ELBOW/FOREARM LAB
advertisement

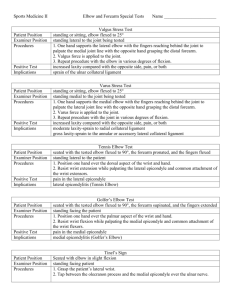
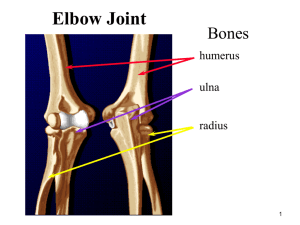
ELBOW/FOREARM LAB A.Mazaherinezhad MD. Assistant professor, Sports medicine Department, IUMS Assessment of the Elbow History Past history Mechanism of injury When and where does it hurt? Motions that increase or decrease pain Type of, quality of, duration of, pain? Sounds or feelings? How long were you disabled? Swelling? Previous treatments? Physical exam Inspection bruising atrophy swelling Observations Deformities and swelling? Carrying angle Cubitus valgus versus cubitus varus Flexion and extension Cubitus recurvatum Elbow at 45 degrees Isosceles triangle (olecranon and epicondyles) •Palpation: Bony and Soft Tissue Humerus Medial and lateral epicondyles Olecranon process Radial head Radius Ulna Medial and lateral collateral ligaments Annular ligament Biceps brachii Brachialis Brachioradialis Pronator teres Triceps Supinator Wrist flexors and extensors Palpation BONY PALPATION Medial epicondyle Medial supracondylar line Lateral epicondyle Lateral supracondylar line Olecranon process Olecranon fossa Radial head Radius Ulna SOFT TISSUE PALPATION Anterior Cubital fossa -Biceps brachii -Brachial artery -Median nerve -Musculocutaneous nerve Brachialis Brachioradialis SOFT TISSUE PALPATION Posterior Triceps Supinator SOFT TISSUE PALPATION Medial Ulnar collateral ligament Wrist flexors -pronator teres -flexor carpi radialis -palmaris longus -flexor carpi ulnaris Ulnar nerve Supracondylar lymph nodes SOFT TISSUE PALPATION Lateral Radial collateral ligament Wrist extensors brachioradialis extensor carpi radialis longus extensor carpi radialis brevis Annular ligament SENSORY EXAM •Functional Evaluation Pain and weakness are evaluated through AROM, PROM and RROM Flexion, extension, pronation and supination ROM of pronation and supination are particularly noted Examination for ligament stability Valgus stress test applied to elbow in both full etension and in 20 degree of flexion will determine the stability of the medial collateral ligament. Examination for ligament stability Varus stress test applied to elbow will determine any damage to the lateral collateral ligament TENNIS ELBOW Test for lat epicondyle For inflammation or injury of the extensor tendons of the wrist ( especially ext carpi radialis tendon in tennis elbow ) Resisted extension of the wrist will elicite pain at the lat epicondyle. Resisted wrist extension test Cozen test Resisted mid finger extension test Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer’s Elbow) Test for medial epicondylitis Resisted flexion of the wrist will illicit discomfort at medial epicondyle in patients with inflamation of the flexor tendons of the wrist Circulatory and Neurological Function Pulse should be taken at brachial artery and radial artery Skin sensation should be checked - determine presence of nerve root compression or irritation in cervical or shoulder region Tinel’s sign Ulnar nerve test Tap on ulnar nerve (in ulnar groove) Positive test is found when athlete complains of sensation along the forearm and hand Tinnel cubital tunnel Pinch Grip Test Pinch thumb and index finger together Inability to touch fingers together indicates entrapment of anterior interosseous nerve between heads of pronator muscle Pronator Teres Syndrome Test Forearm pronation is resisted Increased pain proximally over pronator teres indicates a positive test