Elbow and Forearm Special Tests
advertisement
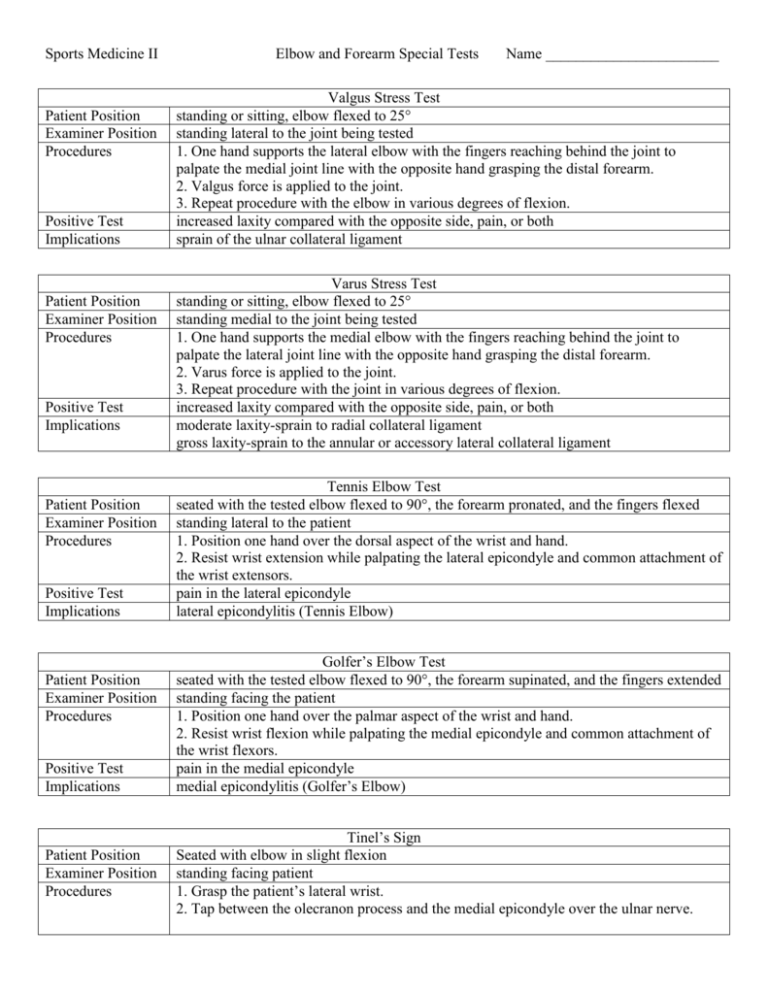
Sports Medicine II Patient Position Examiner Position Procedures Positive Test Implications Patient Position Examiner Position Procedures Positive Test Implications Patient Position Examiner Position Procedures Positive Test Implications Patient Position Examiner Position Procedures Positive Test Implications Patient Position Examiner Position Procedures Elbow and Forearm Special Tests Name _______________________ Valgus Stress Test standing or sitting, elbow flexed to 25° standing lateral to the joint being tested 1. One hand supports the lateral elbow with the fingers reaching behind the joint to palpate the medial joint line with the opposite hand grasping the distal forearm. 2. Valgus force is applied to the joint. 3. Repeat procedure with the elbow in various degrees of flexion. increased laxity compared with the opposite side, pain, or both sprain of the ulnar collateral ligament Varus Stress Test standing or sitting, elbow flexed to 25° standing medial to the joint being tested 1. One hand supports the medial elbow with the fingers reaching behind the joint to palpate the lateral joint line with the opposite hand grasping the distal forearm. 2. Varus force is applied to the joint. 3. Repeat procedure with the joint in various degrees of flexion. increased laxity compared with the opposite side, pain, or both moderate laxity-sprain to radial collateral ligament gross laxity-sprain to the annular or accessory lateral collateral ligament Tennis Elbow Test seated with the tested elbow flexed to 90°, the forearm pronated, and the fingers flexed standing lateral to the patient 1. Position one hand over the dorsal aspect of the wrist and hand. 2. Resist wrist extension while palpating the lateral epicondyle and common attachment of the wrist extensors. pain in the lateral epicondyle lateral epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow) Golfer’s Elbow Test seated with the tested elbow flexed to 90°, the forearm supinated, and the fingers extended standing facing the patient 1. Position one hand over the palmar aspect of the wrist and hand. 2. Resist wrist flexion while palpating the medial epicondyle and common attachment of the wrist flexors. pain in the medial epicondyle medial epicondylitis (Golfer’s Elbow) Tinel’s Sign Seated with elbow in slight flexion standing facing patient 1. Grasp the patient’s lateral wrist. 2. Tap between the olecranon process and the medial epicondyle over the ulnar nerve. Positive Test Implications Tingling along the ulnar distribution of the forearm, hand, and fingers ulnar nerve trauma