austenitic. ferritic. 12 The property that determines a metal’s ability to permanently deform under a compressive load is called: a. b. c. d. elasticity. plasticity. creep. malleability. 13 Three of the basic types of stresses are: a. b. c. d. bending, fatigue, thermal. tensile, plastic, elastic. torsional, compressive, shear. thermal, creep, bending. 14 Hardness, strength, and ductility of a material increase: a. with an increase in temperature. b. when it is annealed. c. with a decrease in temperature. 3 Refer to the following figure for questions 15 and 16. 15 If a thin section of SAE 1070 steel is heated to 1475 °F (802 °C) then quickly quenched to a temperature of 572 °F (300 °C) and held at that temperature for a considerable time, it will transform to: a. b. c. d. e. pearlite. martensite. bainite. ferrite. a eutectoid. 16 If a thin section of SAE 1070 steel is heated to 1475 °F (802 °C) then quickly quenched to a temperature of 1110 °F (600 °C) and held at that temperature for a considerable time, it will transform to: a. b. c. d. e. pearlite martensite bainite ferrite a eutectoid 4 17 Metals with _____________ crystal structures are least likely to have a Nil Ductility Temperature (NDT). a. b. c. d. BCT (body centered tetragonal) BCC (body centered cubic) HCP (hexagonal closed packed) FCC (face centered cubic) 18 A measure of the amount of energy that gets absorbed by a material as it fractures is called: a. b. c. d. resilience. ultimate strength. endurance limit. toughness. 19 A(n) __________________ bond is formed in such a matter that the valence electrons associated with the bond atoms form a pool and are free to move throughout the volume of the crystal. a. b. c. d. e. covalent Van der Waal ionic metallic ceramic 20 Materials which are good conductors of heat and electricity are held by: a. b. c. d. Van der Waal forces. covalent bonds. metallic bonds. ionic bonds. 21 As it is used in the steel industry, the term killing refers to: a. the use of acids to remove oxides and remove scale on hot worked steels. b. hot dipping of steel in a preservative to increase its corrosion resistance. c. the addition of elements such as silicon or aluminum to remove dissolved oxygen. 22 Which of the following is not a type of tool steel? a. b. c. d. mold shock resisting high strength high speed 5 23 What is the percentage of carbon content in a eutectoid carbon steel? a. b. c. d. e. 0.95 0.20 0.77 0.40 0.18 24 SAE/AISI specifications are based on: a. b. c. d. properties. application. composition. cost. 25 What name is given to a mixture of two metals that have different melting points but when combined melt at a single melting point lower than either of the two? a. b. c. d. e. homogenous. pearlite. eutectic. eutectoid. austenite. 26 The “pipe” defect in a steel ingot is due to: a. the purer metal solidifying first leaving the impurities in the center. b. steel that has solidified in the space where the depression was created by the oxygen blown at supersonic speed from a pipe (during refining). c. volumetric shrinkage of metal in the center when the solidification starts at the outer surface of the ingot. 27 In the SAE system of designating steel alloys, the last 2 digits of an alloy indicate: a. the primary alloying element. b. the carbon content in hundredths of a percent. c. the secondary alloying element in hundredths of a percent. 28 Which of the following quenching media would cause the fastest cooling rate? a. b. c. d. e. brine oil cold water vegetable oil caustic soda – 5% solution 6 29 The purpose of the normalizing heat treatment process is: a. b. c. d. e. grain refinement. reducing the material to its softest state. diffusing the carbon into the areas which have been decarburized. stress relieving the material to retain its normal strength. to harden the metal. 30 In which of the following heat treatment processes is the temperature of steel kept below the austenitic transition temperature? a. b. c. d. e. full annealing quench hardening nitriding normalizing chromizing 31 In order to toughen quench hardened steel parts, the type of heat treatment used is: a. b. c. d. normalizing. tempering. spheroidizing. annealing. 32 The maximum solubility of carbon in steel is: a. b. c. d. e. 0.77% 0.022% 2.1% 6.67% 0.45% 33 Which of the following statements is not characteristic of a binary solution of two metals? a. There is only one identifiable phase in its microstructure. b. The two metals are in solution in solid state. c. They could solidify as a eutectic. 34 The stress relieving process is often required for: a. b. c. d. weldments that require machining of welded areas. cold-formed parts. castings that require significant machining. all of the above 35 Screw dislocations are classified as: a. line defects. b. point defects. c. point or line defects depending upon their location. 7 36 In which of the following processes is the presence of alloying elements such as aluminum, chromium, or tungsten needed to achieve good case hardening of steel? a. b. c. d. flame hardening gas carburizing induction hardening nitriding 37 Allotropic transformation is defined as: a. a change from liquid to liquid (with different physical properties but of the same chemical properties). b. a change from solid to liquid (with different physical properties but of the same chemical properties). c. a change in crystal structure (with different physical properties but of the same chemical properties). 38 The unit cell structure of austenite is: a. b. c. d. BCC. FCC. BCT. HCP. 39 Addition of alloying elements such as chromium and molybdenum will result in shifting the TTT curve: a. to the left of the TTT curve of the steel with the same amount of carbon but without any of the alloying elements mentioned above. b. to the right of the TTT curve of the steel with the same amount of carbon but without any of the alloying elements mentioned above. c. neither to the left or the right (i.e. does not shift the TTT curve of steel). 40 Which of the following processes occurs at a temperature below 727 ºC? a. b. c. d. carbonitriding chromizing gas carburizing nitriding 41 Hypereutectoid steels contain: a. b. c. d. more carbon than tool steels less carbon than alloy steels less than 0.77 percent carbon content more than 0.77 percent carbon content 8 42 Below is the phase diagram of Cadmium (Cd) and Bismuth (Bi). At the composition of 25% Bi (shown by vertical line 1-1), which of the following combination of products is likely to appear at room temperature? a. b. c. d. eutectic and metal bismuth solid solution of cadmium and bismuth bismuth and eutectoid of bismuth and cadmium eutectic and metal cadmium 43 The most common test performed to estimate toughness is: a. b. c. d. a hardness test. a tension test. an impact test. microscopic examination. 44 What is the stress [in psi] in a 3 inch square bar (3x3) which carries a load of 81000 lbs? a. b. c. d. e. 10,000 9000 90 0.111 data given is not sufficient to calculate the stress 45 Which of the following describes dendrite structure? a. b. c. d. e. equiaxed eutectic tree-like symmetric flakes of dried skin 9 46 To quench harden a high-carbon steel, the minimum temperature to which it must be heated is: a. b. c. d. 1015 °F (546 °C). 1341 °F (727 °C). 1650 °F (899 °C). 1800 °F (982 °C). 47 With reference to the binary phase diagram below, the solidus is represented by: a. b. c. d. e. the number 5 the number 2 the number 4 the number 3 the number 1 48 The microstructure of a slowly cooled eutectoid steel is called: a. b. c. d. e. martensite. ferrite. bainite. pearlite. austenite. 49 The yield point of a material is found by drawing a line parallel to the linear portion of its stress-strain curve at an offset of: a. b. c. d. 0.002% strain. 0.02% strain. 0.2% strain. 2.0% strain. 10 PART C: SHORT ANSWER – Fully answer each of the questions. 1 What is the difference between the Rockwell B and C scales of hardness? Comment in terms of load used and type of indenter. (2 marks) 2 Explain the difference between ferrite formers and austenite formers and give an example of each. (2 marks) 3 What is the main difference between steel and cast iron? (1 marks) 4 List 4 mechanical properties that can be determined from a tension test. (2 marks) 5 What is the difference between coarse and fine pearlite? (1 mark) 11 PART D: CALCULATIONS – Show all your work in the space provided. 1 The following data was obtained during a tension test: Initial Diameter: 0.505 in. Gage length: 2 in. (8 marks) Formulas: l l0 % elongation l f l0 l0 100 From the above data, show calculations for determining: a) Stress at a load of 6000 lb b) Strain at a load of 8000 lb 12 E F A c) Modulus of elasticity d) Ultimate tensile strength e) % elongation at fracture 13